
The least count of Beckmann's thermometer is___________.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: the Beckman thermometer is mercury-based. Unlike normal thermometers, it cannot measure the absolute temperature. But it can measure the difference between the temperature. It can accurately measure the small temperature difference in the freezing point of the solvent and solution.
Complete step by step answer:
The thermometers are used to measure the temperature changes of the solvent or solution. There are various types of thermometers based on the requirement.
Beckman thermometer is one of the unique types of thermometer. It is used to measure the small temperature changes in the freezing point of pure solvent and solution. It is not used to determine the absolute value of the freezing temperature, but it has wide use in measuring the difference between the temperature changes associated with the freezing point of the solution and pure solvent.
The Beckman thermometer is also called the differential thermometer. It can measure the temperature difference of even the $\text{ }0.01\text{K }$ or $\text{ }{{0.01}^{0}}\text{C}$.we know that the minimum value which can be measured by an instrument is called the least count.
Therefore, the least count of Beckmann thermometers is$\text{ }{{0.01}^{0}}\text{C}$.
Additional information:
The Beckman thermometer is as shown below,
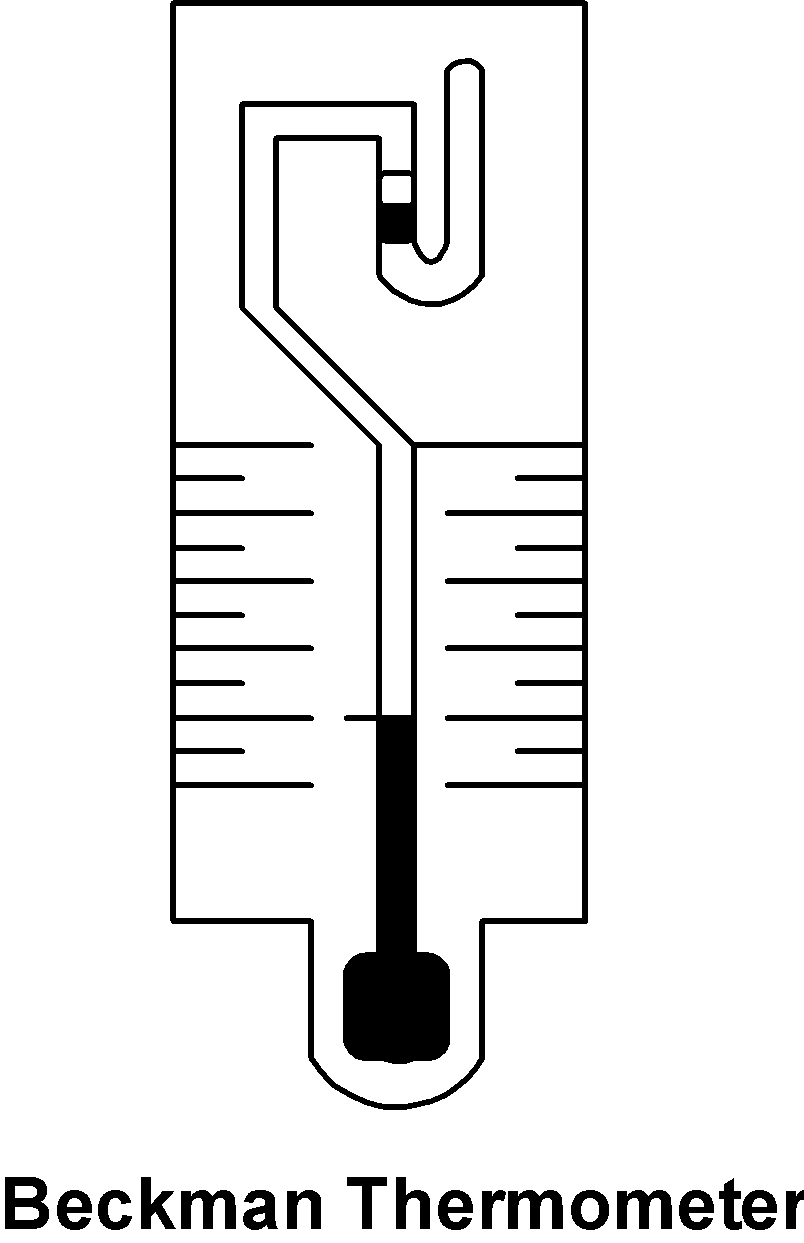
It consists of a capillary which is joined to the large thermometer bulb. The capillary is connected to the reservoir of mercury. The capillary has the fine bore thus, the small change in the temperatures is considered as the considerable change in the height of the mercury in the capillary. The complete-scale on the Beckman thermometer is equal to$\text{ }6\text{K }$. The Beckman thermometer has a wide application in measuring the difference in the freezing point and the boiling point. The temperature difference is very small and can be easily detected by the Beckman thermometer. The difference in the two readings gives the depression at freezing point$\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{T}}_{\text{f}}}\text{ }$. From the depression in the freezing point, we can determine the mass of the non-volatile solute. The relation of the freezing point and mass is given as follows: $\text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ = }\dfrac{{{\text{K}}_{\text{f}}}}{\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{T}}_{\text{f}}}}\text{ }\dfrac{{{\text{w}}_{\text{2}}}}{{{\text{w}}_{\text{1}}}}\text{ }$ Where ${{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}$ is the molar mass of the non-volatile solute.
