
The hybridisation of nitrogen in nitrate ion is:
(A) \[sp\]
(B) \[s{p^2}\]
(C) \[s{p^3}\]
(D) \[s{p^3}d\]
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Determine the total number of valence electrons in the nitrate ion. Then draw the Lewis structure. Determine the steric number and then determine the type of hybridization.
Complete answer:
Nitrate ion is obtained from the ionization of nitric acid. When a nitric acid loses a proton, nitrate ion is obtained. The formula of nitric acid is \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] and the formula of nitrate ion is \[{\text{NO}}_3^ - \] . Nitrate ions have a unit negative charge.
\[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + NO}}_3^ - \]
In the nitrate ion, the central atom is nitrogen atom. The number of valence electrons on nitrogen and oxygen atoms are 5 and 6 respectively. Calculate the total number of valence electrons in nitrate ion:
\[{\text{5 + 3}}\left( 6 \right){\text{ + 1 = 24}}\]
Here one additional electron is due to negative charge.
Write the Lewis structure of nitrate ion:
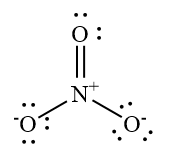
The central nitrogen atom forms a double bond with one oxygen atom, a covalent bond with another oxidation atom and a coordinate bond with a third oxygen atom. Number of lone pairs of electrons on a central nitrogen atom is zero. The number of bonding domains is 3. Hence the steric number is 3. Steric number of 3 is associated with \[s{p^2}\] hybridization and trigonal planar geometry. Hence, the nitrogen atom in nitrate ion has \[s{p^2}\] hybridization.
Hence, the correct option is the option (B).
Note: Steric number is the total number of bond pairs of electrons (or bonding domains) and lone pair of electrons present around the central atom. You can use the steric number to determine the type of hybridisation and the geometry.
Complete answer:
Nitrate ion is obtained from the ionization of nitric acid. When a nitric acid loses a proton, nitrate ion is obtained. The formula of nitric acid is \[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] and the formula of nitrate ion is \[{\text{NO}}_3^ - \] . Nitrate ions have a unit negative charge.
\[{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + NO}}_3^ - \]
In the nitrate ion, the central atom is nitrogen atom. The number of valence electrons on nitrogen and oxygen atoms are 5 and 6 respectively. Calculate the total number of valence electrons in nitrate ion:
\[{\text{5 + 3}}\left( 6 \right){\text{ + 1 = 24}}\]
Here one additional electron is due to negative charge.
Write the Lewis structure of nitrate ion:

The central nitrogen atom forms a double bond with one oxygen atom, a covalent bond with another oxidation atom and a coordinate bond with a third oxygen atom. Number of lone pairs of electrons on a central nitrogen atom is zero. The number of bonding domains is 3. Hence the steric number is 3. Steric number of 3 is associated with \[s{p^2}\] hybridization and trigonal planar geometry. Hence, the nitrogen atom in nitrate ion has \[s{p^2}\] hybridization.
Hence, the correct option is the option (B).
Note: Steric number is the total number of bond pairs of electrons (or bonding domains) and lone pair of electrons present around the central atom. You can use the steric number to determine the type of hybridisation and the geometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




