
The H-zone in the skeletal muscle fiber is due to
A. The absence of myofibrils in the central portion of A-band.
B. The central gap between myosin filaments in the A-band.
C. The central gap between actin filaments extends through myosin filament in the A-band.
D. Extension of myosin filaments in the central portion of the A-band.
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The skeletal muscles are the key components of the muscular system. The H-zone in the skeletal muscle fibers is referred to as the central gap between light filaments extending through dark filaments in the A-band.
Complete step by step answer: The skeletal muscles are generally attached to bones. The individual muscle fibers that make them are long and skinny cells that are wrapped in areolar connective tissue.
-The skeletal muscle fiber consists of Myofibrils as their structural units. These are further made up of two types of filaments. These filaments are actin and myosin. The actin filament is called a thin filament and the myosin filament is called a thick filament.
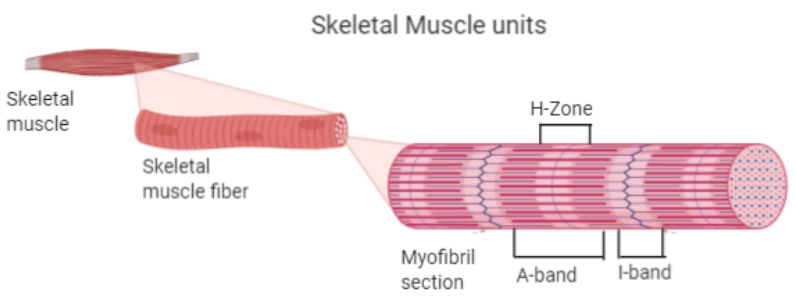
-The light bands in skeletal muscle fibers consist of light bands containing actin. These are called I-bands or Isotropic bands. Also, there are dark bands containing myosin and these are termed as A-bands or Anisotropic bands. These two bands are arranged alternately throughout the length of the myofibrils in skeletal muscle fiber.
-The edges of the actin filaments are present on either side of myosin filaments. These thin or actin filaments partially overlap on the free ends of myosin filaments in the resting phase. This overlapping leaves a central part of the myosin filaments uncovered creating a gap. This non-overlapped central part of the myosin filament is called the H-zone.
-Thus, the H-zone in the skeletal muscle fiber is due to the central gap between actin or thin filaments extending through myosin or thick filament in the A-band.
Hence, the correct option is option C.
Note: Each skeletal muscle consists of hundreds or thousands of myofibrils. The 3000 thin filaments and 1500 thick filaments in each myofibril give the characteristic striated appearance to the skeletal muscles. The interconnected networks made by actin and myosin gives the muscle fiber their ability to stretch and to stay in position.
Complete step by step answer: The skeletal muscles are generally attached to bones. The individual muscle fibers that make them are long and skinny cells that are wrapped in areolar connective tissue.
-The skeletal muscle fiber consists of Myofibrils as their structural units. These are further made up of two types of filaments. These filaments are actin and myosin. The actin filament is called a thin filament and the myosin filament is called a thick filament.

-The light bands in skeletal muscle fibers consist of light bands containing actin. These are called I-bands or Isotropic bands. Also, there are dark bands containing myosin and these are termed as A-bands or Anisotropic bands. These two bands are arranged alternately throughout the length of the myofibrils in skeletal muscle fiber.
-The edges of the actin filaments are present on either side of myosin filaments. These thin or actin filaments partially overlap on the free ends of myosin filaments in the resting phase. This overlapping leaves a central part of the myosin filaments uncovered creating a gap. This non-overlapped central part of the myosin filament is called the H-zone.
-Thus, the H-zone in the skeletal muscle fiber is due to the central gap between actin or thin filaments extending through myosin or thick filament in the A-band.
Hence, the correct option is option C.
Note: Each skeletal muscle consists of hundreds or thousands of myofibrils. The 3000 thin filaments and 1500 thick filaments in each myofibril give the characteristic striated appearance to the skeletal muscles. The interconnected networks made by actin and myosin gives the muscle fiber their ability to stretch and to stay in position.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




