
The hybridization state of beryllium atoms in $BeC{l_2}$ a molecule is x. The type of hybridization changes to y when $BeC{l_2}$ transforms to the solid-state. The x and y are respectively:
A.$sp,s{p^2}$
B.$sp,s{p^3}$
C.$s{p^2},s{p^3}$
D.$sp,sp$
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Hybridization is defined as the concept of intermixing of the orbitals of an atom having nearly the same energy to give exactly equivalent orbitals with the same energy, identical shapes, and symmetrical orientation in space.
Complete step by step answer:
Hybridization of any element can be found by using the formula:
$X = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + M - C + A]$
Where V = number of valence electrons of the central metal atom.
M = number of monovalent groups.
C = number of positive charges.
A = number of negative charges.
We would utilise the same formula to calculate the hybridization of $BeC{l_2}$. Here the central atom is beryllium and since the atomic number of Beryllium is 4 and it belongs to group second hence the number of valence electrons is 2. Since chlorine is a monovalent atom hence, in case of $BeC{l_2}$, there are 2 monovalent atoms. And there are no overall charges hence hybridization will be:
$X = \dfrac{1}{2}[2 + 2]$
$ \Rightarrow X = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 = 2$
Hence the hybridization is $sp$ and the structure is linear at nearly 1200k.
The structure will be:

But in the case of the solid phase, $BeC{l_2}$ has a polymeric chain structure. The polymeric structure of the $BeC{l_2}$ is due to its electron deficiency. Beryllium has only four-electrons in the valence shell hence, it can accept two more electron pairs from neighbouring chlorine chains forming coordination bonds. In this case hybridization of beryllium in $BeC{l_2}$ getting changes to $s{p^3}$. The polymeric chain structure $BeC{l_2}$ is given as:
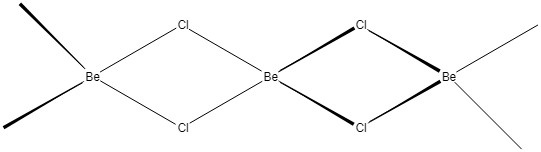
Hence the x and y are respectively $sp$ and $s{p^3}$.
Hence the correct answer is option is B.
Note:
Beryllium chloride acts as a strong lewis base due to its electron-deficient nature and is used as a catalyst in the Friedel-craft reaction. It is a covalent compound hence, it is soluble in the organic solvent.
Complete step by step answer:
Hybridization of any element can be found by using the formula:
$X = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + M - C + A]$
Where V = number of valence electrons of the central metal atom.
M = number of monovalent groups.
C = number of positive charges.
A = number of negative charges.
We would utilise the same formula to calculate the hybridization of $BeC{l_2}$. Here the central atom is beryllium and since the atomic number of Beryllium is 4 and it belongs to group second hence the number of valence electrons is 2. Since chlorine is a monovalent atom hence, in case of $BeC{l_2}$, there are 2 monovalent atoms. And there are no overall charges hence hybridization will be:
$X = \dfrac{1}{2}[2 + 2]$
$ \Rightarrow X = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 = 2$
Hence the hybridization is $sp$ and the structure is linear at nearly 1200k.
The structure will be:

But in the case of the solid phase, $BeC{l_2}$ has a polymeric chain structure. The polymeric structure of the $BeC{l_2}$ is due to its electron deficiency. Beryllium has only four-electrons in the valence shell hence, it can accept two more electron pairs from neighbouring chlorine chains forming coordination bonds. In this case hybridization of beryllium in $BeC{l_2}$ getting changes to $s{p^3}$. The polymeric chain structure $BeC{l_2}$ is given as:

Hence the x and y are respectively $sp$ and $s{p^3}$.
Hence the correct answer is option is B.
Note:
Beryllium chloride acts as a strong lewis base due to its electron-deficient nature and is used as a catalyst in the Friedel-craft reaction. It is a covalent compound hence, it is soluble in the organic solvent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




