
The geometry of methane molecule is:
(A) Tetrahedral
(B) Pyramidal
(C) Octahedral
(D) Square planar
Answer
519.3k+ views
Hint :To answer this question, we need to understand the concept of geometry of carbon-based organic compounds. Geometry is based on the concept of hybridization of atoms.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
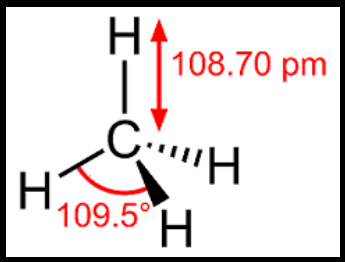
Methane is a saturated hydrocarbon and it contains only single bonds. A molecule of methane has a single carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. The geometry of the methane molecule is tetrahedral. It exhibits sp3 hybridization where a carbon atom is at the center and four hydrogen atoms are at the four corners. The bond length is about 109 pm and the angle between two hydrogen atoms in the arrangement is about 109.5 degrees. The methane molecule has a molecular weight of 16.04.
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Note :
Methane is a principal component of natural gas. When a single molecule of methane is burned in the presence of oxygen it releases one molecule of $CO_2$ (carbon dioxide) and two molecules of $H_2O$ (water). The strength of the carbon hydrogen covalent bond in methane is among the strongest in all hydrocarbons. Pure methane is odorless, but when used as a fuel it is usually mixed with small quantities of strongly-smelling sulfur compounds such as ethyl mercaptan to enable the detection of leaks.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Methane is a saturated hydrocarbon and it contains only single bonds. A molecule of methane has a single carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. The geometry of the methane molecule is tetrahedral. It exhibits sp3 hybridization where a carbon atom is at the center and four hydrogen atoms are at the four corners. The bond length is about 109 pm and the angle between two hydrogen atoms in the arrangement is about 109.5 degrees. The methane molecule has a molecular weight of 16.04.

Hence, the correct option is (a).
Note :
Methane is a principal component of natural gas. When a single molecule of methane is burned in the presence of oxygen it releases one molecule of $CO_2$ (carbon dioxide) and two molecules of $H_2O$ (water). The strength of the carbon hydrogen covalent bond in methane is among the strongest in all hydrocarbons. Pure methane is odorless, but when used as a fuel it is usually mixed with small quantities of strongly-smelling sulfur compounds such as ethyl mercaptan to enable the detection of leaks.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




