
The molecule/molecules that has/have delocalised lone pair(s) of electron is/are:
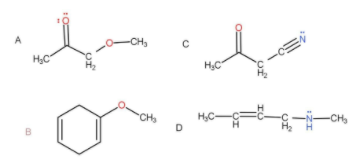
A.A, B and C
B.A, C and D
C.A and B
D.Only B

Answer
573k+ views
Hint: They must be conjugation present for the lone pair to be delocalised. Only delocalised electrons show resonance. The double bond should be present adjacent to the lone pair bearing species.
Complete step by step solution:
Resonance is the displacement or shifting of a lone pair of electrons within the compound. One single resonating structure cannot explain all the properties of the compound so we make different structures by shifting the Pi electrons to define complete physical and chemical properties of the compound. The structures that are formed are known as resonating structure. Resonance helps in the stabilization of the compound. Resonance is a completely hypothetical concept and has no real significance.
There are various types of resonance:
Positive charge pi resonance:This happens when Pi bond is in conjugation with a positive charge and vacant orbital. The condition is that both of them must be present adjacent carbon.
Pi electron lone pair conjugation:Pi bonds in conjugation with lone pair and they are separated by just one sigma bond.
Pi bond free radical: When pi bond is in conjugation with free radical and they are separated by just one sigma bond.
Pi bond conjugation:When 2 Pi bonds are present on alternate positions to each other so that they can conjugate and show resonance.
Lone pair positive charge resonance: Lone pairs and positive charge are separated by just one sigma bond.
In the above molecules given the only molecule that show delocalisation is
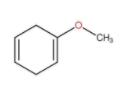
As we can see that the double and lone pair is just separated by one sigma bond, hence resonance takes place.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note:
Lone pairs are those species which do not involve resonance; they usually remain in hybrid orbitals. Delocalized lone pairs are those lone pairs which are in conjugation. They are present in unhybridized orbitals in order to show resonance.
Complete step by step solution:
Resonance is the displacement or shifting of a lone pair of electrons within the compound. One single resonating structure cannot explain all the properties of the compound so we make different structures by shifting the Pi electrons to define complete physical and chemical properties of the compound. The structures that are formed are known as resonating structure. Resonance helps in the stabilization of the compound. Resonance is a completely hypothetical concept and has no real significance.
There are various types of resonance:
Positive charge pi resonance:This happens when Pi bond is in conjugation with a positive charge and vacant orbital. The condition is that both of them must be present adjacent carbon.
Pi electron lone pair conjugation:Pi bonds in conjugation with lone pair and they are separated by just one sigma bond.
Pi bond free radical: When pi bond is in conjugation with free radical and they are separated by just one sigma bond.
Pi bond conjugation:When 2 Pi bonds are present on alternate positions to each other so that they can conjugate and show resonance.
Lone pair positive charge resonance: Lone pairs and positive charge are separated by just one sigma bond.
In the above molecules given the only molecule that show delocalisation is

As we can see that the double and lone pair is just separated by one sigma bond, hence resonance takes place.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note:
Lone pairs are those species which do not involve resonance; they usually remain in hybrid orbitals. Delocalized lone pairs are those lone pairs which are in conjugation. They are present in unhybridized orbitals in order to show resonance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




