
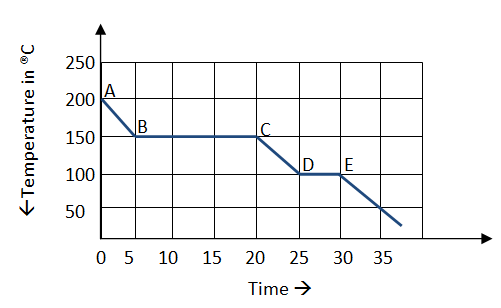
The graph alongside represents a cooling curve for a substance being cooled from a higher temperature to a lower temperature.
Why is the region DE shorter than the region BC?

Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint
The straight horizontal lines in the cooling curve represent the release of latent heat of vaporization (BC) and latent heat of fusion respectively when there is a change of state from gaseous to liquid and liquid to solid.
Complete step-by-step answer
The cooling curve of a substance being cooled is a temperature v/s time curve that determines the change in temperature with constant cooling supplied. The straight horizontal lines are the regions when the temperature of the substance remains constant despite constant cooling supplied.
This is the region where the change of state occurs. In a change of state, for example from gaseous to liquid, the substance releases the latent heat of vaporization which keeps the temperature of the substance being cooled at a constant value despite cooling being continuous. Similarly, during the transition from a liquid to solid, the latent heat of fusion is released and the temperature remains constant despite continuous cooling.
The time for which the Latent heat of vaporization shows its effect in maintaining the temperature constant is different than the time for which the latent heat of fusion shows its effect in making the temperature constant because the amount of these latent heats are different. The latent heat of fusion is always less than the latent heat of vaporization. This is explained below:
In solids, the molecules are very close together and the attraction between the molecules is great and the molecules have little freedom to move. In the case of a liquid, the molecules are closely spaced; they have more freedom to move and the intermolecular forces are weaker than that of a solid but the attraction still exists. However, in a gas, the molecules are sufficiently far apart that there are little to no attractive forces. Hence, the energy required to completely separate the molecules, moving from liquid to gas, is much greater than if you were just to reduce their separation, solid to liquid. This is the reason why the latent heat of vaporization is greater than the latent heat of fusion. And hence the region BC is much longer than the region DE.
Note
The latent heat of fusion and the latent heat of vaporization are phenomena occurring due to the change in kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance, when a substance changes state from liquid to solid for example, the latent heat of fusion is released because some of the kinetic energy of the molecules of the liquid is lost and gets converted to heat energy and the molecules come together to form a solid structure. This is just the effect of the law of conservation of energy. Similarly, the same amount of latent heat of fusion is absorbed when a solid is heated to melt to form a liquid to facilitate the change in state which requires the molecules of the solid to gain kinetic energy to spread out and the substance changes state to liquid. The temperature of the solid does not change at the melting point in a similar fashion.
The straight horizontal lines in the cooling curve represent the release of latent heat of vaporization (BC) and latent heat of fusion respectively when there is a change of state from gaseous to liquid and liquid to solid.
Complete step-by-step answer
The cooling curve of a substance being cooled is a temperature v/s time curve that determines the change in temperature with constant cooling supplied. The straight horizontal lines are the regions when the temperature of the substance remains constant despite constant cooling supplied.
This is the region where the change of state occurs. In a change of state, for example from gaseous to liquid, the substance releases the latent heat of vaporization which keeps the temperature of the substance being cooled at a constant value despite cooling being continuous. Similarly, during the transition from a liquid to solid, the latent heat of fusion is released and the temperature remains constant despite continuous cooling.
The time for which the Latent heat of vaporization shows its effect in maintaining the temperature constant is different than the time for which the latent heat of fusion shows its effect in making the temperature constant because the amount of these latent heats are different. The latent heat of fusion is always less than the latent heat of vaporization. This is explained below:
In solids, the molecules are very close together and the attraction between the molecules is great and the molecules have little freedom to move. In the case of a liquid, the molecules are closely spaced; they have more freedom to move and the intermolecular forces are weaker than that of a solid but the attraction still exists. However, in a gas, the molecules are sufficiently far apart that there are little to no attractive forces. Hence, the energy required to completely separate the molecules, moving from liquid to gas, is much greater than if you were just to reduce their separation, solid to liquid. This is the reason why the latent heat of vaporization is greater than the latent heat of fusion. And hence the region BC is much longer than the region DE.
Note
The latent heat of fusion and the latent heat of vaporization are phenomena occurring due to the change in kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance, when a substance changes state from liquid to solid for example, the latent heat of fusion is released because some of the kinetic energy of the molecules of the liquid is lost and gets converted to heat energy and the molecules come together to form a solid structure. This is just the effect of the law of conservation of energy. Similarly, the same amount of latent heat of fusion is absorbed when a solid is heated to melt to form a liquid to facilitate the change in state which requires the molecules of the solid to gain kinetic energy to spread out and the substance changes state to liquid. The temperature of the solid does not change at the melting point in a similar fashion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




