
The hydrolytic enzymes are found in:
A. Peroxisomes
B. Lysosomes
C. Lomasomes
D. None of these
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: Hydrolytic enzymes exist in the form of minute crystalline or semicrystalline granules. Sizes of these granules vary from 5-8 nm. These are digestive enzymes and need an acidic medium to perform thier function. Hence, these enzymes are also called acid hydrolases.
Complete step-by-step answer:
1. Lysosomes are the small vesicle-like organelles found solely in eukaryotic cells. They contain many hydrolytic enzymes such as proteases, nucleases, and lipases.
2. In prokaryotes, there are no membrane-bound organelles. Hence lysosomes are absent, but the hydrolytic enzymes are present in the cytoplasm along with inclusion bodies.
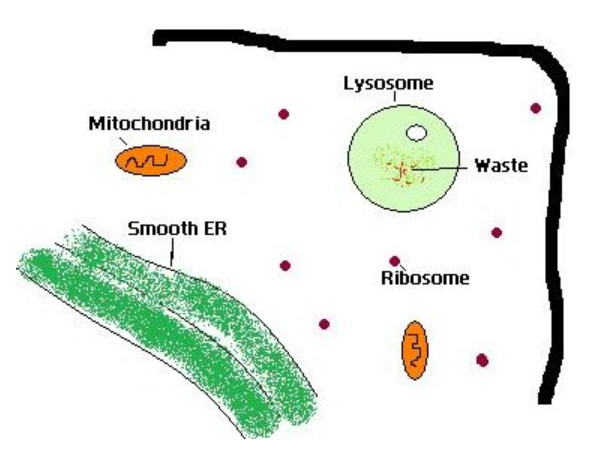
3. Their function is to breakdown cellular wastes and debris by engulfing and breaking down with hydrolytic enzymes. Apart from breaking down biological polymers, lysosomes are also involved in various other cell processes such as counting discharged materials, energy metabolism, cell signaling (communication processes that govern basic activities of cells and coordinate multiple-cell actions), and restoration of the plasma membrane.
4. The pH level of the lumen of lysosome lies between 4.5 and 5.0, which is acidic.
5. Lysosomes are also known as suicide bags of the cell because their digestive enzymes may also damage the lysosomes themselves, and this can result in cell death. This is termed as autolysis.
So, the correct answer is “Option B Lysosomes”.
Note:
1. Peroxisomes (also known as a microbody) are membrane-bound organelles, found in the cytoplasm of almost all of the eukaryotic cells. They are oxidative organelles and they frequently use molecular oxygen as a co-substrate, to form hydrogen peroxide ($H_2O_2$). This helps/ defends the cell from dangerous free radicals and other powerful oxidative substances.
2. Lomasomes are para mural bodies that are continuous with the cell wall. They (para mural bodies) are membranous or vesicular structures located between the cell walls and cell membranes of plant and fungal cells. Para mural bodies are referred to as Plasmalemmasomes if they are associated with the plasmalemma.
Complete step-by-step answer:
1. Lysosomes are the small vesicle-like organelles found solely in eukaryotic cells. They contain many hydrolytic enzymes such as proteases, nucleases, and lipases.
2. In prokaryotes, there are no membrane-bound organelles. Hence lysosomes are absent, but the hydrolytic enzymes are present in the cytoplasm along with inclusion bodies.

3. Their function is to breakdown cellular wastes and debris by engulfing and breaking down with hydrolytic enzymes. Apart from breaking down biological polymers, lysosomes are also involved in various other cell processes such as counting discharged materials, energy metabolism, cell signaling (communication processes that govern basic activities of cells and coordinate multiple-cell actions), and restoration of the plasma membrane.
4. The pH level of the lumen of lysosome lies between 4.5 and 5.0, which is acidic.
5. Lysosomes are also known as suicide bags of the cell because their digestive enzymes may also damage the lysosomes themselves, and this can result in cell death. This is termed as autolysis.
So, the correct answer is “Option B Lysosomes”.
Note:
1. Peroxisomes (also known as a microbody) are membrane-bound organelles, found in the cytoplasm of almost all of the eukaryotic cells. They are oxidative organelles and they frequently use molecular oxygen as a co-substrate, to form hydrogen peroxide ($H_2O_2$). This helps/ defends the cell from dangerous free radicals and other powerful oxidative substances.
2. Lomasomes are para mural bodies that are continuous with the cell wall. They (para mural bodies) are membranous or vesicular structures located between the cell walls and cell membranes of plant and fungal cells. Para mural bodies are referred to as Plasmalemmasomes if they are associated with the plasmalemma.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




