
The geometry of $XeO{{F}_{4}}$ according to VSEPR theory is:
A. Octahedral
B. Pentagonal planar
C. Square pyramidal
D. Trigonal bipyramidal
Answer
542.7k+ views
Hint: To know the geometry of $XeO{{F}_{4}}$, we should draw the Lewis structure of this compound. It will help in determining the bonding in the compound and helps in predicting the shape of the compound. In this compound, Xenon is the central atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory which is also abbreviated as VSEPR theory. In this theory, the pair of valence electrons will always have some repulsion between them and therefore they will tend to arrange themselves in a manner where the repulsion between the valence electrons is minimum. The arrangement of the atom will help in determining the geometry of the molecule.
In determining the shape of the molecule, we must follow these steps-
The least electronegative atom will be placed in the centre of the molecule.
Total number of electrons present in the outermost shell of the central atom must be counted.
The total numbers of electrons that belong to the other atom are used in bonding with the central atom and it should also be counted.
After that, these values must be added to obtain valence shell electron pair number (VSEP).
If the VSEP number is 2, then it is linear. If the VSEP number is 3, it is trigonal planar. If the VSEP number is 4, it is tetrahedral, if the VSEP number is 5, then it is trigonal bipyramidal. If the VSEP number is 6, it is octahedral and if the VSEP number is 7, then it is pentagonal bipyramidal.
The xenon contains eight electrons in their valence shell, hence its electronic configuration is-
Xenon is a central atom which is bonded with oxygen atom and fluorine atom
$Xe:\,\,[Kr]4{{d}^{10}}5{{s}^{2}}5{{p}^{6}}$
Ground state
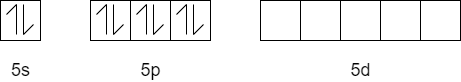
Excited state:

The hybridization of $XeO{{F}_{4}}$ is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$
Here, the central atom $Xe$ has one lone pair of electrons and five bond pairs.
Therefore, the geometry of $XeO{{F}_{4}}$ is square pyramidal.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
The structure of $XeO{{F}_{4}}$ :
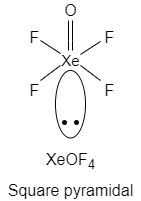
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Limitations of VSEPR theory:
It fails to explain the isoelectronic species. These species may vary in shape and they have the same number of electrons.
It does not explain about transition metals. The structures of such compounds are not described correctly by this theory.
It predicts that the halides of group $II$ elements will always show a linear structure, but their actual structure is bent.
Complete step by step answer:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory which is also abbreviated as VSEPR theory. In this theory, the pair of valence electrons will always have some repulsion between them and therefore they will tend to arrange themselves in a manner where the repulsion between the valence electrons is minimum. The arrangement of the atom will help in determining the geometry of the molecule.
In determining the shape of the molecule, we must follow these steps-
The least electronegative atom will be placed in the centre of the molecule.
Total number of electrons present in the outermost shell of the central atom must be counted.
The total numbers of electrons that belong to the other atom are used in bonding with the central atom and it should also be counted.
After that, these values must be added to obtain valence shell electron pair number (VSEP).
If the VSEP number is 2, then it is linear. If the VSEP number is 3, it is trigonal planar. If the VSEP number is 4, it is tetrahedral, if the VSEP number is 5, then it is trigonal bipyramidal. If the VSEP number is 6, it is octahedral and if the VSEP number is 7, then it is pentagonal bipyramidal.
The xenon contains eight electrons in their valence shell, hence its electronic configuration is-
Xenon is a central atom which is bonded with oxygen atom and fluorine atom
$Xe:\,\,[Kr]4{{d}^{10}}5{{s}^{2}}5{{p}^{6}}$
Ground state
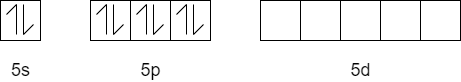
Excited state:

The hybridization of $XeO{{F}_{4}}$ is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$
Here, the central atom $Xe$ has one lone pair of electrons and five bond pairs.
Therefore, the geometry of $XeO{{F}_{4}}$ is square pyramidal.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
The structure of $XeO{{F}_{4}}$ :

So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Limitations of VSEPR theory:
It fails to explain the isoelectronic species. These species may vary in shape and they have the same number of electrons.
It does not explain about transition metals. The structures of such compounds are not described correctly by this theory.
It predicts that the halides of group $II$ elements will always show a linear structure, but their actual structure is bent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




