
The filiform apparatus is present in
A. Synergids
B. Egg cell
C. Antipodals
D. Secondary nucleus
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: These cells are present on both the two sides of the egg cell inside the embryo sac and help in guiding the entry of the pollen tube.
Complete answer
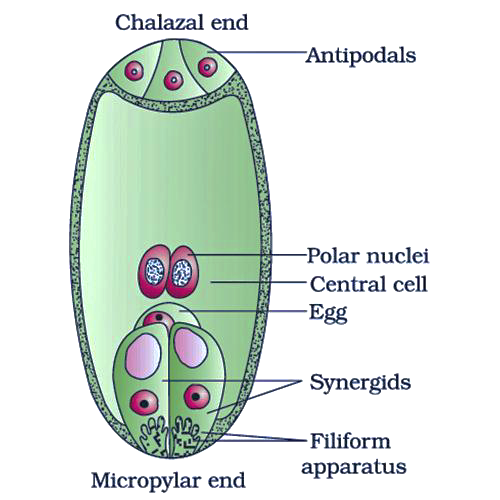
The filiform apparatus is the thickened and prominent structure present in the synergids cells of the embryo sac. They are the finger-like projections that are located near the micropylar end of the embryo sac.
Additional information
- The ovule is the structure that gives rise to the female reproductive cells.
- The ovule has three parts: integument (outer layer), nucellus (remains of megasporangium), and female gametophyte (formed by a haploid megaspore).
- The female gametophyte is also called the embryo sac which produces egg cells for the process of fertilization.
- This embryo sac consists of seven cells and eight nuclei in the case of angiosperms.
- The cells and nucleus of the embryo sac are egg cell, two synergid cells, three antipodal cells, and two polar nuclei.
- The cell which is near to the micropylar end develops into the egg cell.
- The egg cell consists of two synergid cells at either of its sides.
- These synergids cells undergo prolongation resulting in the filiform apparatus.
- The filiform apparatus helps in guiding the entry of the pollen tube in the embryo sac and also in the release of the sperms.
- The filiform apparatus along with synergid cells help in nourishing the pollen grain.
So, the correct answer is ‘Synergids'.
Note:
The antipodal cells formed in the embryo sac are located towards the chalazal end of the embryo sac which later degenerates. In the center of the embryo sac, a large central cell is present which contains two polar nuclei. These two polar nuclei will fuse with one of the sperm released and form a triploid endosperm. The other sperm released will fuse with the egg cell resulting in a diploid zygote.
Complete answer
The filiform apparatus is the thickened and prominent structure present in the synergids cells of the embryo sac. They are the finger-like projections that are located near the micropylar end of the embryo sac.
Additional information
- The ovule is the structure that gives rise to the female reproductive cells.
- The ovule has three parts: integument (outer layer), nucellus (remains of megasporangium), and female gametophyte (formed by a haploid megaspore).
- The female gametophyte is also called the embryo sac which produces egg cells for the process of fertilization.
- This embryo sac consists of seven cells and eight nuclei in the case of angiosperms.
- The cells and nucleus of the embryo sac are egg cell, two synergid cells, three antipodal cells, and two polar nuclei.
- The cell which is near to the micropylar end develops into the egg cell.
- The egg cell consists of two synergid cells at either of its sides.
- These synergids cells undergo prolongation resulting in the filiform apparatus.
- The filiform apparatus helps in guiding the entry of the pollen tube in the embryo sac and also in the release of the sperms.
- The filiform apparatus along with synergid cells help in nourishing the pollen grain.
So, the correct answer is ‘Synergids'.

Note:
The antipodal cells formed in the embryo sac are located towards the chalazal end of the embryo sac which later degenerates. In the center of the embryo sac, a large central cell is present which contains two polar nuclei. These two polar nuclei will fuse with one of the sperm released and form a triploid endosperm. The other sperm released will fuse with the egg cell resulting in a diploid zygote.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




