
The mesophyll of leaf consists of
(a) Spongy parenchyma cells
(b) Palisade parenchyma cells
(c) Both spongy and parenchyma cells
(d) Pith cells
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Mesophyll present in the leaves of most of the flowering plants is divided into two layers that are the primary location for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is stored in the tissues present in these layers.
Complete answer:
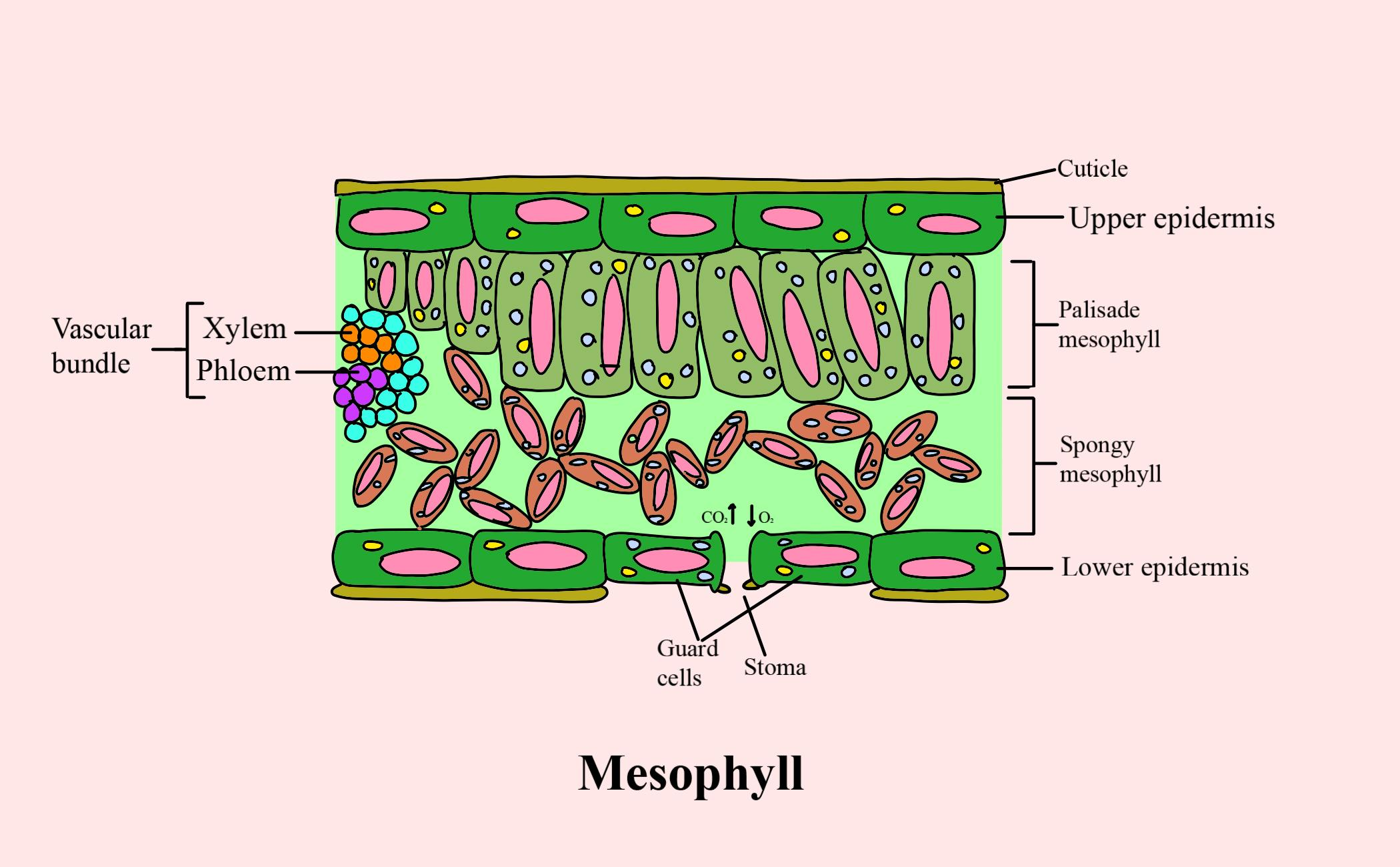
Parenchyma or collenchyma present in between the upper and lower layers of the epidermis is called mesophyll. It is the primary photosynthetic tissue in most plants. In most of the flowering plants and ferns, mesophyll is divided into two layers namely the palisade layer and the spongy layer. The Palisade layer consists of palisade parenchyma and the spongy layer consists of spongy parenchyma. The green color leaf is due to the presence of a pigment in the mesophyll called chlorophyll.
Additional Information: - The tissue present inside the mesophyll is called assimilation tissue, the primary location for photosynthesis, and the products of photosynthesis are called assimilates
- Vertically long elongated cells are present in the palisade layer. They are present directly beneath the adaxial epidermis. They have intercellular cells between them.
- Number of chloroplasts is more in the palisade layer when compared to the spongy layer.
- Maximum absorption of carbon dioxide is due to the slight separation between the cells.
- Spongy layer is present below the palisade layer that contains cells with more branches and they are loosely packed, and have large intercellular space between them.
So, the correct answer is ‘ both spongy and parenchyma cells’.
Note: In the leaves which are exposed to sunlight, parenchyma is multilayered whereas, in the leaves present in the shade or in older leaves, parenchyma is single-layered
Substomatal chambers are connected to the interstellar spaces of spongy and palisade parenchyma to diffuse oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapour.
Complete answer:
Parenchyma or collenchyma present in between the upper and lower layers of the epidermis is called mesophyll. It is the primary photosynthetic tissue in most plants. In most of the flowering plants and ferns, mesophyll is divided into two layers namely the palisade layer and the spongy layer. The Palisade layer consists of palisade parenchyma and the spongy layer consists of spongy parenchyma. The green color leaf is due to the presence of a pigment in the mesophyll called chlorophyll.
Additional Information: - The tissue present inside the mesophyll is called assimilation tissue, the primary location for photosynthesis, and the products of photosynthesis are called assimilates
- Vertically long elongated cells are present in the palisade layer. They are present directly beneath the adaxial epidermis. They have intercellular cells between them.
- Number of chloroplasts is more in the palisade layer when compared to the spongy layer.
- Maximum absorption of carbon dioxide is due to the slight separation between the cells.
- Spongy layer is present below the palisade layer that contains cells with more branches and they are loosely packed, and have large intercellular space between them.
So, the correct answer is ‘ both spongy and parenchyma cells’.

Note: In the leaves which are exposed to sunlight, parenchyma is multilayered whereas, in the leaves present in the shade or in older leaves, parenchyma is single-layered
Substomatal chambers are connected to the interstellar spaces of spongy and palisade parenchyma to diffuse oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapour.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




