
The final product of chlorination of methane in the sunlight is?
A. \[C{H_3}Cl\]
B. \[C{H_2}C{l_2}\]
C. \[CHC{l_3}\]
D. \[CC{l_4}\]
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: Chlorination is the process of addition of chlorine atom to a molecule by substituting another atom. This chlorination reaction takes place in both thermal and photochemical conditions.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction takes place following a free radical mechanism. The chlorination of methane in presence of sunlight occurs in a stepwise manner. The steps involve initiation, propagation and termination.
The initiation step involves formation of chlorine radicals by absorption of light.
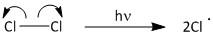
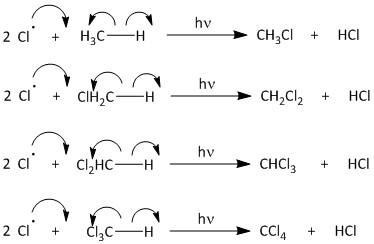
The propagation begins by attack of the chlorine radical to methane molecule. A molecule of methane reacts with chlorine radicals to produce \[C{H_3}Cl\] and \[HCl\]. The \[C{H_3}Cl\] then reacts with chlorine radical to produce \[C{H_2}C{l_2}\]. This upon further reaction yields \[CHC{l_3}\] and finally results in formation of \[CC{l_4}\]. The propagation step goes on producing carbon tetrachloride until the radical is consumed in other reactions.
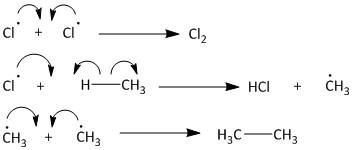
The termination step leads to various products like chlorine gas or ethane gas. The chlorine gas is produced by a combination of two chlorine radicals. The chlorine radical upon combination with methane produces \[HCl\] gas and methyl radical. Two of these methyl radicals combine to produce ethane gas. The termination of radical is also known as quenching of radical ions. The termination step is as follows:
Thus the final product of chlorination of methane in the sunlight is carbon tetrachloride, i.e. option D is the correct answer.
Note:
The chlorination of methane also takes place in thermal conditions. If the amount of chlorine is limited then the major product is methyl chloride i.e. \[C{H_3}Cl\]. If the amount of chlorine is unlimited then only the major product is carbon tetrachloride i.e. \[CC{l_4}\].
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction takes place following a free radical mechanism. The chlorination of methane in presence of sunlight occurs in a stepwise manner. The steps involve initiation, propagation and termination.
The initiation step involves formation of chlorine radicals by absorption of light.
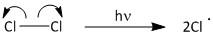
The propagation begins by attack of the chlorine radical to methane molecule. A molecule of methane reacts with chlorine radicals to produce \[C{H_3}Cl\] and \[HCl\]. The \[C{H_3}Cl\] then reacts with chlorine radical to produce \[C{H_2}C{l_2}\]. This upon further reaction yields \[CHC{l_3}\] and finally results in formation of \[CC{l_4}\]. The propagation step goes on producing carbon tetrachloride until the radical is consumed in other reactions.

The termination step leads to various products like chlorine gas or ethane gas. The chlorine gas is produced by a combination of two chlorine radicals. The chlorine radical upon combination with methane produces \[HCl\] gas and methyl radical. Two of these methyl radicals combine to produce ethane gas. The termination of radical is also known as quenching of radical ions. The termination step is as follows:

Thus the final product of chlorination of methane in the sunlight is carbon tetrachloride, i.e. option D is the correct answer.
Note:
The chlorination of methane also takes place in thermal conditions. If the amount of chlorine is limited then the major product is methyl chloride i.e. \[C{H_3}Cl\]. If the amount of chlorine is unlimited then only the major product is carbon tetrachloride i.e. \[CC{l_4}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




