
The major monochlorination product that forms upon treatment of 1,1,2-trimethyl cyclopentane with $C{l_2}$/hv is:
A. 2-chloro 1,1,2-trimethyl cyclopentane
B. 1-chloro 2,2,3-trimethyl cyclopentane
C. 1-chloro 2,3,3-trimethyl cyclopentane
D. 1-chloro 1,2,2-trimethyl cyclopentane
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The above process of heating alkane with $C{l_2}$ is called halogenations and since the halogen is Cl, the process is selectively called chlorination. This will lead to the addition of chlorine atom to the carbon by removing hydrogen atom.
Step by step answer: Chlorination may be brought about by photo irradiation, heat or catalysts. The extent of chlorination depends largely on the amount of chlorine used. A mixture of all possible isomeric monochlorides is obtained, but the isomers are formed in unequal amounts, due to difference in reactivity of primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen atoms. The order of ease of substitution is:
Tertiary hydrogen> secondary hydrogen > primary hydrogen
The tertiary hydrogen is replaced about 5 times as fast as primary hydrogen where we know that degree of hydrogen depends upon the degree of carbon they are attachéd to. Since in the question we are given with 1,1,2 trimethyl cyclopentane from its structure we can conclude that it has three different types of hydrogen hence the probability of the isomeric products formed are three. Out of which the major product will be formed by chlorination at the tertiary hydrogen.
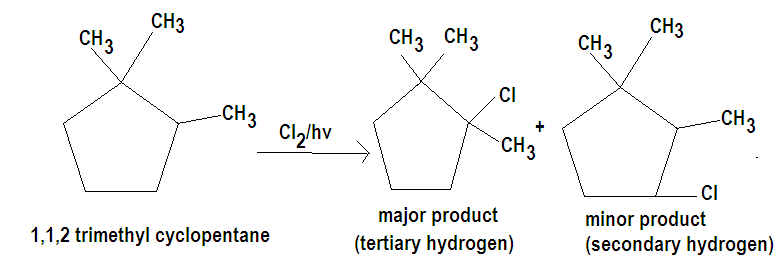
The major product thus formed is 1-chloro 1,2,2 trimethyl cyclopentane and the other products formed will be due to chlorination at secondary and primary hydrogen.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: There are three factors that affect the yield of the isomeric products they are:
-Probability factor
-Reactivity of H atom
-Reactivity of X atom in the halogenations reaction, it is maximum for fluorine and does not occur with iodine.
Step by step answer: Chlorination may be brought about by photo irradiation, heat or catalysts. The extent of chlorination depends largely on the amount of chlorine used. A mixture of all possible isomeric monochlorides is obtained, but the isomers are formed in unequal amounts, due to difference in reactivity of primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen atoms. The order of ease of substitution is:
Tertiary hydrogen> secondary hydrogen > primary hydrogen
The tertiary hydrogen is replaced about 5 times as fast as primary hydrogen where we know that degree of hydrogen depends upon the degree of carbon they are attachéd to. Since in the question we are given with 1,1,2 trimethyl cyclopentane from its structure we can conclude that it has three different types of hydrogen hence the probability of the isomeric products formed are three. Out of which the major product will be formed by chlorination at the tertiary hydrogen.

The major product thus formed is 1-chloro 1,2,2 trimethyl cyclopentane and the other products formed will be due to chlorination at secondary and primary hydrogen.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: There are three factors that affect the yield of the isomeric products they are:
-Probability factor
-Reactivity of H atom
-Reactivity of X atom in the halogenations reaction, it is maximum for fluorine and does not occur with iodine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




