
The motile bacteria are able to move with the help of
(a)flagella
(b)cilia
(c)pili
(d)fimbriae
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: The long whip-like locomotor organ that comes out of the plasma membrane of a cell which is found in mastigophoran protozoans.
Complete answer:
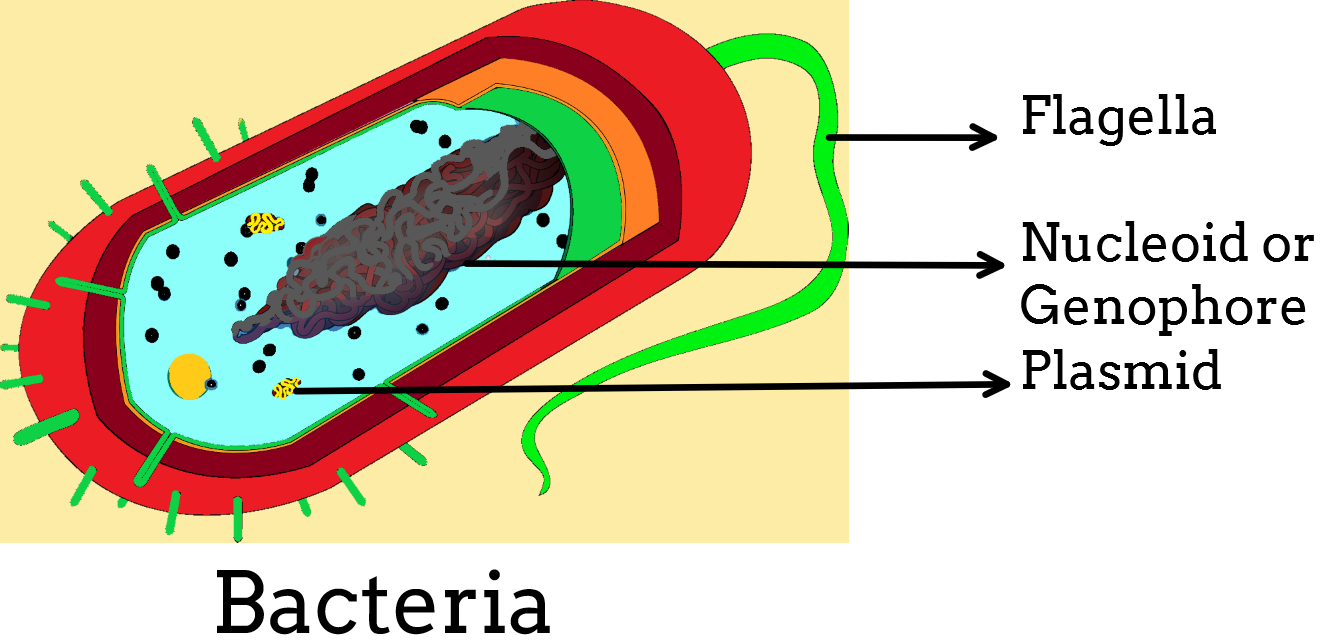
The ability of an organism to move from one place to another is called locomotion. The main locomotor structures present in microorganisms are cilia and flagella. Depending upon the movement bacteria are divided into motile and non-motile bacteria. Motile bacteria contain a locomotor organ called flagella which helps in movement. Flagella in motile bacteria are structurally different from the eukaryotic flagella.
Additional Information: - Motile bacteria can perform locomotion by flagella and gliding movement. Most motile bacteria move by using flagella which is threadlike extending from the plasma membrane of a cell.
- Normally flagella measures up to 15 to 20 micrometers long.
- Bacterium flagella consist of 3 parts: filament, basal body, and hook.
- The longest portion which extends from cell surface to tip is filament and the structure which is embedded in the cell that attaches flagellum to the cell is called the basal body. A short curved segment present outside the cell wall which connects filament to the basal body is the hook.
- The flagella is in the shape of a rigid helix. Rotation of this helix causes the movement of bacteria. The basal body is used to rotate the helix.
- There are five types of flagella namely stichonematic, pantomematic, acronematic, pantacronematic, and ane-matic flagella
So, the correct answer is ‘flagella’
Note: Flagella in bacteria are small and simple made up of proteins and perform the movement by rotation whereas, in eukaryotes, flagella are large and complex structures and are made up of tubulin.
Examples of different types of flagella are:
Stichonematic: euglena, Astasia
Pantone Matic: peranema, Monas
Acronematic: chlamydomonas, polytoma
Pantocronematic: urceolus
Ane matic: chilomonas, cryptomonas.
Complete answer:
The ability of an organism to move from one place to another is called locomotion. The main locomotor structures present in microorganisms are cilia and flagella. Depending upon the movement bacteria are divided into motile and non-motile bacteria. Motile bacteria contain a locomotor organ called flagella which helps in movement. Flagella in motile bacteria are structurally different from the eukaryotic flagella.
Additional Information: - Motile bacteria can perform locomotion by flagella and gliding movement. Most motile bacteria move by using flagella which is threadlike extending from the plasma membrane of a cell.
- Normally flagella measures up to 15 to 20 micrometers long.
- Bacterium flagella consist of 3 parts: filament, basal body, and hook.
- The longest portion which extends from cell surface to tip is filament and the structure which is embedded in the cell that attaches flagellum to the cell is called the basal body. A short curved segment present outside the cell wall which connects filament to the basal body is the hook.
- The flagella is in the shape of a rigid helix. Rotation of this helix causes the movement of bacteria. The basal body is used to rotate the helix.
- There are five types of flagella namely stichonematic, pantomematic, acronematic, pantacronematic, and ane-matic flagella
So, the correct answer is ‘flagella’
Note: Flagella in bacteria are small and simple made up of proteins and perform the movement by rotation whereas, in eukaryotes, flagella are large and complex structures and are made up of tubulin.
Examples of different types of flagella are:
Stichonematic: euglena, Astasia
Pantone Matic: peranema, Monas
Acronematic: chlamydomonas, polytoma
Pantocronematic: urceolus
Ane matic: chilomonas, cryptomonas.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




