
The flow chart given here shows the functional organization of the human neural system. Identify A to E and select the correct options.
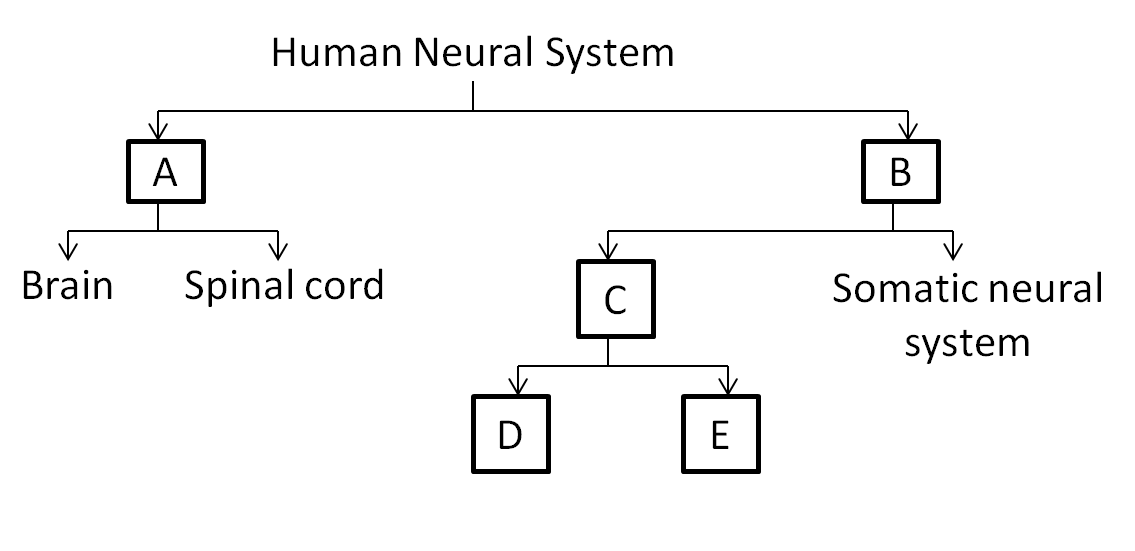
(a) A - PNS, B - CNS, C - ANS, D - Sympathetic neural system, E - Parasympathetic neural system
(b) A - ANS, B - CNS, C - PNS, D - Parasympathetic neural system, E - Sympathetic neural system
(c) A - CNS, B - PNS, C - ANS, D - Sympathetic neural system, E - Parasympathetic neural system
(d) A - ANS, B - PNS, C - CNS, D - Parasympathetic neural system, E - Sympathetic neural system

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: A system consists of the brain and the spinal cord which is immersed in the cerebrospinal fluid. For B this is the division of the nervous system consisting of all nerves outside the CNS.
For C this is also known as the visceral nervous system which is the part of the peripheral nervous system.
For D this system prepares the body for intense physical activity.
For E this system helps in relaxing the body and inhibits or slows many high energy functions.
Complete step by step answer:
CNS or Central Nervous System
- This is composed of two major interconnected organs:– The brain– The spinal cord.
- The differential distribution of myelin in the central nervous system is responsible for these differences: The main component of white matter is myelinated axons and the myelin- producing oligodendrocytes.
- White matter does not contain neuronal cell bodies.
- As the absence of connective tissue, fresh CNS tissue has a very soft, somewhat jelly- like consistency.
PNS or Peripheral Nervous System
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a collection of peripheral nerves, ganglia and specialized sensory structures that, as a system, carries sensory and motor information between the central nervous system and all other organs and tissues of the body.
- The peripheral nervous system is functionally divided into two major divisions:–
The Sensory or Afferent Division
The Motor or Efferent Division which is further divided into the Somatic Nervous System and the Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System.
- The primary role of PNS is to connect the CNS to the organs, limbs and skin.
ANS or Autonomic Nervous System
- Carries impulses from the central nervous system glands, various smooth muscles, cardiac muscle and various membranes.
- The autonomic nervous system or visceral nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls function.
- The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activities of cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands.
- It is classically divided into two subsystems: the sympathetic neural system and parasympathetic neural system.
Sympathetic neural system
- This system allows the body to function under stress like fight or flight.
- This system primes the body for intense skeletal muscle activity.
- The sympathetic nervous system is located in the sympathetic chain, which connects to the skin, blood vessels and organs in the body cavity.
- Role of the sympathetic neural system
Stimulates heartbeat
Raises blood pressure
Dilates the pupils Dilates the trachea and bronchi
Stimulates glycogenolysis — the conversion of liver glycogen into glucose
Inhibits peristalsis in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract
Inhibits contraction of the bladder and rectum
Parasympathetic neural system
- The parasympathetic system is the branch of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) responsible for the body’s ability to recuperate and return to a balanced state (known as "homeostasis") after experiencing pain or stress.
- This system maintenance functions like rest- anD - digest.
- This helps in counterbalancing sympathetic functions.
