
The IUPAC name of the compound given below is:
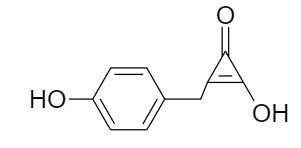
(A) $ \text{2}-\text{Hydroxy}-\text{3}\left( \text{4 }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }-\text{hydroxyphenyl} \right)\text{cycloprop}-\text{2}-\text{en}-\text{1}-\text{one} $
(B) $ \text{2}-\text{Hydroxy}-\text{3}\left( \text{4 }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }-\text{hydroxyphenylmethyl} \right)\text{cycloprop}-\text{2}-\text{en}-\text{1}-\text{one} $
(C) $ \text{4}-(\text{2 }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }-\text{Hydroxy}-\text{3 }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }-\text{oxocycloprop}-1'-\text{enylmethyl)phenol} $
(D) $ \text{4}-(1\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }-\text{Hydroxy}-\text{3 }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }-\text{oxocycloprop}-1'-\text{enylmethyl)phenol} $

Answer
519k+ views
Hint : In organic chemistry, IUPAC nomenclature is a method of naming organic compounds according to standards set by the international union of pure and applied chemistry. But due to its long and tedious names, generally common names are more preferred over IUPAC names.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As the given compound is an aromatic compound consisting of a benzene ring. So, rules for naming an organic compound according to IUPAC nomenclature are as follows:
For substituted benzene rings having more than six carbon atoms, the benzene ring is denoted by the word phenyl as the prefix of the alkane present which means for the given case, the base of the IUPAC name will consist of the cycloalkane part.
Ketone group has higher preference than that of hydroxyl group i.e., the IUPAC name will end with suffix -one rather than the suffix -ol.
The position of double bond and the substituent groups in the ring are located in such a way that the minimum possible number is assigned to the groups according to the priority order.
Therefore, for the given compound the numbering is done as follows:
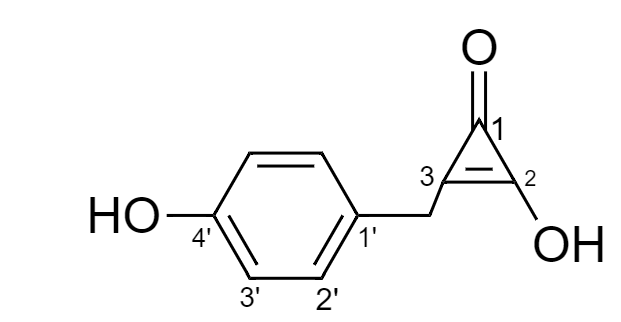
Hence, IUPAC name for the given compound is as follows:
$ \text{2}-\text{Hydroxy}-\text{3}\left( \text{4 }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }-\text{hydroxyphenylmethyl} \right)\text{cycloprop}-\text{2}-\text{en}-\text{1}-\text{one} $
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note :
It is important to note that the cyclopropane ring is not directly connected to the benzene ring but is connected via methyl group that is why methyl word is also used in the naming of substituent at third carbon. Also, due to the presence of a cyclic group as a substituent on benzene ring, the ring will not have a root or base name as phenol.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As the given compound is an aromatic compound consisting of a benzene ring. So, rules for naming an organic compound according to IUPAC nomenclature are as follows:
For substituted benzene rings having more than six carbon atoms, the benzene ring is denoted by the word phenyl as the prefix of the alkane present which means for the given case, the base of the IUPAC name will consist of the cycloalkane part.
Ketone group has higher preference than that of hydroxyl group i.e., the IUPAC name will end with suffix -one rather than the suffix -ol.
The position of double bond and the substituent groups in the ring are located in such a way that the minimum possible number is assigned to the groups according to the priority order.
Therefore, for the given compound the numbering is done as follows:

Hence, IUPAC name for the given compound is as follows:
$ \text{2}-\text{Hydroxy}-\text{3}\left( \text{4 }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }-\text{hydroxyphenylmethyl} \right)\text{cycloprop}-\text{2}-\text{en}-\text{1}-\text{one} $
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note :
It is important to note that the cyclopropane ring is not directly connected to the benzene ring but is connected via methyl group that is why methyl word is also used in the naming of substituent at third carbon. Also, due to the presence of a cyclic group as a substituent on benzene ring, the ring will not have a root or base name as phenol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




