
What will be the formula and electron-dot structure of cyclopentane?
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Along with the straight chain compounds, we can also form ring-like structures. These can even have double bonds in them. Cyclopentane is a cyclic saturated compound. It has five members in the ring. It has two hydrogen atoms less than its parent alkane-pentane.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrocarbons are the compounds containing carbon and hydrogen. There are two main types-saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. A saturated hydrocarbon has only a carbon-carbon single bond. Unsaturated hydrocarbons have double or triple bonds in them.
Saturated hydrocarbons constitute a family of straight or branched chain compounds called alkanes. They have carbon-carbon single bonds and only carbon and hydrogen. The first member of the alkane series is methane. It has a carbon atom and three hydrogen are attached to carbon by a single bond. It can be represented as $C{H_4}$ . Now the alkane containing two carbon atoms is ethane. Its molecular formula is ${C_2}{H_6}$ . So the members of alkane family can be shown as-
The names of members of the alkane family end with ‘–ane’.
Now let us talk about the cyclic compounds. In cyclic compounds atoms are connected to each other and form a ring-like structure. Cyclopentane can be formed from pentane by joining end carbon atoms. The structure of cyclopentane will be-
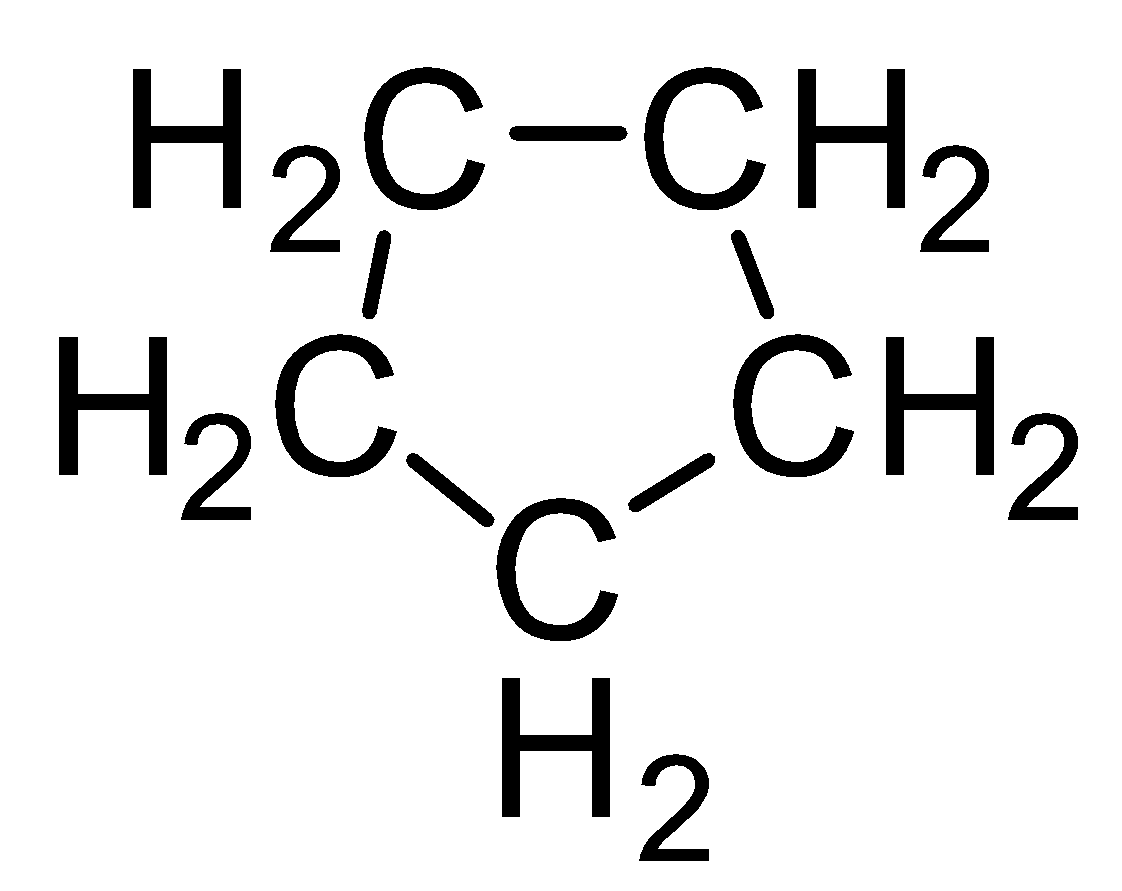
In this structure there are five groups of atoms connected to each other by a single carbon-carbon bond. The formula of cyclopentane can be determined from the above structure too. It is given as ${C_5}{H_{10}}$ .
