
The longest cell in the human body is
A. Neuron
B. Muscle fiber
C. Epithelial cell
D. Bone cell
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint:Various degrees of organization are exhibited by life. Atoms are combined to form molecules, molecules, are fused to form organelles and all organelles together form a cell. Depending upon the function the cell regulates, the size and length of the cell vary.
Complete answer:Cell theory states that all living organisms are made up of cells. The cell is the basic, smallest, and functional unit of life. The existing cells are produced from pre-existing cells. Cells can be further classified as prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells are surrounded by plasma membranes with a characteristic cell wall whose composition may differ depending on the organism. Eukaryotes have distinct nuclei bound by a nuclear membrane. They consist of membrane-bound organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. The shape and size of cells vary depending upon their function. Neuron or nerve cell has a body called soma, many extensions called dendrites, and an axon. The length of neurons is about 3 feet long. Muscle fibers are made up of smaller units called myofibers. The length of the muscle fibers is a few centimeters. Epithelial cells form the inner lining of many organs of the body and their length is about a few microns. Bone cells are of four types. They are osteocytes, osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and bone lining cells. The length of bone cells is a few micrometers. Therefore, the longest cell in the human body is the neuron.
So, option A is the correct answer.
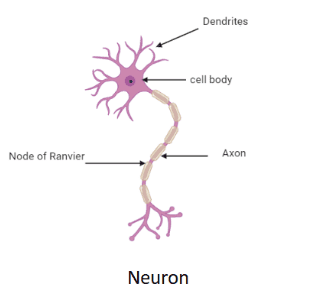
Note:The ovum found in the human body is the largest cell present in the human body and is 20 times bigger than the sperm cells. The diameter of the ovum is 0.1mm. The smallest cell in the human body is Cerebellum’s Granule Cell and its size ranges from 4 micrometers to 4.5 micrometers long.
Complete answer:Cell theory states that all living organisms are made up of cells. The cell is the basic, smallest, and functional unit of life. The existing cells are produced from pre-existing cells. Cells can be further classified as prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells are surrounded by plasma membranes with a characteristic cell wall whose composition may differ depending on the organism. Eukaryotes have distinct nuclei bound by a nuclear membrane. They consist of membrane-bound organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. The shape and size of cells vary depending upon their function. Neuron or nerve cell has a body called soma, many extensions called dendrites, and an axon. The length of neurons is about 3 feet long. Muscle fibers are made up of smaller units called myofibers. The length of the muscle fibers is a few centimeters. Epithelial cells form the inner lining of many organs of the body and their length is about a few microns. Bone cells are of four types. They are osteocytes, osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and bone lining cells. The length of bone cells is a few micrometers. Therefore, the longest cell in the human body is the neuron.
So, option A is the correct answer.

Note:The ovum found in the human body is the largest cell present in the human body and is 20 times bigger than the sperm cells. The diameter of the ovum is 0.1mm. The smallest cell in the human body is Cerebellum’s Granule Cell and its size ranges from 4 micrometers to 4.5 micrometers long.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




