
The IUPAC name of the compound is:
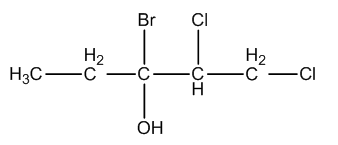
A. 3-Bromo-4,5-dichloropentan-3-ol
B. 3-Bromo-1,2-dichloro-3-hydroxypentane
C. 3-Bromo-1,2-dichloropentan-3-ol
D. 3-Bromo-4,5-dichloro-3-hydroxypentane

Answer
597k+ views
Hint: According to IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry), whenever we are going to write the name of the compound, we have to give numbering first to functional groups. Means lower numbering should become a functional group present in the molecule or compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Whenever we are going to write the IUPAC name, we should identify the parent chain or long chain in the given compound and we have to identify the functional groups present in the given compound.
In the given molecule, one bromine atom, two chlorine atoms, one alcohol functional group are present.
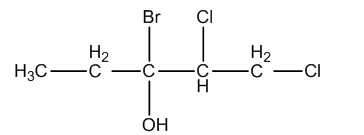
After numbering the structure of the given molecule is as follows.
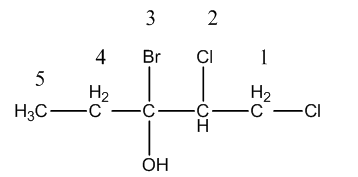
On carbon-1 and on carbon-2, chlorine atoms are present, on carbon-3 one bromine and one alcohol functional group is present.
Coming to given options, option A, 3-Bromo-4,5-dichloropentan-3-ol. The option A is wrong because the chlorine atoms are present on carbon-1 and carbon-2.
Coming to option B, 3-Bromo-1,2-dichloro-3-hydroxypentane. The option B is wrong because the alcohol functional group should not be named as hydroxyl.
Coming to option D, 3-Bromo-4,5-dichloro-3-hydroxypentane. The option D is wrong because the chlorine atoms are on carbon-1 and carnbon-2 and alcohol group is present in the given molecule.
So, the correct option is, option c. 3-Bromo-1,2-dichloropentan-3-ol
Note: Don’t be confused while giving numbering and names to the functional groups.
The carbon which is attached to functional groups should be number first and we have to identify the longest carbon chain in the given compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Whenever we are going to write the IUPAC name, we should identify the parent chain or long chain in the given compound and we have to identify the functional groups present in the given compound.
In the given molecule, one bromine atom, two chlorine atoms, one alcohol functional group are present.

After numbering the structure of the given molecule is as follows.

On carbon-1 and on carbon-2, chlorine atoms are present, on carbon-3 one bromine and one alcohol functional group is present.
Coming to given options, option A, 3-Bromo-4,5-dichloropentan-3-ol. The option A is wrong because the chlorine atoms are present on carbon-1 and carbon-2.
Coming to option B, 3-Bromo-1,2-dichloro-3-hydroxypentane. The option B is wrong because the alcohol functional group should not be named as hydroxyl.
Coming to option D, 3-Bromo-4,5-dichloro-3-hydroxypentane. The option D is wrong because the chlorine atoms are on carbon-1 and carnbon-2 and alcohol group is present in the given molecule.
So, the correct option is, option c. 3-Bromo-1,2-dichloropentan-3-ol
Note: Don’t be confused while giving numbering and names to the functional groups.
The carbon which is attached to functional groups should be number first and we have to identify the longest carbon chain in the given compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




