
The near point and far point of a person are 40 cm and 250 cm respectively.
Determine the power of the lens he/she should use while reading a book kept at a distance 25 cm from the eye.
A. 2.5 D
B. 5.0 D
C. 1.5 D
D. 3.5 D
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: The person will be able to read the book if its image can be formed at 40 cm from his eyes. But the book is at a distance of 25 cm. So, we need a converging lens (convex) of appropriate focal length. It can be better understood from the diagram.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
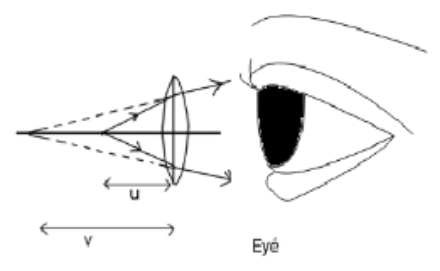
The image distance must be $v = -40cm$. The negative sign is due to the fact that it is measured in the opposite of the direction of light. The object distance is clearly $u=-25 cm$. So, from the lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Taking LCM, we get
$\dfrac{u-v}{vu}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Taking reciprocal and substituting the values, we get
$\begin{align}
& f=\dfrac{uv}{u-v} \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{(-40)(-25)}{(-25)-(-40)} \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{1000}{15} \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{200}{3}cm \\
\end{align}$
$f=\dfrac{2}{3} m$
Power of the lens is,
$P=\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{3}{2}=1.5D$
Hence option C is the correct answer.
Additional information:
When a person cannot see objects that are very close to him but can see the things that are far away, the problem or defect is called Hypermetropia. In this condition, the person has to use a convex lens. When a person can’t see things that are away from him but can see things close to him, the problem is called Myopia. It’s treated by using a concave lens. In both cases, virtual images are formed by the lenses.
Note: Take good care of the sign convention. Usually in case of virtual images, both the image and the object are on the same side of the lens. To avoid mistakes, notice that power is given in Diopter when the focal length is given in meters. The power is always positive for convex lenses and negative for concave lenses.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete step-by-step solution:

The image distance must be $v = -40cm$. The negative sign is due to the fact that it is measured in the opposite of the direction of light. The object distance is clearly $u=-25 cm$. So, from the lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Taking LCM, we get
$\dfrac{u-v}{vu}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Taking reciprocal and substituting the values, we get
$\begin{align}
& f=\dfrac{uv}{u-v} \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{(-40)(-25)}{(-25)-(-40)} \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{1000}{15} \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{200}{3}cm \\
\end{align}$
$f=\dfrac{2}{3} m$
Power of the lens is,
$P=\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{3}{2}=1.5D$
Hence option C is the correct answer.
Additional information:
When a person cannot see objects that are very close to him but can see the things that are far away, the problem or defect is called Hypermetropia. In this condition, the person has to use a convex lens. When a person can’t see things that are away from him but can see things close to him, the problem is called Myopia. It’s treated by using a concave lens. In both cases, virtual images are formed by the lenses.
Note: Take good care of the sign convention. Usually in case of virtual images, both the image and the object are on the same side of the lens. To avoid mistakes, notice that power is given in Diopter when the focal length is given in meters. The power is always positive for convex lenses and negative for concave lenses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




