
The functional group present in \[C{H_3}COO{C_2}{H_5}\]is.
A. Ketonic
B. Aldehydic
C. Ester
D. Carboxylic
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: As we can see the molecule is given with a specific functional group, so to identify the functional group we need to look for the alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl carbon. For that, we need to know different functions attached to the alkyl group.
So first, let's see the structure of the given compound that is \[C{H_3}COO{C_2}{H_5}\]. The name of this compound is ethyl ethanoate.
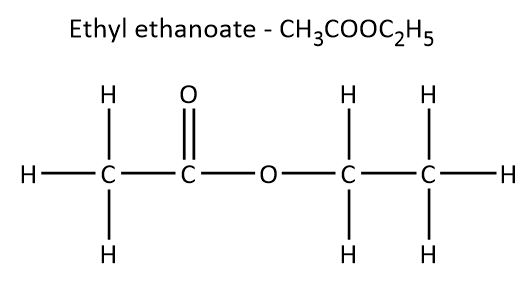
In ester, the carbon is attached to the two oxygen atoms and out of two oxygen atoms, one will attach to the carbon of the alkyl group. And the other oxygen will remain unattached which will be reactive. In ester, the alkyl group can be the same or it can be different.
Ester is formed when carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid as a catalyst. Simple esters are colourless. Esters have a fruity smell and it has low density and low boiling point. They are less soluble in water but dissolves in organic solvent.
The table shows different functional groups with the example so that we can easily differentiate the types of functional groups attached to the alkyl group. The table shown below is the reason why we have to eliminate other options.
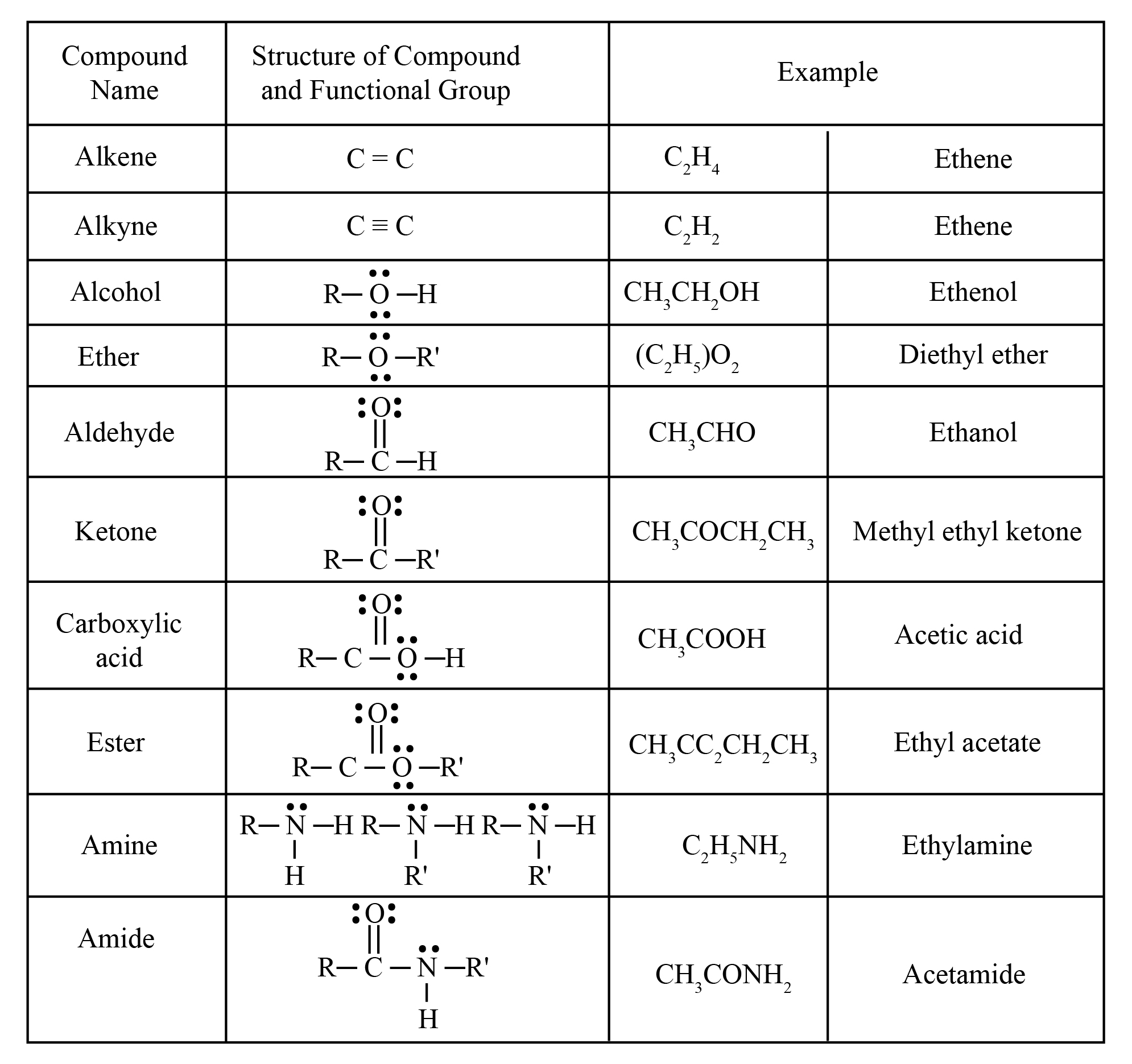
In the given table, the different functional group is shown with examples which will help to differentiate the given options. The way oxygen binds to the carbon will change the reactivity and the naming of the functional group. In a carboxylic functional group, the carbon is attached to the two oxygen but the oxygen is further attached to the hydrogen and not to the alkyl group which generates the difference between the ester and acidic functional group.
As per the IUPAC nomenclature rule the names are assigned.
Hence, the answer is (C) Ester.
The properties of esters are: it is widely used as flavoring agent and as perfumes. As it has the functional group similar to that of carboxylic acid few properties are almost similar to it.
Note:
Each and every compound has a specific name assigned as per their functional group attached. The functional isomer can be derived if we are aware of the different functional groups.
So first, let's see the structure of the given compound that is \[C{H_3}COO{C_2}{H_5}\]. The name of this compound is ethyl ethanoate.

In ester, the carbon is attached to the two oxygen atoms and out of two oxygen atoms, one will attach to the carbon of the alkyl group. And the other oxygen will remain unattached which will be reactive. In ester, the alkyl group can be the same or it can be different.
Ester is formed when carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid as a catalyst. Simple esters are colourless. Esters have a fruity smell and it has low density and low boiling point. They are less soluble in water but dissolves in organic solvent.
The table shows different functional groups with the example so that we can easily differentiate the types of functional groups attached to the alkyl group. The table shown below is the reason why we have to eliminate other options.

In the given table, the different functional group is shown with examples which will help to differentiate the given options. The way oxygen binds to the carbon will change the reactivity and the naming of the functional group. In a carboxylic functional group, the carbon is attached to the two oxygen but the oxygen is further attached to the hydrogen and not to the alkyl group which generates the difference between the ester and acidic functional group.
As per the IUPAC nomenclature rule the names are assigned.
Hence, the answer is (C) Ester.
The properties of esters are: it is widely used as flavoring agent and as perfumes. As it has the functional group similar to that of carboxylic acid few properties are almost similar to it.
Note:
Each and every compound has a specific name assigned as per their functional group attached. The functional isomer can be derived if we are aware of the different functional groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




