
The girth of stem increases due to ---.
(a) Apical meristem
(b) Lateral meristem
(c) Intercalary meristem
(d) All of the above
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: The girth of an object, for instance, the body of a human or an animal, is its width or thickness, considered to be the measure around its circumference. Stem girth means stem thickening.
Complete answer:
Stem girth increases due to lateral meristematic tissues. They are found as thin layers under the bark (called the cork cambium) and in vascular bundles of dicot roots and stems (called the vascular change) . This increase in the plant's diameter and girth is termed secondary growth.
The apical meristem is located at the rising tip of the stems, the root, and also at the leaf apices. They cause elongation, i.e. increase in plant height. Located at the base of the leaf and the internode, intercalary meristem causes an increase in the length of an organ.
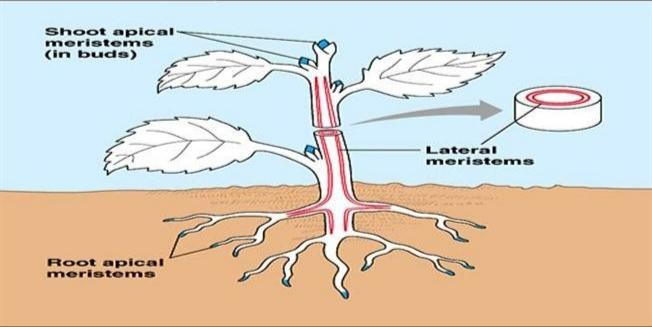
So, the correct answer is, ‘Lateral meristem’..
Additional Information:
- The lateral meristem occurs in the vascular bundles and the cork area.
- These meristematic regions possess cells capable of dividing and forming new cells for secondary development.
- The lateral meristematic tissue is responsible for an increase in plant diameter or girth.
Note: Meristem is undifferentiated plant tissue that is present in plant growth areas. Intercalary, apical, and lateral are the three types of meristematic tissue. The vascular change in plants is the principal route by which the stems and roots expand. The tissue consists of xylem to the outside and the internal phloem. Cork Cambium is found in mainly woody and some herbaceous plants, forming a cork or bark coating on the outside of the stem and secondary growth in the roots' epidermis.
Complete answer:
Stem girth increases due to lateral meristematic tissues. They are found as thin layers under the bark (called the cork cambium) and in vascular bundles of dicot roots and stems (called the vascular change) . This increase in the plant's diameter and girth is termed secondary growth.
The apical meristem is located at the rising tip of the stems, the root, and also at the leaf apices. They cause elongation, i.e. increase in plant height. Located at the base of the leaf and the internode, intercalary meristem causes an increase in the length of an organ.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Lateral meristem’..
Additional Information:
- The lateral meristem occurs in the vascular bundles and the cork area.
- These meristematic regions possess cells capable of dividing and forming new cells for secondary development.
- The lateral meristematic tissue is responsible for an increase in plant diameter or girth.
Note: Meristem is undifferentiated plant tissue that is present in plant growth areas. Intercalary, apical, and lateral are the three types of meristematic tissue. The vascular change in plants is the principal route by which the stems and roots expand. The tissue consists of xylem to the outside and the internal phloem. Cork Cambium is found in mainly woody and some herbaceous plants, forming a cork or bark coating on the outside of the stem and secondary growth in the roots' epidermis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




