
The kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted on irradiating a metal surface with frequency $\upsilon $ is related by $K.E = h\upsilon - \phi $ . The plot of \[K.E\] vs incidental frequency $\upsilon $ shows:
A. A straight line with slope equal to Planck’s constant.
B. A straight line with intercept on the x-axis equal to the product of threshold frequency and Planck’s constant.
C. A straight line with extrapolated intercept on y-axis equal to threshold energy.
D. A straight line with intercept on x-axis equal to threshold frequency.
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid state and quantum chemistry to draw inferences about the properties of atoms, molecules and solids.
Complete step by step answer:
In 1905, Einstein proposed a theory of the photoelectric effect using a concept first put forward by Max Planck that light consists of tiny packets of energy known as photons or light quanta. Each packet carries energy equal to $h\upsilon $ that is proportional to the frequency $\upsilon $ of the corresponding electromagnetic wave. The proportionality constant is known as the Planck’s constant. The maximum kinetic energy of the electrons that were delivered this much energy before being removed from their atomic binding is equal to:
$K.E = h\upsilon - \phi $
Where, $K.E = $ kinetic energy of the electron released from the metal surface
$h\upsilon = $ Energy of the incident electron
$\upsilon = $Frequency of the incident photon
$\phi = h{\upsilon _o}$= work function of the metal surface = The minimum energy required to remove an electron from the surface of the material.
${\upsilon _o} = $threshold frequency
The graph of kinetic energy along y-axis and frequency along x-axis is plotted as follows:
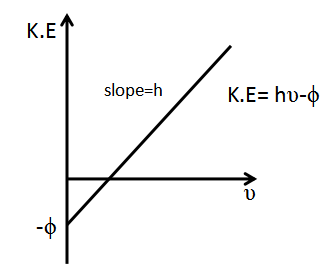
The plot of \[K.E\] vs incidental frequency $\upsilon $ shows that it is a straight line with slope equal to the Planck’s constant. The plot is a straight line with extrapolated intercept on y-axis equal to threshold energy and a straight line with intercept on x-axis equal to threshold frequency.
So, the correct answer is Option A,C,D.
Note:
In classical electromagnetic theory, the photoelectric effect would be attributed to the transfer of energy from the continuous light waves to an electron. An alteration in the intensity of light would change the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, and sufficiently dim light would result in the emission delayed by the time it would take the electrons to accumulate enough energy to leave the material.
Complete step by step answer:
In 1905, Einstein proposed a theory of the photoelectric effect using a concept first put forward by Max Planck that light consists of tiny packets of energy known as photons or light quanta. Each packet carries energy equal to $h\upsilon $ that is proportional to the frequency $\upsilon $ of the corresponding electromagnetic wave. The proportionality constant is known as the Planck’s constant. The maximum kinetic energy of the electrons that were delivered this much energy before being removed from their atomic binding is equal to:
$K.E = h\upsilon - \phi $
Where, $K.E = $ kinetic energy of the electron released from the metal surface
$h\upsilon = $ Energy of the incident electron
$\upsilon = $Frequency of the incident photon
$\phi = h{\upsilon _o}$= work function of the metal surface = The minimum energy required to remove an electron from the surface of the material.
${\upsilon _o} = $threshold frequency
The graph of kinetic energy along y-axis and frequency along x-axis is plotted as follows:

The plot of \[K.E\] vs incidental frequency $\upsilon $ shows that it is a straight line with slope equal to the Planck’s constant. The plot is a straight line with extrapolated intercept on y-axis equal to threshold energy and a straight line with intercept on x-axis equal to threshold frequency.
So, the correct answer is Option A,C,D.
Note:
In classical electromagnetic theory, the photoelectric effect would be attributed to the transfer of energy from the continuous light waves to an electron. An alteration in the intensity of light would change the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, and sufficiently dim light would result in the emission delayed by the time it would take the electrons to accumulate enough energy to leave the material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




