
The magnetic moment of a diamagnetic atom is
(A) Much greater than one
(B) One
(C) Between zero and one
(D) Equal to zero
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: Atoms which have paired electrons have the magnetic moment zero. Because diamagnetism is the intrinsic property of every material and it is generated due to mutual interaction between the applied magnetic field and orbital motion of electrons.
Complete step by step solution
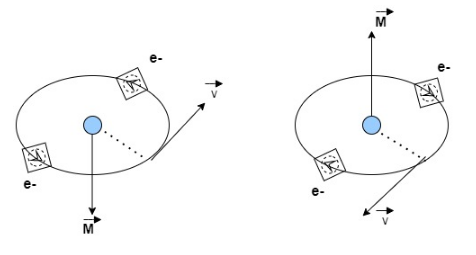
We know that each electron in an atom is revolving in an orbital around the nucleus. The revolving loop is equivalent to a tiny loop of current. Therefore, it possesses some orbital magnetic moment. \[\overrightarrow{\text{M}}\]
$\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{l}}}}=$current$\times $area of loop
In addition to the orbital motion, every electron is assumed to have a spin motion around its axis. Therefore, magnetic moment is $\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{s}}}}$
The vector sum of $\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{l}}}}$ and$\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{s}}}}$provides the net magnetic moment \[\overrightarrow{\text{M}}\] to the atom.
In diagrammatic material
$\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{l}}}}$and $\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{s}}}}$cancel each other for every atom so that the atom has no net magnetic dipole moment. Therefore, motion of all the electrons in an atom of a diamagnetic material is assured to be reduced to motion of two electrons revolving with same angular velocity in a circular orbit of same radius, but in opposite sense. Hence, the magnetic field of two being equal and opposite, cancel each other (in the absence of any external magnetic field), net magnetic moment is zero.
So the option (D) Equal to zero is the correct answer.
Note
When diamagnetic substances are placed in an external magnetising field, they get feebly magnetised in a direction opposite to the magnetising field. Example: Copper, Lead, Gold, Water, Air, Hydrogen, etc.
Susceptibility of diamagnetic does not change with temperature.
Complete step by step solution
We know that each electron in an atom is revolving in an orbital around the nucleus. The revolving loop is equivalent to a tiny loop of current. Therefore, it possesses some orbital magnetic moment. \[\overrightarrow{\text{M}}\]
$\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{l}}}}=$current$\times $area of loop
In addition to the orbital motion, every electron is assumed to have a spin motion around its axis. Therefore, magnetic moment is $\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{s}}}}$
The vector sum of $\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{l}}}}$ and$\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{s}}}}$provides the net magnetic moment \[\overrightarrow{\text{M}}\] to the atom.
In diagrammatic material
$\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{l}}}}$and $\overrightarrow{{{\text{M}}_{\text{s}}}}$cancel each other for every atom so that the atom has no net magnetic dipole moment. Therefore, motion of all the electrons in an atom of a diamagnetic material is assured to be reduced to motion of two electrons revolving with same angular velocity in a circular orbit of same radius, but in opposite sense. Hence, the magnetic field of two being equal and opposite, cancel each other (in the absence of any external magnetic field), net magnetic moment is zero.
So the option (D) Equal to zero is the correct answer.

Note
When diamagnetic substances are placed in an external magnetising field, they get feebly magnetised in a direction opposite to the magnetising field. Example: Copper, Lead, Gold, Water, Air, Hydrogen, etc.
Susceptibility of diamagnetic does not change with temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




