
The heart of an amphibian is usually
a. Two chambered
b. Four chambered
c. Three chambered
d. Three and half chambered
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: Amphibians have a closed circulatory system, where the blood is moved in the closed vessels, and this system is closed unless there is an abnormal mutation, where amphibians have one heart to pump blood throughout the body.
Complete answer:
- Amphibians have 3 chambered hearts which contain two atria and one ventricle.
- When coming to blood circulation, blood leaves the ventricles and passes into one of the vessels, it either travels through the pulmonary arteries leading to the lungs.
- Blood may travel through the forced aorta leading to the rest of the body.
- Oxygenated blood returning to the heart from the lungs through pulmonary veins which passes to the left atrium.
- As well as deoxygenated blood returning from the body through the sinus venous passes into the right atrium.
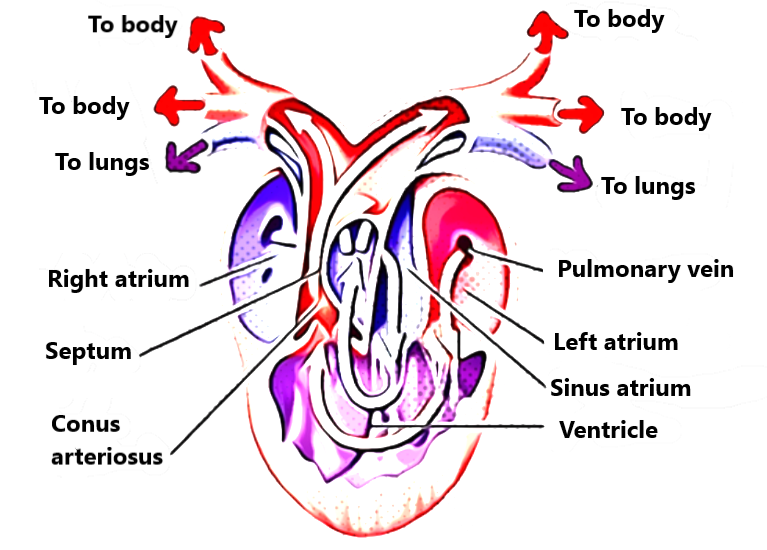
Amphibians heart
- Whereas both atria empty into a single ventricle, which results in the mixing of oxygen-rich blood returning from the lungs with oxygen-depleted blood from the body tissues.
- While the system of the amphibians assures that some blood always passes through the lungs and back to the heart.
- Whereas the mixing of the blood in the single ventricle means that where the organs of the amphibians are not getting the blood that is saturated with the oxygen.
- Even though this is not a 4 chamber heart system, which feels that two circuits separate, the thing is that it is sufficient for cold blooded organisms.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Along with the normal pulmonary circuit present in the amphibians, frogs also have a Pulmo cutaneous circuit, where the deoxygenated blood is transported to the skin, to pick up the oxygen and also to undergo the exchange of the gases.
Complete answer:
- Amphibians have 3 chambered hearts which contain two atria and one ventricle.
- When coming to blood circulation, blood leaves the ventricles and passes into one of the vessels, it either travels through the pulmonary arteries leading to the lungs.
- Blood may travel through the forced aorta leading to the rest of the body.
- Oxygenated blood returning to the heart from the lungs through pulmonary veins which passes to the left atrium.
- As well as deoxygenated blood returning from the body through the sinus venous passes into the right atrium.

Amphibians heart
- Whereas both atria empty into a single ventricle, which results in the mixing of oxygen-rich blood returning from the lungs with oxygen-depleted blood from the body tissues.
- While the system of the amphibians assures that some blood always passes through the lungs and back to the heart.
- Whereas the mixing of the blood in the single ventricle means that where the organs of the amphibians are not getting the blood that is saturated with the oxygen.
- Even though this is not a 4 chamber heart system, which feels that two circuits separate, the thing is that it is sufficient for cold blooded organisms.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Along with the normal pulmonary circuit present in the amphibians, frogs also have a Pulmo cutaneous circuit, where the deoxygenated blood is transported to the skin, to pick up the oxygen and also to undergo the exchange of the gases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