Note: note that, when used a magnifier with the Beckman thermometer, we can estimate the temperature changes up to the $\text{ 0}\text{.001K }$ or $\text{0}\text{.00}{{\text{1}}^{\text{0}}}\text{C}$. The Beckman thermometer can measure the difference in the temperature at either high or low temperatures. However, ordinary thermometers have fixed values up to a certain range.
Complete step by step answer:
The thermometers are used to measure the temperature changes of the solvent or solution. There are various types of thermometers based on the requirement.
Beckman thermometer is one of the unique types of thermometer. It is used to measure the small temperature changes in the freezing point of pure solvent and solution. It is not used to determine the absolute value of the freezing temperature, but it has wide use in measuring the difference between the temperature changes associated with the freezing point of the solution and pure solvent.
The Beckman thermometer is also called the differential thermometer. It can measure the temperature difference of even the $\text{ }0.01\text{K }$ or $\text{ }{{0.01}^{0}}\text{C}$.we know that the minimum value which can be measured by an instrument is called the least count.
Therefore, the least count of Beckmann thermometers is$\text{ }{{0.01}^{0}}\text{C}$.
Additional information:
The Beckman thermometer is as shown below,

It consists of a capillary which is joined to the large thermometer bulb. The capillary is connected to the reservoir of mercury. The capillary has the fine bore thus, the small change in the temperatures is considered as the considerable change in the height of the mercury in the capillary. The complete-scale on the Beckman thermometer is equal to$\text{ }6\text{K }$. The Beckman thermometer has a wide application in measuring the difference in the freezing point and the boiling point. The temperature difference is very small and can be easily detected by the Beckman thermometer. The difference in the two readings gives the depression at freezing point$\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{T}}_{\text{f}}}\text{ }$. From the depression in the freezing point, we can determine the mass of the non-volatile solute. The relation of the freezing point and mass is given as follows: $\text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ = }\dfrac{{{\text{K}}_{\text{f}}}}{\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{T}}_{\text{f}}}}\text{ }\dfrac{{{\text{w}}_{\text{2}}}}{{{\text{w}}_{\text{1}}}}\text{ }$ Where ${{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}$ is the molar mass of the non-volatile solute.
Note: note that, when used a magnifier with the Beckman thermometer, we can estimate the temperature changes up to the $\text{ 0}\text{.001K }$ or $\text{0}\text{.00}{{\text{1}}^{\text{0}}}\text{C}$. The Beckman thermometer can measure the difference in the temperature at either high or low temperatures. However, ordinary thermometers have fixed values up to a certain range.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




