
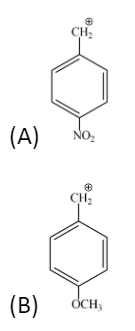
The most stable carbocation?


Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Substitution on the benzene ring can affect the placement of additional substituents on that ring during Electrophilic atomic substitution. The formation of products and its stability depends on the nature of electron-donating groups and electron-withdrawing groups.
Complete step by step solution:
When an electron releasing or an electron-withdrawing species is introduced to chain atoms, the corresponding negative or positive charge is relayed through the carbon chain by the atoms or groups cause’ permanent dipole to arise in the molecule is an inductive effect.
In an aromatic benzene ring, electron-donating groups increase the stability of the carbocation with resonance structures.
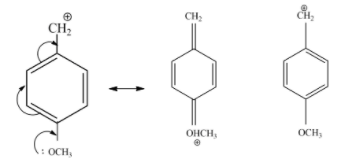
$-OC{{H}_{3}}$ The group is an electron-donating group, which increases the stability of carbocation by resonance. This electron-donating group can be recognized by lone pairs on the atom adjacent to the $\pi $ system.
The functional groups $-CN,-N{{O}_{2}}$ are electron-withdrawing groups. These groups can be recognized either by an atom adjacent to the $\pi $system having several bonds to more electronegative atoms, or having a formal positive charge or partial positive charge. These electron-withdrawing groups remove electron density from the benzene ring of the $\pi $system making it less nucleophilic.
Hence the most stable carbocation is option B.
Note: These substituent effects are caused mainly due to resonance and inductive effects. These effects are playing a key role in other reactions and properties like the stability of canonical forms, the acidity of the substituted benzoic acids, and the acidity of unsaturated organic compounds.
Complete step by step solution:
When an electron releasing or an electron-withdrawing species is introduced to chain atoms, the corresponding negative or positive charge is relayed through the carbon chain by the atoms or groups cause’ permanent dipole to arise in the molecule is an inductive effect.
In an aromatic benzene ring, electron-donating groups increase the stability of the carbocation with resonance structures.
$-OC{{H}_{3}}$ The group is an electron-donating group, which increases the stability of carbocation by resonance. This electron-donating group can be recognized by lone pairs on the atom adjacent to the $\pi $ system.

The functional groups $-CN,-N{{O}_{2}}$ are electron-withdrawing groups. These groups can be recognized either by an atom adjacent to the $\pi $system having several bonds to more electronegative atoms, or having a formal positive charge or partial positive charge. These electron-withdrawing groups remove electron density from the benzene ring of the $\pi $system making it less nucleophilic.
Hence the most stable carbocation is option B.
Note: These substituent effects are caused mainly due to resonance and inductive effects. These effects are playing a key role in other reactions and properties like the stability of canonical forms, the acidity of the substituted benzoic acids, and the acidity of unsaturated organic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




