
The gasoline internal combustion engine [petrol engine] operates in a cycle that consists of six operations, out of which four are called strokes. Although processes of the cycle are actually irreversible, and friction and heat losses are present, we may assume the entire cycle as an idealised quasi- static cycle, as shown in the figure.
This cycle is known as the "Air-standard Otto cycle. Throughout this idealised cycle the working substance is treated as if it were an ideal gas of adiabatic exponent \[\gamma = 1.4\] alone, ignoring the fuel vapours and combustion products.
$I.$ "Isobaric intake stroke" in which the volume increases from zero to \[{V_a}\] at atmospheric pressure into the cylinder.
$II.$ Adiabatic compression stroke: The inlet valve is closed and the gasoline - air mixture is compressed adiabatically from \[{V_a}\] to \[{V_b}\] . Here \[r = \dfrac{{{V_a}}}{{{V_b}}}\] is known as the compression ratio of the engine \[\left[ {r = 6} \right]\]. If
\[r > 7\] then the temperature \[{T_b}\] that is reached at the end is sufficiently high to ignite the fuel mixture before the occurrence of spark. Such pre-ignition causes "knocking" and loss of power.
$III.$ Constant volume ignition: A spark is produced and mixture of air-gasoline vapour is ignited.
$IV.$ Adiabatic expansion or Power stroke: The heated air and combustion products expand against and drive the piston. This is the stroke that delivers power to the crankshaft.
$V.$ Constant volume exhaust: At the end of power stroke the exhaust valve is opened; this causes a sudden partial escape of cylinder gases. No piston motion takes place in this part of the cycle.
VI. Isobaric exhaust stroke: The moving piston drives out the residual cylinder gases to restore the initial condition of the engine. The ignition of air- gasoline vapour takes place at:
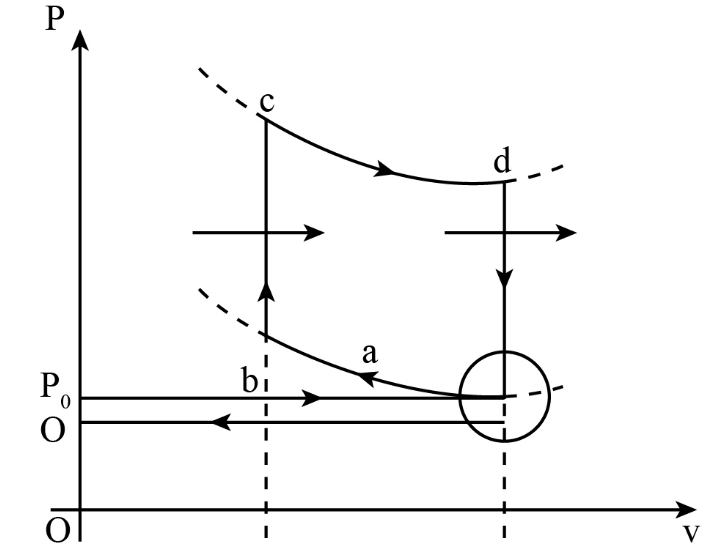
A. a
B. b
C. c
D. d

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: The above problem can be resolved by using the concept as well as the fundamentals of the petrol engine. The various strokes of the piston are analysed to obtain the correct knowledge of the ignition process of the engine.
Complete answer:
The ignition will take place at point a. In the given P-V diagram for the Air Standard Otto cycle, when moving from point d to b the piston in the cylinder starts moving from the Bottom Dead Centre (BDC) to Top Dead Centre (TDC). During this stroke the pressure inside the engine cylinder keeps on rising by decreasing the volume, due to this increased pressure the air inside the cylinder is compressed with rise in temperature to start the ignition at respective point a. Moreover, at point b the compression stroke completes and the residual gases leaves the engine stroke from the exit valve. Therefore, the ignition of the petrol engine starts at point a.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:In order to resolve the given problem, one must have the idea of the otto cycle and diesel cycle, along with the various processes occurring in the given Air-Standard cycle. The firm knowledge of the multiple stages of the air standard cycle and some specific points like knocking, Pre-ignition, scavenging, and many more are to be applied. Moreover, the detailed description of each stage in the engine is also known to achieve the correct solution of the given condition.
Complete answer:
The ignition will take place at point a. In the given P-V diagram for the Air Standard Otto cycle, when moving from point d to b the piston in the cylinder starts moving from the Bottom Dead Centre (BDC) to Top Dead Centre (TDC). During this stroke the pressure inside the engine cylinder keeps on rising by decreasing the volume, due to this increased pressure the air inside the cylinder is compressed with rise in temperature to start the ignition at respective point a. Moreover, at point b the compression stroke completes and the residual gases leaves the engine stroke from the exit valve. Therefore, the ignition of the petrol engine starts at point a.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:In order to resolve the given problem, one must have the idea of the otto cycle and diesel cycle, along with the various processes occurring in the given Air-Standard cycle. The firm knowledge of the multiple stages of the air standard cycle and some specific points like knocking, Pre-ignition, scavenging, and many more are to be applied. Moreover, the detailed description of each stage in the engine is also known to achieve the correct solution of the given condition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




