
The most suitable reagent for the following conversion is:
A. \[{\text{Na/liquid N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
B. \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, Pd/C quinoline}}\]
C. \[{\text{Zn/HCl}}\]
D. \[{\text{H}}{{\text{g}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}{\text{/}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{, }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]

Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint:Out of the given options, select the options that can selectively reduce the carbon-carbon triple bond to double bond. Out of the selected options, select the option that selectively forms cis alkene.
Complete step by step solution:
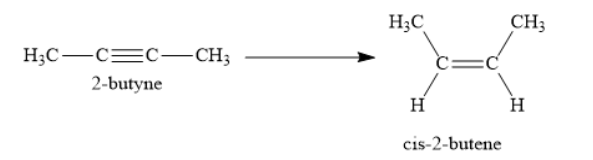
Consider the following reaction:
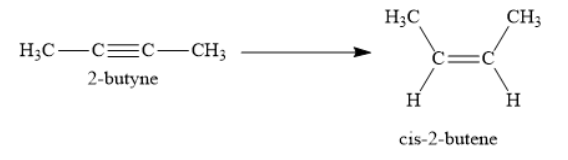
In the above reaction, 2-butyne is reduced to cis-2-butene. Further reduction of cis-2-butene to butane is not carried out in this reaction. Thus, the reduction is stopped at cis-2-butene in this reaction.
2-butyne is an alkyne as it contains a carbon-carbon triple bond. Cis-2-butene is an alkene as it contains carbon-carbon double bond. When 2-butyne is reduced selectively to cis-2-butene, a carbon-carbon triple bond is reduced to cis carbon-carbon double bond. Usually, complete reduction of alkynes gives alkanes. In these reduction reactions, the carbon-carbon triple bond is reduced to the carbon-carbon single bond. For this purpose, you can use hydrogen gas in presence of platinum, palladium or nickel. However, sometimes complete reduction of alkynes to alkanes is not desirable. You want the reduction to stop at the intermediate alkene stage. For this purpose, you use the reagent \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, Pd/C quinoline}}\].
Hydrogen gas is passed through 2-butyne in presence of palladium metal. Palladium metal is supported on either carbon or barium sulphate. Palladium metal is partially poisoned with quinoline or sulphur to decrease its reactivity. Since, you have poisoned the palladium catalyst, it will only reduce 2-butyene to cis-2-butene. Further reduction to butane will not occur.
Note:
The catalyst will only reduce 2-butyne to cs-2-butene. It will not give you trans 2-butene. If you want trans isomer, then you need to carry out the reaction with sodium metal in liquid ammonia \[({\text{Na/liquid N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}})\]
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the following reaction:
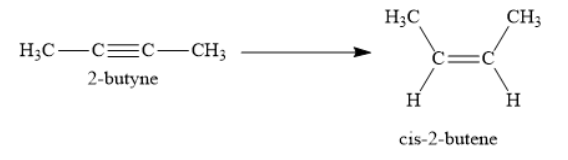
In the above reaction, 2-butyne is reduced to cis-2-butene. Further reduction of cis-2-butene to butane is not carried out in this reaction. Thus, the reduction is stopped at cis-2-butene in this reaction.
2-butyne is an alkyne as it contains a carbon-carbon triple bond. Cis-2-butene is an alkene as it contains carbon-carbon double bond. When 2-butyne is reduced selectively to cis-2-butene, a carbon-carbon triple bond is reduced to cis carbon-carbon double bond. Usually, complete reduction of alkynes gives alkanes. In these reduction reactions, the carbon-carbon triple bond is reduced to the carbon-carbon single bond. For this purpose, you can use hydrogen gas in presence of platinum, palladium or nickel. However, sometimes complete reduction of alkynes to alkanes is not desirable. You want the reduction to stop at the intermediate alkene stage. For this purpose, you use the reagent \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, Pd/C quinoline}}\].
Hydrogen gas is passed through 2-butyne in presence of palladium metal. Palladium metal is supported on either carbon or barium sulphate. Palladium metal is partially poisoned with quinoline or sulphur to decrease its reactivity. Since, you have poisoned the palladium catalyst, it will only reduce 2-butyene to cis-2-butene. Further reduction to butane will not occur.
Note:
The catalyst will only reduce 2-butyne to cs-2-butene. It will not give you trans 2-butene. If you want trans isomer, then you need to carry out the reaction with sodium metal in liquid ammonia \[({\text{Na/liquid N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}})\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