In the electron-dot structure, the valence electrons of atoms are represented around them as dots. The number of dots is equal to the valence electrons in an atom. The electron-dot structure of cyclopentane is-
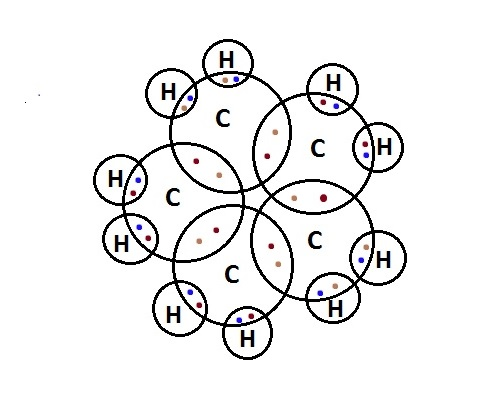
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember we show only valence electrons in the electron-dot structure of a compound. Cyclopentane has two hydrogen atoms less than straight chain compound pentane. These two hydrogen atoms are lost during the formation of a ring.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrocarbons are the compounds containing carbon and hydrogen. There are two main types-saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. A saturated hydrocarbon has only a carbon-carbon single bond. Unsaturated hydrocarbons have double or triple bonds in them.
Saturated hydrocarbons constitute a family of straight or branched chain compounds called alkanes. They have carbon-carbon single bonds and only carbon and hydrogen. The first member of the alkane series is methane. It has a