
The hottest region of the Bunsen flame shown in the figure below is-
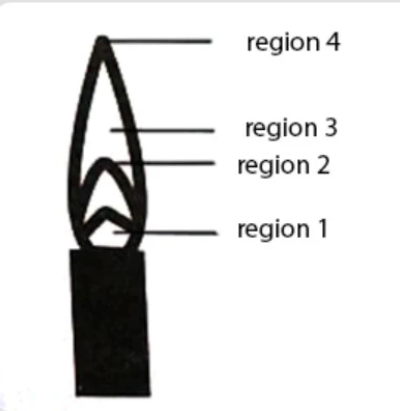
[A] Region 2
[B] Region 3
[C] Region 4
[D] Region 1

Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: In a Bunsen burner, the flames are divided into different categories depending upon their level of combustion. Due to which different coloured flames are observed. The flame flows from base to tip and as the gas is combusted, more and more heat is produced, thus making it the hottest.
Complete step by step solution: A Bunsen burner is a kind of gas burner used in laboratories. This is used to safely burn continuous streams of flammable gases like mixtures of liquefied petroleum gases like butane, propane, or natural gases like methane.
It has a rubber hose through which the gas passes and there are holes for passing air. There are holes for air and also a screw for controlling the air passage through the gas. A lighter or matchstick is used to light the gas.
Bunsen burners flame depends on the flow of air in the holes.
If the holes are closed i.e. the gas only mixes with the air at the point of combustion, then the flame is lighter and bright yellow in colour, also known as safety flame or default. This flame is yellow due to incomplete combustion due to lack of air and contains soot.
When the holes are fully opened i.e. air is allowed to pass through the gas, the flame burns blue and is the strongest. Here, complete combustion of the gases takes place.
There are three zones in the Bunsen burner flame- Inner zone, middle zone and the outer zone.
The inner zone is the unburned gas.
The middle zone is the oxygen deficient zone and is called the reduction zone.
The outer zone is the oxidizing zone.
The coolest part of the flame is the middle zone and the hottest part is the tip of the inner.
In the figure, the tip of the inner plane is marked as region 2, which is the hottest part.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [A] Region 2
Note: A Bunsen burner has different varieties of flames. However, in every kind of flame (blue or yellow) the hottest portion is the tip of the middle zone and the coolest part is the whole of the middle zone except the tip. The blue flame is considered to be the hotter than yellow flame as the blue flame transfers more energy due to complete combustion. Incomplete combustion forms yellow flame.
Complete step by step solution: A Bunsen burner is a kind of gas burner used in laboratories. This is used to safely burn continuous streams of flammable gases like mixtures of liquefied petroleum gases like butane, propane, or natural gases like methane.
It has a rubber hose through which the gas passes and there are holes for passing air. There are holes for air and also a screw for controlling the air passage through the gas. A lighter or matchstick is used to light the gas.
Bunsen burners flame depends on the flow of air in the holes.
If the holes are closed i.e. the gas only mixes with the air at the point of combustion, then the flame is lighter and bright yellow in colour, also known as safety flame or default. This flame is yellow due to incomplete combustion due to lack of air and contains soot.
When the holes are fully opened i.e. air is allowed to pass through the gas, the flame burns blue and is the strongest. Here, complete combustion of the gases takes place.
There are three zones in the Bunsen burner flame- Inner zone, middle zone and the outer zone.
The inner zone is the unburned gas.
The middle zone is the oxygen deficient zone and is called the reduction zone.
The outer zone is the oxidizing zone.
The coolest part of the flame is the middle zone and the hottest part is the tip of the inner.
In the figure, the tip of the inner plane is marked as region 2, which is the hottest part.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [A] Region 2
Note: A Bunsen burner has different varieties of flames. However, in every kind of flame (blue or yellow) the hottest portion is the tip of the middle zone and the coolest part is the whole of the middle zone except the tip. The blue flame is considered to be the hotter than yellow flame as the blue flame transfers more energy due to complete combustion. Incomplete combustion forms yellow flame.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




