
The hybridization of the orbitals of oxygen in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is __________.
A.$s{p^3}d$
B.$sp$
C.$s{p^2}$
D.$s{p^3}$
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: The mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals which are suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds is known as hybridization.
Complete step by step answer:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The valence electrons of ${\text{H}}$ are ${\text{1}}$ and the valence electrons of ${\text{O}}$ are ${\text{6}}$. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of H}}} \right) + \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of O}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {2 \times 1} \right) + \left( {2 \times 6} \right)$
$ = 2 + 12$
Valence electrons of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 14$
The structure of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is,
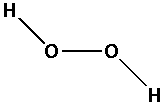
As three bonds are formed, six electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons $ = 14 - 6 = 8$
Place the remaining ${\text{8}}$ electrons around the oxygen atoms to complete their octets Thus,
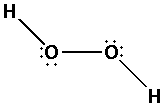
The eight electrons get placed along the oxygen atoms thus completing the octets of all the oxygen atoms.
The oxygen atoms have two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons.
Thus, the hybridization of the orbitals of oxygen in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is $s{p^3}$.
Thus, the correct option is option (D).
Note:
The $s{p^3}$ hybridization is a result of mixing one ${\text{2s}}$ orbital and three ${\text{2p}}$ orbitals. This mixing creates four hybrid orbitals having the same characteristics. For an atom to be $s{p^3}$ hybridised, it should have one s orbital and three p orbitals.
The hybridisation of any atom can be determined by the number of bond pairs and the number of lone pairs on it.
The number of bond pairs and the number of lone pairs can be determined from the Lewis structure. The diagram which shows the bonding between the atoms of a molecule is known as Lewis structure or electron-dot structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The valence electrons of ${\text{H}}$ are ${\text{1}}$ and the valence electrons of ${\text{O}}$ are ${\text{6}}$. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of H}}} \right) + \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of O}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {2 \times 1} \right) + \left( {2 \times 6} \right)$
$ = 2 + 12$
Valence electrons of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 14$
The structure of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is,

As three bonds are formed, six electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons $ = 14 - 6 = 8$
Place the remaining ${\text{8}}$ electrons around the oxygen atoms to complete their octets Thus,

The eight electrons get placed along the oxygen atoms thus completing the octets of all the oxygen atoms.
The oxygen atoms have two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons.
Thus, the hybridization of the orbitals of oxygen in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is $s{p^3}$.
Thus, the correct option is option (D).
Note:
The $s{p^3}$ hybridization is a result of mixing one ${\text{2s}}$ orbital and three ${\text{2p}}$ orbitals. This mixing creates four hybrid orbitals having the same characteristics. For an atom to be $s{p^3}$ hybridised, it should have one s orbital and three p orbitals.
The hybridisation of any atom can be determined by the number of bond pairs and the number of lone pairs on it.
The number of bond pairs and the number of lone pairs can be determined from the Lewis structure. The diagram which shows the bonding between the atoms of a molecule is known as Lewis structure or electron-dot structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