carbon atom and three hydrogen are attached to carbon by a single bond. It can be represented as $C{H_4}$ . Now the alkane containing two carbon atoms is ethane. Its molecular formula is ${C_2}{H_6}$ . So the members of alkane family can be shown as-
| Alkane | Structure or formula |
| Methane | 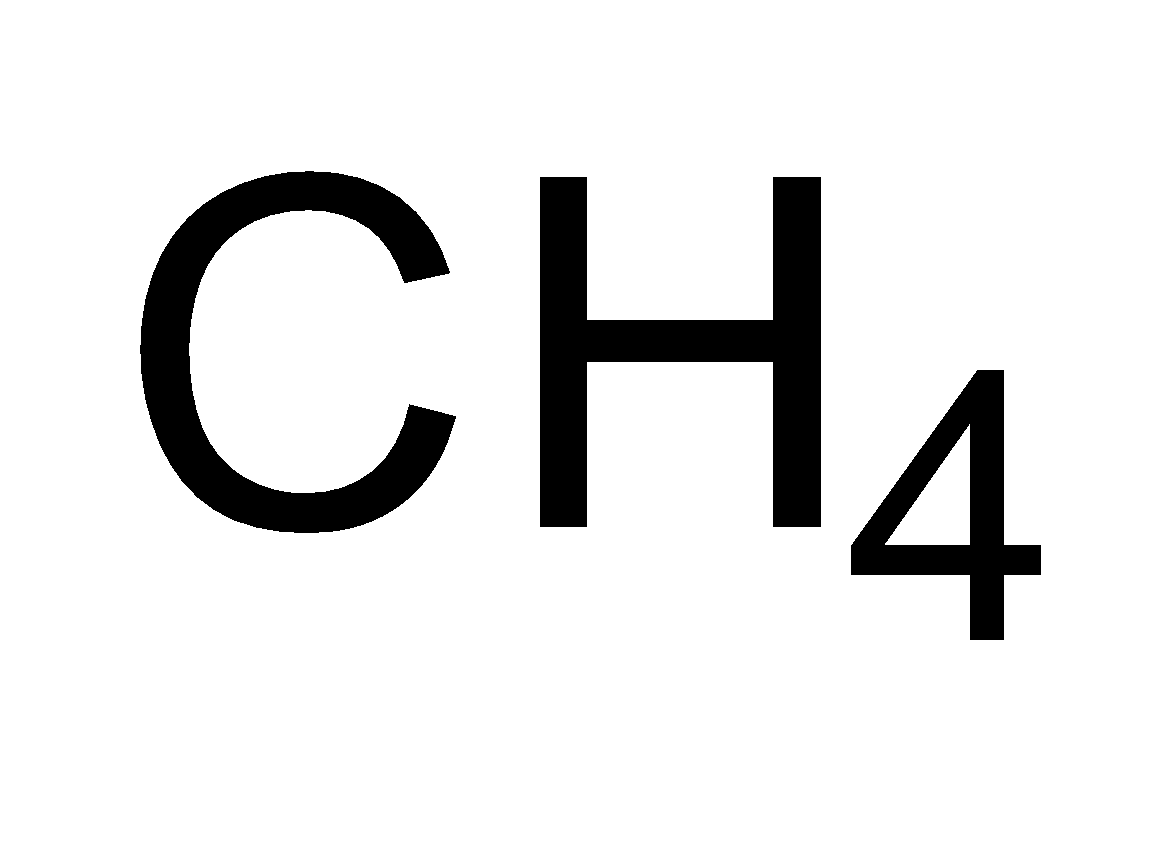
|
| Ethane | 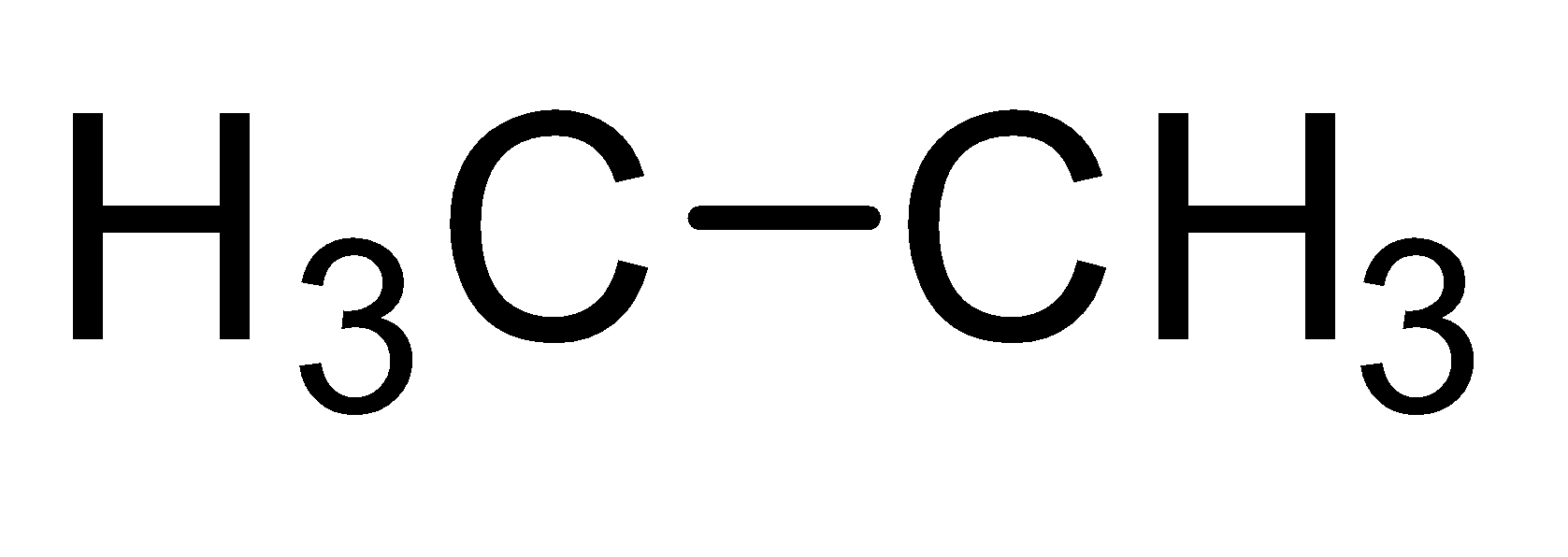
|
| Propane | 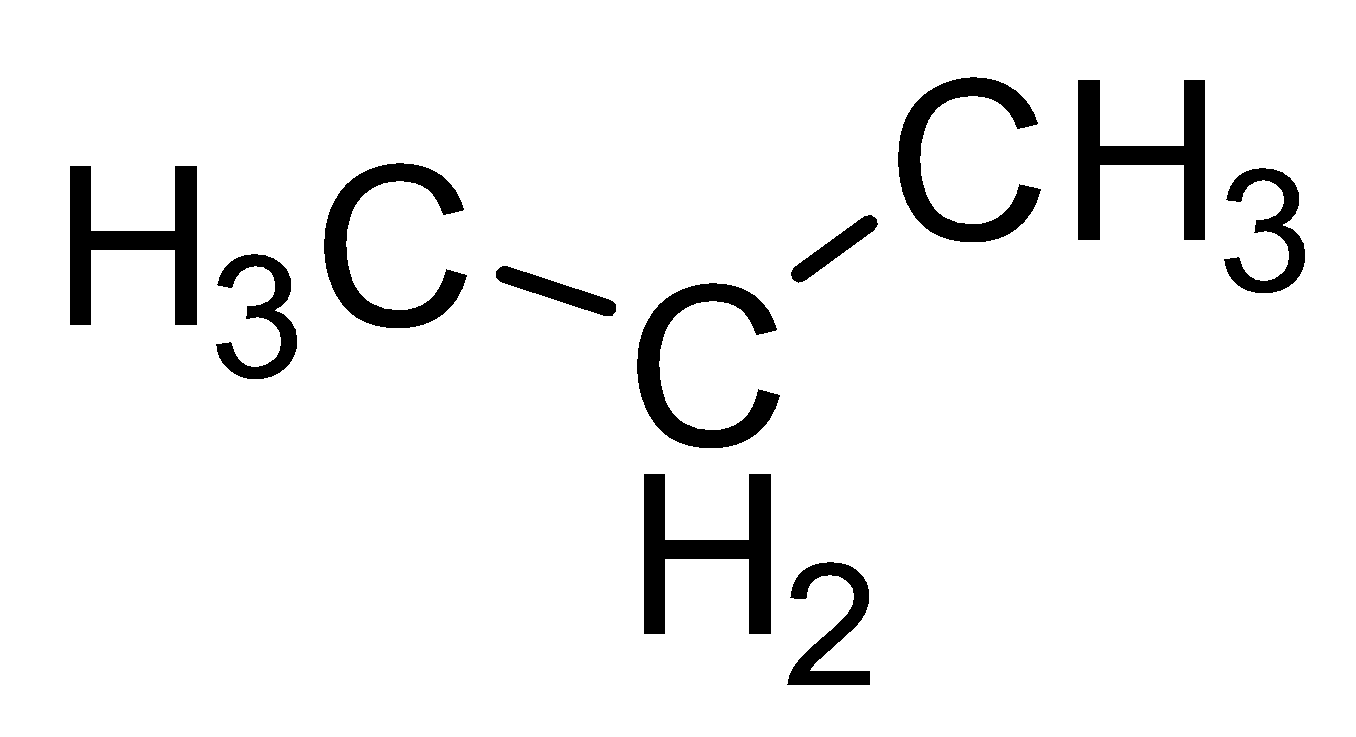
|
| Butane | 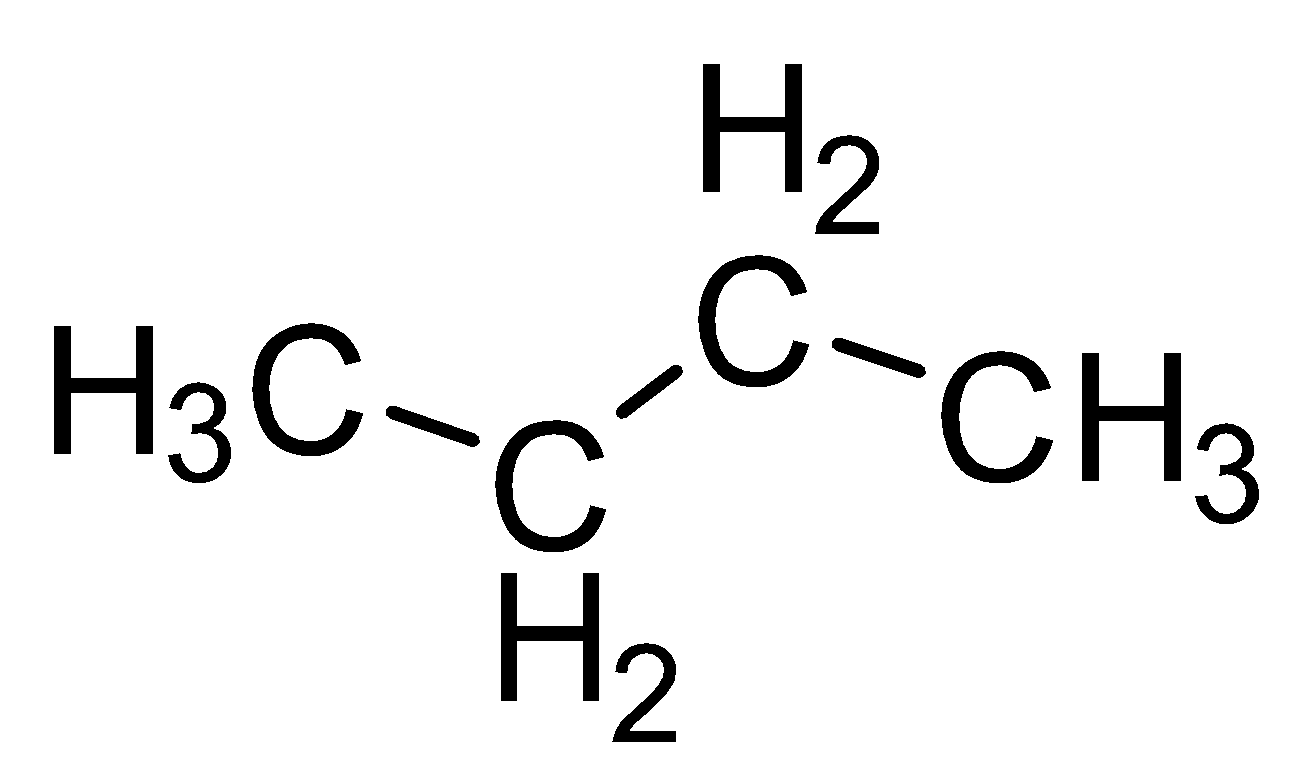
|
| pentane | 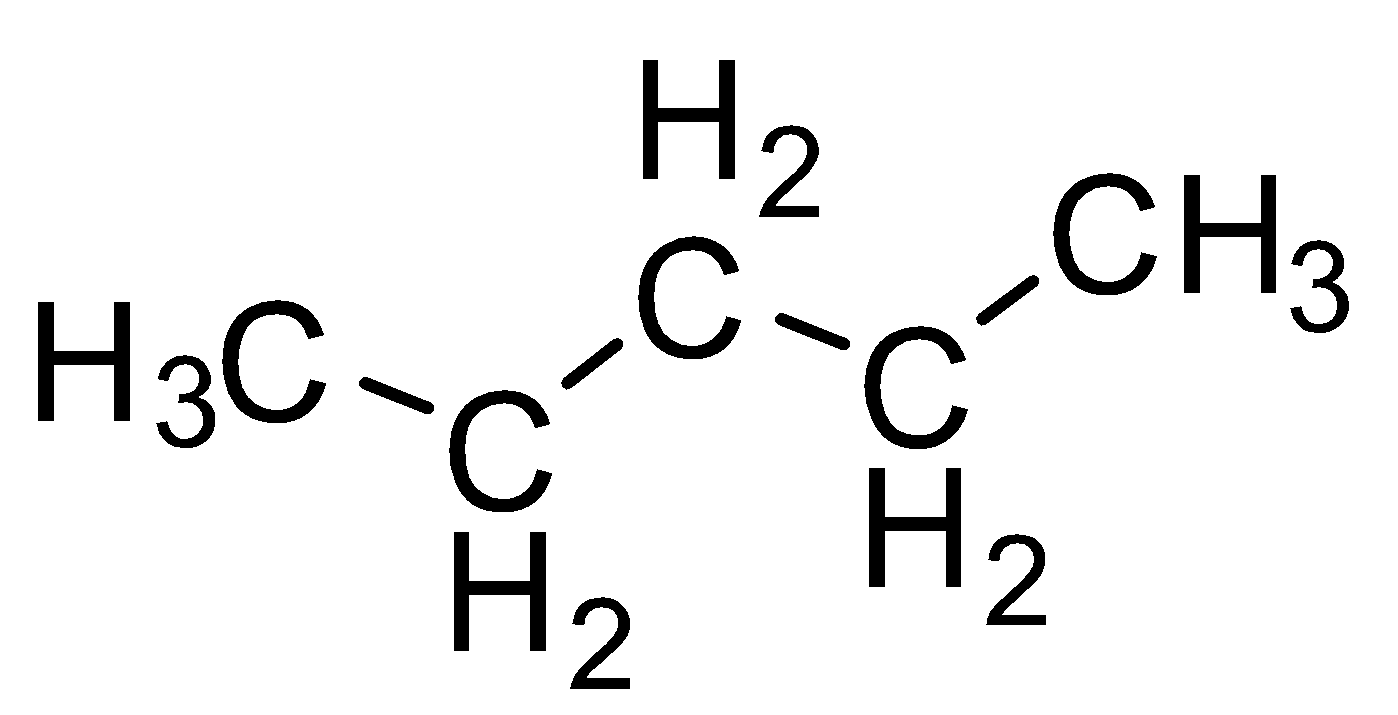
|
The names of members of the alkane family end with ‘–ane’.
Now let us talk about the cyclic compounds. In cyclic compounds atoms are connected to each other and form a ring-like structure. Cyclopentane can be formed from pentane by joining end carbon atoms. The structure of cyclopentane will be-

In this structure there are five groups of atoms connected to each other by a single carbon-carbon bond. The formula of cyclopentane can be determined from the above structure too. It is given as ${C_5}{H_{10}}$ .
In the electron-dot structure, the valence electrons of atoms are represented around them as dots. The number of dots is equal to the valence electrons in an atom. The electron-dot structure of cyclopentane is-

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember we show only valence electrons in the electron-dot structure of a compound. Cyclopentane has two hydrogen atoms less than straight chain compound pentane. These two hydrogen atoms are lost during the formation of a ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




