
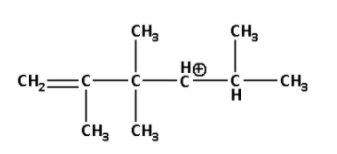
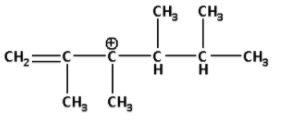
The following carbocation rearranges to:
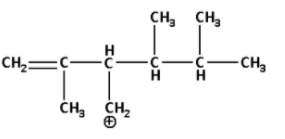
A)
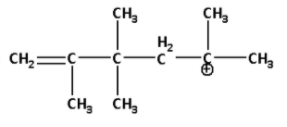
B)
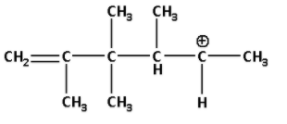
C)
D)





Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: We know that carbocation is a positively charged carbon atom. The carbocation with the least partial positive charge is more stable. This is because the charge is distributed among neighbouring carbons. Higher the charge density on the carbon atom, more unstable is the carbocation.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given a carbocation in which the positively charged carbon atom is attached to two alkyl groups.
When a positively charged carbon atom is attached to two alkyl groups it is known as a secondary carbocation.
Thus, the carbocation given to us is a secondary carbocation.
All carbocations have a unique property of rearrangement. The carbocations rearrange themselves to form a more stable carbocation.
Now, the given secondary carbocation will rearrange itself to form a more stable carbocation i.e. a tertiary carbocation. The rearrangement of secondary carbocation is as follows:
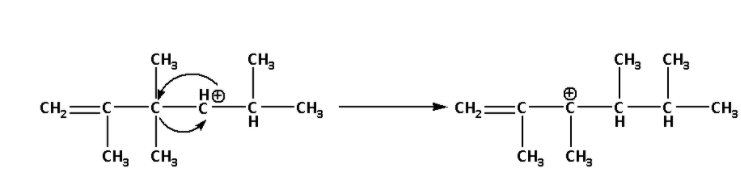
In the rearranged carbocation, we can see that the positively charged carbon atom is attached to three alkyl groups.
When a positively charged carbon atom is attached to three alkyl groups it is known as a tertiary carbocation.
Thus, the rearranged carbocation is a tertiary carbocation which is more stable.
Thus, the correct option is (D).
Note: When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to only one alkyl group it is known as a primary carbocation. When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to two other alkyl groups it is known as a secondary carbocation. When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to three other alkyl groups it is known as a tertiary carbocation. A tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation which is more stable than the primary carbocation.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given a carbocation in which the positively charged carbon atom is attached to two alkyl groups.
When a positively charged carbon atom is attached to two alkyl groups it is known as a secondary carbocation.
Thus, the carbocation given to us is a secondary carbocation.
All carbocations have a unique property of rearrangement. The carbocations rearrange themselves to form a more stable carbocation.
Now, the given secondary carbocation will rearrange itself to form a more stable carbocation i.e. a tertiary carbocation. The rearrangement of secondary carbocation is as follows:

In the rearranged carbocation, we can see that the positively charged carbon atom is attached to three alkyl groups.
When a positively charged carbon atom is attached to three alkyl groups it is known as a tertiary carbocation.
Thus, the rearranged carbocation is a tertiary carbocation which is more stable.
Thus, the correct option is (D).
Note: When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to only one alkyl group it is known as a primary carbocation. When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to two other alkyl groups it is known as a secondary carbocation. When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to three other alkyl groups it is known as a tertiary carbocation. A tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation which is more stable than the primary carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




