
The geometry of a methyl carbocation and methyl carbanion is likely to be respectively:
(A) Octahedral and linear
(B) Tetrahedral and planar
(C) Planar and tetrahedral
(D) Linear and tetrahedral
Answer
540.6k+ views
Hint :To approach this question we should know the VSEPR theory. The VSEPR theory is the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. It helps in predicting the shape of the molecule from the pairs of the electrons which surround the central atom of the molecule. This theory was presented by sidgwick and Powell.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The postulates of the VSEPR theory are that in the polyatomic molecules the one of the atoms is identified as the central atom to which the other atoms are linked. The total number of the valence shell electron pairs determines the shape of the molecule. The pairs of the electron tend to orient themselves in such a way that the electron electron repulsion is minimized. If the central atom of the molecule is being surrounded by the bond pairs of the electron then the asymmetrically shape of the molecule is expected.
The methyl carbocation has the molecular formula of $ C{{H}_{3}}^{+} $ . In this molecule we have two lone pairs and three bond pairs with a positive charge on carbon atoms. So it has three bond pairs so it will be $ s{{p}^{2}} $ hybridise. It will have trigonal planar geometry. The structure of molecule is :
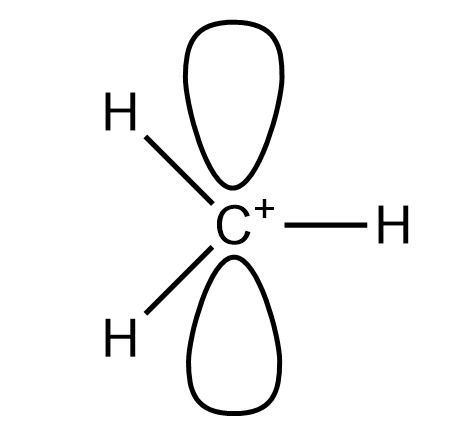
So this the structure of methyl carbocation.
The methyl anion has the molecular formula of $ C{{H}_{3}}^{-} $ . In this molecule we have one lone pair and three bond pairs with a negative charge on the carbon atom. This molecule is $ s{{p}^{3}} $ hybridised. It has a tetrahedral geometry. The structure of molecule is:
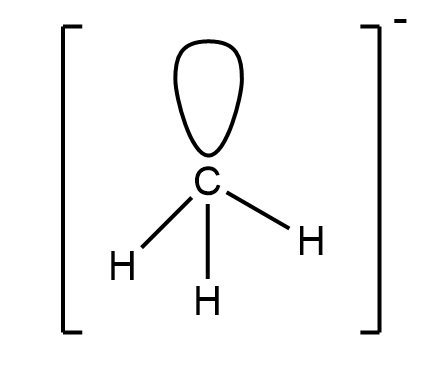
So this is the structure of methyl anion.
So the correct option is option c.
Note :
The limitation of VSEPR theory is that it was not able to explain the shape and structure of the isoelectronic species. This theory does not shed any light on the structure of the transition metals. It predicted that the halides of the group 2 elements would have linear structure but they actually have bent structure.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The postulates of the VSEPR theory are that in the polyatomic molecules the one of the atoms is identified as the central atom to which the other atoms are linked. The total number of the valence shell electron pairs determines the shape of the molecule. The pairs of the electron tend to orient themselves in such a way that the electron electron repulsion is minimized. If the central atom of the molecule is being surrounded by the bond pairs of the electron then the asymmetrically shape of the molecule is expected.
The methyl carbocation has the molecular formula of $ C{{H}_{3}}^{+} $ . In this molecule we have two lone pairs and three bond pairs with a positive charge on carbon atoms. So it has three bond pairs so it will be $ s{{p}^{2}} $ hybridise. It will have trigonal planar geometry. The structure of molecule is :

So this the structure of methyl carbocation.
The methyl anion has the molecular formula of $ C{{H}_{3}}^{-} $ . In this molecule we have one lone pair and three bond pairs with a negative charge on the carbon atom. This molecule is $ s{{p}^{3}} $ hybridised. It has a tetrahedral geometry. The structure of molecule is:

So this is the structure of methyl anion.
So the correct option is option c.
Note :
The limitation of VSEPR theory is that it was not able to explain the shape and structure of the isoelectronic species. This theory does not shed any light on the structure of the transition metals. It predicted that the halides of the group 2 elements would have linear structure but they actually have bent structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




