
The joint between carpal and metacarpal of thumb in primate mammals is-
A. Pivot joint
B. Hinge joint
C. Ball and socket joint
D. Saddle joint
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: There are many types of joints to join bones in our body. In our body different bones are joined according to such a manner that movement is possible according to the function of that organ.
Complete step-by-step answer:
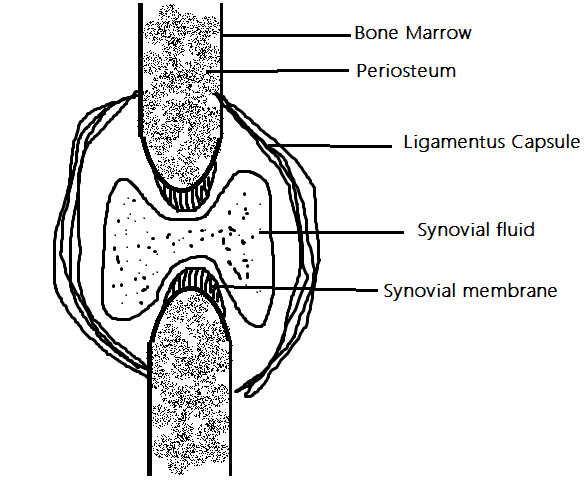
1. Saddle joint is a type of synovial joint.
2. Synovial joint allows free movement of bones.
3. Many types of synovial joints are found such as ball and socket joint, synovial joint, hinge joint, pivot joint, gliding joint and condylar joint.
4. A synovial joint at the ends of bone synovial membranes secretes slimy liquid that is called synovial fluid. This provides lubrication to bones.
5. Saddle joint is a small form of ball and socket joint.
Additional information: There are six types of synovial joints. These are a pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball and socket joints. The pivot joint is a type of synovial joint that allows rotation. The joint between the atlas and axis is pivot joint which allows the movement of the head back and forth. The hinge joint is a type of synovial joint which allows movement only in one axis, that is flexion and extension. Knee joint, ankle joint are examples of the hinge joint. Ball and socket joint allows rotation in multiple directions. In this type of joint, the ball-shaped surface of one joint lies in the socket-like depression of another joint. The hip joint is an example of a ball and socket joint. Saddle joint is the joint present between the carpal and metacarpal of thumb. It allows flexion, extension, adduction, abduction and circumduction movements. It provides stability and flexibility to bones.
So, the correct answer is “Option D. saddle joint ”.
Note: Saddle joint is found also between bones of thumb. Synovial fluid found between two bones also provides stability.
Complete step-by-step answer:

1. Saddle joint is a type of synovial joint.
2. Synovial joint allows free movement of bones.
3. Many types of synovial joints are found such as ball and socket joint, synovial joint, hinge joint, pivot joint, gliding joint and condylar joint.
4. A synovial joint at the ends of bone synovial membranes secretes slimy liquid that is called synovial fluid. This provides lubrication to bones.
5. Saddle joint is a small form of ball and socket joint.
Additional information: There are six types of synovial joints. These are a pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball and socket joints. The pivot joint is a type of synovial joint that allows rotation. The joint between the atlas and axis is pivot joint which allows the movement of the head back and forth. The hinge joint is a type of synovial joint which allows movement only in one axis, that is flexion and extension. Knee joint, ankle joint are examples of the hinge joint. Ball and socket joint allows rotation in multiple directions. In this type of joint, the ball-shaped surface of one joint lies in the socket-like depression of another joint. The hip joint is an example of a ball and socket joint. Saddle joint is the joint present between the carpal and metacarpal of thumb. It allows flexion, extension, adduction, abduction and circumduction movements. It provides stability and flexibility to bones.
So, the correct answer is “Option D. saddle joint ”.
Note: Saddle joint is found also between bones of thumb. Synovial fluid found between two bones also provides stability.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




