
The movement of an amoeba is depicted in the diagram. Which of the following structures is responsible for the amoebic movement?

A. Cilia
B. Flagella
C. Cell wall
D. Cytoskeleton

Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint:An amoeba is a unicellular organism that is able to alter its shape by primarily extending one or more pseudopods. Amoeba is not an individual group of organisms, they occur as amoeboid cells in fungi, algae, protozoa, etc. Amoeba lacks a cell wall which allows them to move freely. Bulges of cytoplasm perform feeding and movement functions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Amoeba is single-celled free-living or parasitic organisms that move and catch food by protoplasmic extensions. They form finger-like projections from their cytoplasm which allows them to move and catch food. They are mostly found in damp-environments.
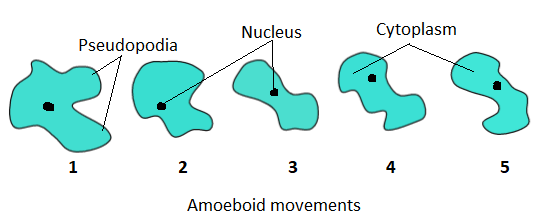
A temporary cytoplasmic projection that occurs from the cell is called pseudopodia. The pseudopodium means false feet and it helps in amoeboid movements. The endoplasm of the amoeba moves in the direction of movement making one or more pseudopodia. The endoplasm present at the tip of the pseudopodia is converted into ectoplasm. On the other hand, at the trailing edge of amoeba, the ectoplasm converts to endoplasm. Small contracting filaments called actin microfilaments induce such contractions of ectoplasm by pushing the cell membrane of amoeba. Several proteins also stimulate ectoplasm contraction. This movement theory is also known as the sol-gel theory. Sol and Gel state that interchangeable states of cytoplasm allow for amoeboid movements.
Hence, it is the cytoskeleton of the amoeba that causes movement. Therefore, option D is the right answer.
Note: The diet source for amoeba is usually dead and decaying matter or they predate over other protists. The food ingestion also occurs through pseudopodia which extends and forms an engulfing structure. The mechanism through which food is ingested is called phagocytosis.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Amoeba is single-celled free-living or parasitic organisms that move and catch food by protoplasmic extensions. They form finger-like projections from their cytoplasm which allows them to move and catch food. They are mostly found in damp-environments.

A temporary cytoplasmic projection that occurs from the cell is called pseudopodia. The pseudopodium means false feet and it helps in amoeboid movements. The endoplasm of the amoeba moves in the direction of movement making one or more pseudopodia. The endoplasm present at the tip of the pseudopodia is converted into ectoplasm. On the other hand, at the trailing edge of amoeba, the ectoplasm converts to endoplasm. Small contracting filaments called actin microfilaments induce such contractions of ectoplasm by pushing the cell membrane of amoeba. Several proteins also stimulate ectoplasm contraction. This movement theory is also known as the sol-gel theory. Sol and Gel state that interchangeable states of cytoplasm allow for amoeboid movements.
Hence, it is the cytoskeleton of the amoeba that causes movement. Therefore, option D is the right answer.
Note: The diet source for amoeba is usually dead and decaying matter or they predate over other protists. The food ingestion also occurs through pseudopodia which extends and forms an engulfing structure. The mechanism through which food is ingested is called phagocytosis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




