
The main function of sieve tubes is
(a)Food conduction
(b) Protein transfer
(c)Enzyme transfer
(d) Transcription
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Sieve tubes are the major component of phloem. They are composed of several Sieve tube elements which join end to end to form a channel for conduction. They are involved in the translocation of simple sugars and complex carbohydrates throughout the body. They are known to transport necessary molecules with the help of companion cells.
Complete answer:
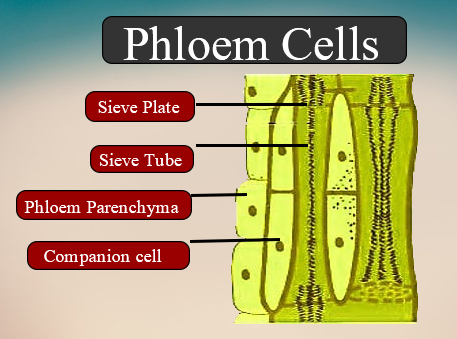
The main function of the sieve tube is the transport of carbohydrates, primarily sucrose, in the plant. The interface of the tubes contains pores which help in conduction. Each sieve tube element is normally associated with one or more nucleated companion cells, to which they are connected by plasmodesmata. Sieve tube elements are the relatively advanced type of phloem cells, found in angiosperms. Mature sieve tube elements are long, tubular, and non nucleated cells, with non-lignified secondary wall and terminal sieve plate. Their protoplast is devoid of the nucleus, ER, mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles. In the feature, they resemble-prokaryotic cells. On one side of the sieve tube cell, there will be or more companion cells. True sieve-tube members are absent in gymnosperms and pteridophytes. Still, forms like Gnetum, selaginella, etc. are exceptions in having sieve tube cells. Gnetum is a gymnosperm, and selaginella is a pteridophyte.
Additional Information: - Sieve tube members are arranged end-to-end, forming several tubular columns, called sieve tubes.
-These correspond to the xylem vessels. The end wall or cross wall between adjacent cells is an oblique and porous plate, called a sieve plate.
-The slightly depressing part of the sieve plate, perforated by a cluster of sieve pores, is called the sieve area. Sieve plates with only a single sieve area are called simple sieve plates, and those with several sieve areas are called compound sieve plates.
So, the correct answer is 'Food conduction'.
Note: -Sieve plates are comparable to the perforation plates of xylem vessels. Each sieve tube element contains fine cytoplasmic strands.
-Through the sieve pores the cytoplasmic strands of one cell enter the next cell and become continuous with its strands. In dicot plants sieve tubes contain a viscous and proteinous substance, called slime. It accumulates in the sieve area and forms the slime plug.
-When the cell is injured, this plug closes up the broken tip and thus prevents the exudation of the cell content. As a sieve element matures, its tonoplast ruptures and vacuole sap mixes with the cytoplasm.
Complete answer:
The main function of the sieve tube is the transport of carbohydrates, primarily sucrose, in the plant. The interface of the tubes contains pores which help in conduction. Each sieve tube element is normally associated with one or more nucleated companion cells, to which they are connected by plasmodesmata. Sieve tube elements are the relatively advanced type of phloem cells, found in angiosperms. Mature sieve tube elements are long, tubular, and non nucleated cells, with non-lignified secondary wall and terminal sieve plate. Their protoplast is devoid of the nucleus, ER, mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles. In the feature, they resemble-prokaryotic cells. On one side of the sieve tube cell, there will be or more companion cells. True sieve-tube members are absent in gymnosperms and pteridophytes. Still, forms like Gnetum, selaginella, etc. are exceptions in having sieve tube cells. Gnetum is a gymnosperm, and selaginella is a pteridophyte.
Additional Information: - Sieve tube members are arranged end-to-end, forming several tubular columns, called sieve tubes.
-These correspond to the xylem vessels. The end wall or cross wall between adjacent cells is an oblique and porous plate, called a sieve plate.
-The slightly depressing part of the sieve plate, perforated by a cluster of sieve pores, is called the sieve area. Sieve plates with only a single sieve area are called simple sieve plates, and those with several sieve areas are called compound sieve plates.
So, the correct answer is 'Food conduction'.
Note: -Sieve plates are comparable to the perforation plates of xylem vessels. Each sieve tube element contains fine cytoplasmic strands.
-Through the sieve pores the cytoplasmic strands of one cell enter the next cell and become continuous with its strands. In dicot plants sieve tubes contain a viscous and proteinous substance, called slime. It accumulates in the sieve area and forms the slime plug.
-When the cell is injured, this plug closes up the broken tip and thus prevents the exudation of the cell content. As a sieve element matures, its tonoplast ruptures and vacuole sap mixes with the cytoplasm.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




