
The molar heat capacity of ethanol is \[{\text{110}}{\text{.4J/K}}{\text{.}}\]. What is its specific heat capacity?
Answer
594k+ views
Hint:Specific Heat capacity of any compound or element depends on the Molar heat Capacity and molar mass of the given substance.
Complete step by step answer:
The specific heat capacity, (symbol ${C_p}$) is an amount of or the physical measure of the ability of a substance to absorb heat. It is basically the amount of energy that must be added, in the form of heat, to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in its temperature.
Specific Heat is also an intensive property of a substance. Intensive properties are properties of the given substance that are not dependent on the amount of substance present. Some other examples of intensive properties are density, colour, etc
Getting back to our question, as discussed earlier, the specific heat of a substance is dependent on: 1. Molar heat capacity and 2. molar mass
If we were to represent this relation in the form of a formula, it would be:
\[\]${C_p}$\[\; = \;\] $\dfrac{{{C_{mol}}}}{n}$
Where ${C_p}$ = specific heat capacity
${C_{mol}}$= Molar heat capacity
n = molar mass
Now, to calculate the molar mass of ethanol:
${\text{No}}{\text{. of Moles of ethanol = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Weight of the given sample of ethanol}}}}{{{\text{molecular weight of ethanol}}}}$
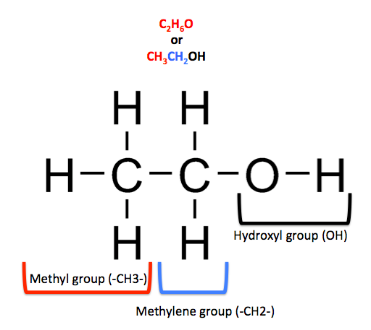
mol. weight of ethanol
\[
= {\text{ }}2\left( {atomic{\text{ }}weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}carbon} \right){\text{ }} + 6\left( {atomic{\text{ }}weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}hydrogen} \right) + 1\left( {atomic{\text{ }}weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}oxygen} \right) \\
n{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2\left( {12} \right){\text{ }} + 6\left( 1 \right){\text{ }} + 1\left( {16} \right) \\
n{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}46{\text{ }}gm/mol \\
\]
Substituting the value of ‘n’ from and above and the given value of molar heat capacity of \[{\text{ethanol = 110}}{\text{.4J/K}}\]; in the previously mentioned formula for calculating specific heat capacity, we get
${C_p}$ \[ = \] $\dfrac{{110.4}}{{46}} = 2.4J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$
Hence, the specific heat capacity of ethanol is $2.4J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$
Note:
Specific Heat Capacity and Heat Capacity are two different things. Specific heat capacity is a measure of the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of one gram of a pure substance by one-degree K.; while Heat capacity is the ratio of the amount of heat energy transferred to an object to the resulting increase in its temperature
Complete step by step answer:
The specific heat capacity, (symbol ${C_p}$) is an amount of or the physical measure of the ability of a substance to absorb heat. It is basically the amount of energy that must be added, in the form of heat, to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in its temperature.
Specific Heat is also an intensive property of a substance. Intensive properties are properties of the given substance that are not dependent on the amount of substance present. Some other examples of intensive properties are density, colour, etc
Getting back to our question, as discussed earlier, the specific heat of a substance is dependent on: 1. Molar heat capacity and 2. molar mass
If we were to represent this relation in the form of a formula, it would be:
\[\]${C_p}$\[\; = \;\] $\dfrac{{{C_{mol}}}}{n}$
Where ${C_p}$ = specific heat capacity
${C_{mol}}$= Molar heat capacity
n = molar mass
Now, to calculate the molar mass of ethanol:
${\text{No}}{\text{. of Moles of ethanol = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Weight of the given sample of ethanol}}}}{{{\text{molecular weight of ethanol}}}}$

mol. weight of ethanol
\[
= {\text{ }}2\left( {atomic{\text{ }}weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}carbon} \right){\text{ }} + 6\left( {atomic{\text{ }}weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}hydrogen} \right) + 1\left( {atomic{\text{ }}weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}oxygen} \right) \\
n{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2\left( {12} \right){\text{ }} + 6\left( 1 \right){\text{ }} + 1\left( {16} \right) \\
n{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}46{\text{ }}gm/mol \\
\]
Substituting the value of ‘n’ from and above and the given value of molar heat capacity of \[{\text{ethanol = 110}}{\text{.4J/K}}\]; in the previously mentioned formula for calculating specific heat capacity, we get
${C_p}$ \[ = \] $\dfrac{{110.4}}{{46}} = 2.4J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$
Hence, the specific heat capacity of ethanol is $2.4J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$
Note:
Specific Heat Capacity and Heat Capacity are two different things. Specific heat capacity is a measure of the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of one gram of a pure substance by one-degree K.; while Heat capacity is the ratio of the amount of heat energy transferred to an object to the resulting increase in its temperature
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




