
The function of the cork cambium is to produce.
(a) Secondary xylem and secondary phloem
(b) Cork and secondary cortex
(c) Secondary cortex and phloem
(d) Cork
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: Cork cambium is a tissue found as a portion of the epidermis in many vascular plants. It's one of the many bark layers between the cork and the main phloem. The role of cork cambium is to produce both the phelloderm and the tough protective material.
Complete answer:
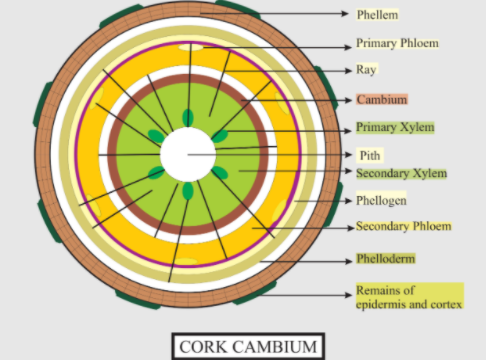
Cork cambium is a tissue found as a portion of the epidermis in many vascular plants. It's one of the many bark layers between the cork and the main phloem. It is found in woody dicots, gymnosperms, and some monocots and many herbal dicots. It is one of the meristems of the plant-the collection of tissues from which the plant develops consisting of embryonic disc (incompletely distinguished) cells. Cork cambium has the purpose of producing cork, a hard-protective material and a secondary cortex.
Therefore, the epidermis consists of three distinct layers:
-Phelloderm-composed of living parenchyma cells inside the cork cambium
-Phellogen (cork cambium)-a meristem which produces peridermis
-Phellem (cork)-dead at maturity; on the outside, air-filled safety tissue
Cork cambium growth and development varies greatly between different species and is also highly dependent on age and growing conditions, as can be seen from various bark surfaces that may be smooth, fissured, tessellated, scaly, or flaking off.
So, the answer is, “Cork and secondary cortex.”
Note: -The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for secondary growth in roots and stems that replaces the epidermis.
- Typically, monocots lack secondary growth.
-A phelloderm is also known as the secondary cortex.
-Bark cambium, pericambium, and Phellogen are synonyms for cork cambium. Phellogen is classified as the layer of meristematic cells responsible for the peridermis' growth. Phelloderm is named for cells that expand inward from there, and phellem or cork is named for cells that develop outward.
Complete answer:
Cork cambium is a tissue found as a portion of the epidermis in many vascular plants. It's one of the many bark layers between the cork and the main phloem. It is found in woody dicots, gymnosperms, and some monocots and many herbal dicots. It is one of the meristems of the plant-the collection of tissues from which the plant develops consisting of embryonic disc (incompletely distinguished) cells. Cork cambium has the purpose of producing cork, a hard-protective material and a secondary cortex.
Therefore, the epidermis consists of three distinct layers:
-Phelloderm-composed of living parenchyma cells inside the cork cambium
-Phellogen (cork cambium)-a meristem which produces peridermis
-Phellem (cork)-dead at maturity; on the outside, air-filled safety tissue
Cork cambium growth and development varies greatly between different species and is also highly dependent on age and growing conditions, as can be seen from various bark surfaces that may be smooth, fissured, tessellated, scaly, or flaking off.
So, the answer is, “Cork and secondary cortex.”
Note: -The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for secondary growth in roots and stems that replaces the epidermis.
- Typically, monocots lack secondary growth.
-A phelloderm is also known as the secondary cortex.
-Bark cambium, pericambium, and Phellogen are synonyms for cork cambium. Phellogen is classified as the layer of meristematic cells responsible for the peridermis' growth. Phelloderm is named for cells that expand inward from there, and phellem or cork is named for cells that develop outward.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