- Role of the parasympathetic system:
- Slowing down of the heartbeat
- Lowering of blood pressure
- Constriction of the pupils - Increased blood flow to the skin and viscera
- Peristalsis of the GI tract
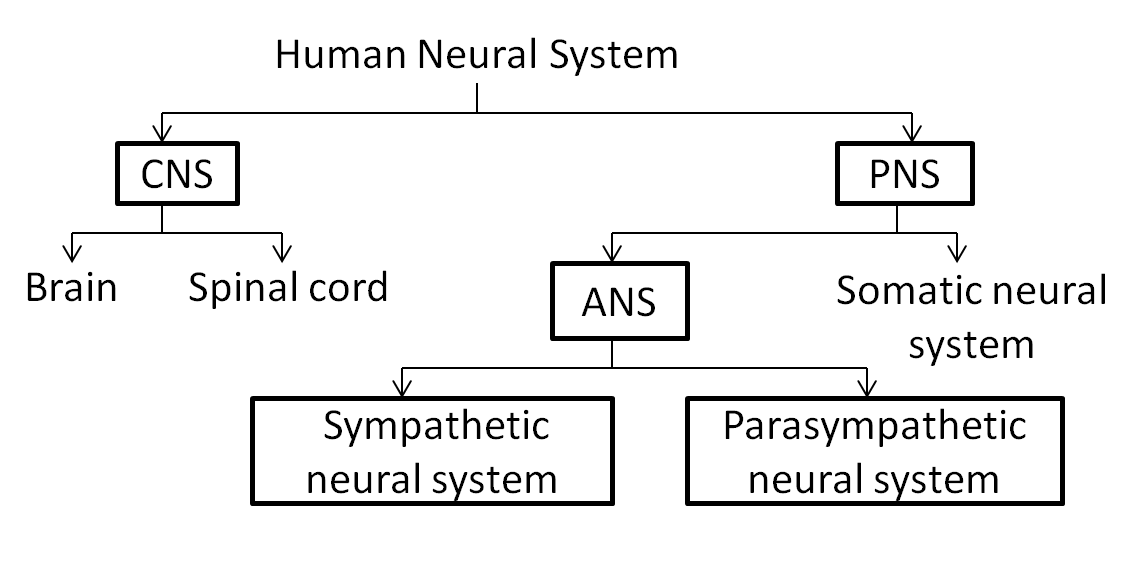
So, the correct answer is, ‘A - CNS, B - PNS, C - ANS, D - Sympathetic neural system, E - Parasympathetic neural system.’
Note:
- This usually shows numerous long processes, and several types of glial cells which have short processes, support and protect neurons, and participate in neural activity, neural nutrition, and the defence processes of the central nervous system.
- This propagation, called the action potential, or nerve impulse, is capable of travelling long distances; it transmits information to other neurons, muscles, and glands.
For C this is also known as the visceral nervous system which is the part of the peripheral nervous system.
For D this system prepares the body for intense physical activity.
For E this system helps in relaxing the body and inhibits or slows many high energy functions.
Complete step by step answer:
CNS or Central Nervous System
- This is composed of two major interconnected organs:– The brain– The spinal cord.
- The differential distribution of myelin in the central nervous system is responsible for these differences: The main component of white matter is myelinated axons and the myelin- producing oligodendrocytes.
- White matter does not contain neuronal cell bodies.
- As the absence of connective tissue, fresh CNS tissue has a very soft, somewhat jelly- like consistency.
PNS or Peripheral Nervous System
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a collection of peripheral nerves, ganglia and specialized sensory structures that, as a system, carries sensory and motor information between the central nervous system and all other organs and tissues of the body.
- The peripheral nervous system is functionally divided into two major divisions:–
The Sensory or Afferent Division
The Motor or Efferent Division which is further divided into the Somatic Nervous System and the Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System.
- The primary role of PNS is to connect the CNS to the organs, limbs and skin.
ANS or Autonomic Nervous System
- Carries impulses from the central nervous system glands, various smooth muscles, cardiac muscle and various membranes.
- The autonomic nervous system or visceral nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls function.
- The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activities of cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands.
- It is classically divided into two subsystems: the sympathetic neural system and parasympathetic neural system.
Sympathetic neural system
- This system allows the body to function under stress like fight or flight.
- This system primes the body for intense skeletal muscle activity.
- The sympathetic nervous system is located in the sympathetic chain, which connects to the skin, blood vessels and organs in the body cavity.
- Role of the sympathetic neural system
Stimulates heartbeat
Raises blood pressure
Dilates the pupils Dilates the trachea and bronchi
Stimulates glycogenolysis — the conversion of liver glycogen into glucose
Inhibits peristalsis in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract
Inhibits contraction of the bladder and rectum
Parasympathetic neural system
- The parasympathetic system is the branch of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) responsible for the body’s ability to recuperate and return to a balanced state (known as "homeostasis") after experiencing pain or stress.
- This system maintenance functions like rest- anD - digest.
- This helps in counterbalancing sympathetic functions.
- Role of the parasympathetic system:
- Slowing down of the heartbeat
- Lowering of blood pressure
- Constriction of the pupils - Increased blood flow to the skin and viscera
- Peristalsis of the GI tract

So, the correct answer is, ‘A - CNS, B - PNS, C - ANS, D - Sympathetic neural system, E - Parasympathetic neural system.’
Note:
- This usually shows numerous long processes, and several types of glial cells which have short processes, support and protect neurons, and participate in neural activity, neural nutrition, and the defence processes of the central nervous system.
- This propagation, called the action potential, or nerve impulse, is capable of travelling long distances; it transmits information to other neurons, muscles, and glands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




