
The life cycle of Selaginella/ fern is
(a)Diplontic
(b)Haplo-diplontic
(c)Haplontic
(d)Diplo-haplontic
Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint: In this plant a dominant sporophytic phase and a short-lived gametophytic phase are present. Selaginella is commonly known as ‘spike moss’.
Complete answer:
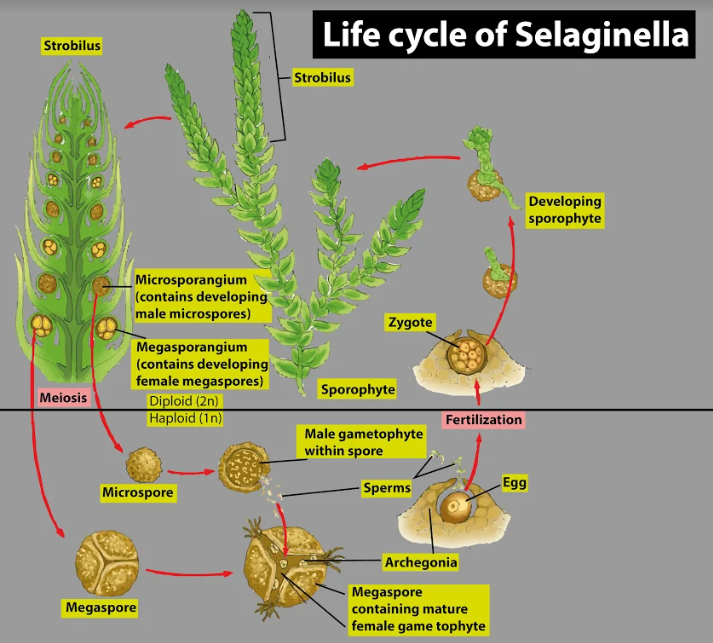
Selaginella is a pteridophyte which is mainly seen in humid temperate and tropical rainforests. Selaginella exhibits a regular alternation between sporophytic and gametophytic generations. It is a free-living plant with a distinct root, stem, and leaves and it grows for a long time. It reproduces asexually by the formation of haploid spores within the sporangia. The spores germinate into separate male and female gametophytes. The gametophytes are haploid, free-living, and exist for a short time only. They represent the second phase in the life cycle of Selaginella. The male gametophyte produces male gamete in the antheridium, while the female gametophyte produces the egg in the archegonium. Male and female gametes fuse, forming a diploid zygote. The first cell of the sporophytic generation is the zygote. From the zygote, a free-living, the sporophyte is produced. Thus, in the life cycle of Selaginella, a distinct alternation between sporophytic that is diploid and gametophytic that is haploid generations can be seen.
So, the correct answer is diplo-haplontic.
Note:
-The male sex organ in non-flowering plants is called an antheridium and the female sex organ in non-flowering plants is the archegonium.
-A gametophyte is a haploid gamete producing form of a plant and a sporophyte is the spore-producing form of the plant.
-The diplohaplontic life cycle is also referred to as haplodiplontic, diplobiontic, or dibiontic life cycle. In this life cycle, multicellular diploid and haploid stages occur and meiosis has occurred in ‘sporic’ condition.
Complete answer:
Selaginella is a pteridophyte which is mainly seen in humid temperate and tropical rainforests. Selaginella exhibits a regular alternation between sporophytic and gametophytic generations. It is a free-living plant with a distinct root, stem, and leaves and it grows for a long time. It reproduces asexually by the formation of haploid spores within the sporangia. The spores germinate into separate male and female gametophytes. The gametophytes are haploid, free-living, and exist for a short time only. They represent the second phase in the life cycle of Selaginella. The male gametophyte produces male gamete in the antheridium, while the female gametophyte produces the egg in the archegonium. Male and female gametes fuse, forming a diploid zygote. The first cell of the sporophytic generation is the zygote. From the zygote, a free-living, the sporophyte is produced. Thus, in the life cycle of Selaginella, a distinct alternation between sporophytic that is diploid and gametophytic that is haploid generations can be seen.
So, the correct answer is diplo-haplontic.
Note:
-The male sex organ in non-flowering plants is called an antheridium and the female sex organ in non-flowering plants is the archegonium.
-A gametophyte is a haploid gamete producing form of a plant and a sporophyte is the spore-producing form of the plant.
-The diplohaplontic life cycle is also referred to as haplodiplontic, diplobiontic, or dibiontic life cycle. In this life cycle, multicellular diploid and haploid stages occur and meiosis has occurred in ‘sporic’ condition.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




