
The masses and radii of earth and moon are${M_1}$, ${R_1}$ and${M_2}$, ${R_2}$ respectively. Their centres are at a distance $d$ apart. The minimum speed with which a particle of mass $m$ should be protected from a point midway between the two centres so as to escape to infinity is:
(A) $\sqrt {\dfrac{{G\left( {{M_1} + {M_2}} \right)}}{d}} $
(B) $\sqrt {\dfrac{{2G\left( {{M_1} + {M_2}} \right)}}{d}} $
(C) $\sqrt {\dfrac{{4G\left( {{M_1} + {M_2}} \right)}}{d}} $
(D) \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{G{M_1} + {M_2}}}{d}} \]
Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint In order to find the escape velocity, we will at first find the potential difference between the potential energies of the two bodies. After this, applying the principle of conservation of mechanical energy and equating it with the kinetic energy, we can find the escape velocity.
Complete Step-By-Step Solution:
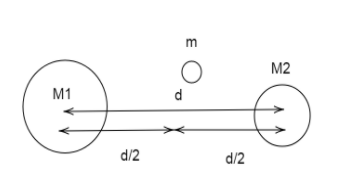
Thus, the mass $m$ is placed at the centre having distance $d/2$on both sides.
Thus, the potential energy difference can be written as:
$p = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{R}$
Where:
$p = $Potential energy
${m_1} = $ Mass of first object
${m_2} = $ Mass of second object
$R = $ Distance between the objects
Now, using this we can write:
Change in potential energy considering the above diagram as:
$\Delta p = - \dfrac{{G{M_2}{m_{}}}}{{d/2}} - \dfrac{{G{M_1}{m_{}}}}{{d/2}}$
This is the total initial energy of the system.
Now, applying conservation of mechanical energy, we know:
Total potential energy is converted to kinetic energy.
The principle states that:
Energy is not created nor destroyed but is converted from one form to another.
Hence, this conversion of energy occurs from potential to kinetic energy.
Hence we can write:
$ - \dfrac{{G{M_2}{m_{}}}}{{d/2}} - \dfrac{{G{M_1}{m_{}}}}{{d/2}} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Where:
${m_{}} = $ Mass of the object
${v_{}} = $ Escape velocity of the object
Escape velocity is defined as the velocity at which the objects sum of gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy results to zero.
On solving the equation, we get:
${v^2} = \dfrac{{4G}}{d}\left( {{M_1} + {M_2}} \right)$
Thus, we get:
$v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{4G}}{d}\left( {{M_1} + {M_2}} \right)} $
This is the correct answer. Therefore, option (C ) is correct.
Note: Kinetic energy of a body is the energy possessed by the body due to virtue its motion. Therefore, when we considered the escape velocity we took the equation for kinetic energy. On the other hand, potential energy is defined as the energy possessed by an object at rest.
Complete Step-By-Step Solution:

Thus, the mass $m$ is placed at the centre having distance $d/2$on both sides.
Thus, the potential energy difference can be written as:
$p = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{R}$
Where:
$p = $Potential energy
${m_1} = $ Mass of first object
${m_2} = $ Mass of second object
$R = $ Distance between the objects
Now, using this we can write:
Change in potential energy considering the above diagram as:
$\Delta p = - \dfrac{{G{M_2}{m_{}}}}{{d/2}} - \dfrac{{G{M_1}{m_{}}}}{{d/2}}$
This is the total initial energy of the system.
Now, applying conservation of mechanical energy, we know:
Total potential energy is converted to kinetic energy.
The principle states that:
Energy is not created nor destroyed but is converted from one form to another.
Hence, this conversion of energy occurs from potential to kinetic energy.
Hence we can write:
$ - \dfrac{{G{M_2}{m_{}}}}{{d/2}} - \dfrac{{G{M_1}{m_{}}}}{{d/2}} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Where:
${m_{}} = $ Mass of the object
${v_{}} = $ Escape velocity of the object
Escape velocity is defined as the velocity at which the objects sum of gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy results to zero.
On solving the equation, we get:
${v^2} = \dfrac{{4G}}{d}\left( {{M_1} + {M_2}} \right)$
Thus, we get:
$v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{4G}}{d}\left( {{M_1} + {M_2}} \right)} $
This is the correct answer. Therefore, option (C ) is correct.
Note: Kinetic energy of a body is the energy possessed by the body due to virtue its motion. Therefore, when we considered the escape velocity we took the equation for kinetic energy. On the other hand, potential energy is defined as the energy possessed by an object at rest.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




