
The number of criteria used as classifying organisms in five-kingdom classification is
A. 5
B. 4
C. 3
D. 1
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: The criteria depend upon the cell structure and functions along with its ancestral history, on this basis several new kingdoms were proposed which involves the developed characters.
Complete answer:
R. H. Whittaker proposed the five-kingdom classification in 1969 based on 5 different characters of organisms like the structure of the cell, mode of nutrition, body organization, phylogenetic relationship, and reproduction. Whittaker’s system of classification is said to be more natural and scientific.
Additional Information: -Five kingdom classification was proposed to distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
-Robert Whittaker recognized an additional kingdom for fungi.
-It was mostly based on the differences in nutrition.
-The kingdom Plantae were autotrophs (they synthesize their food), and heterotrophs (they feed on other organisms).
-The fungi were neither autotrophs nor heterotrophs, instead, they were saprophytes (live on other living organisms to derive food from them).
-Whittaker added some algae in the kingdom Plantae as they synthesize their food and are considered as autotrophs.
-The remaining two kingdoms, Protista and Monera were included in unicellular and simple cellular colonies.
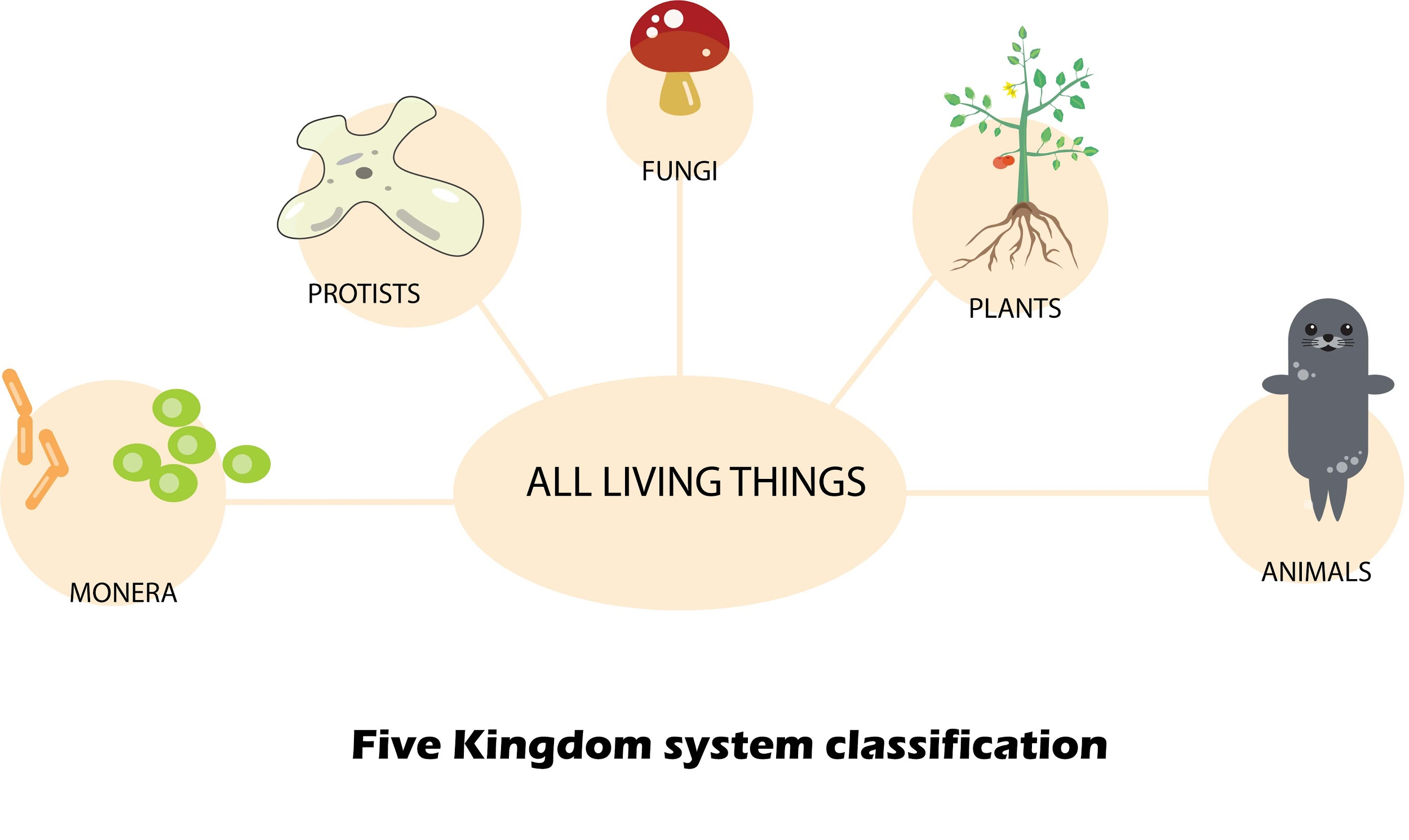
-The five kingdoms of Whittaker’s classification are listed below:
a)Kingdom Monera
b)Kingdom Fungi
c)Kingdom Protista
d)Kingdom Plantae
e)Kingdom Animalia
So, the correct answer is ‘5’.
Note: Kingdom is the second-highest taxonomic rank in biology just below domain. In biology, the ranks system of nomenclature was introduced in 1735 by Carl Linnaeus and was given the name “kingdom “. The kingdom is the highest taxa in classification. There were various classifications proposed, they were: two kingdoms (Aristotle), three kingdoms (Carl Linnaeus), four kingdoms (Herbert. F. Copeland), and five-kingdom classification (R. H Whittaker).
Complete answer:
R. H. Whittaker proposed the five-kingdom classification in 1969 based on 5 different characters of organisms like the structure of the cell, mode of nutrition, body organization, phylogenetic relationship, and reproduction. Whittaker’s system of classification is said to be more natural and scientific.
Additional Information: -Five kingdom classification was proposed to distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
-Robert Whittaker recognized an additional kingdom for fungi.
-It was mostly based on the differences in nutrition.
-The kingdom Plantae were autotrophs (they synthesize their food), and heterotrophs (they feed on other organisms).
-The fungi were neither autotrophs nor heterotrophs, instead, they were saprophytes (live on other living organisms to derive food from them).
-Whittaker added some algae in the kingdom Plantae as they synthesize their food and are considered as autotrophs.
-The remaining two kingdoms, Protista and Monera were included in unicellular and simple cellular colonies.
-The five kingdoms of Whittaker’s classification are listed below:
a)Kingdom Monera
b)Kingdom Fungi
c)Kingdom Protista
d)Kingdom Plantae
e)Kingdom Animalia
So, the correct answer is ‘5’.

Note: Kingdom is the second-highest taxonomic rank in biology just below domain. In biology, the ranks system of nomenclature was introduced in 1735 by Carl Linnaeus and was given the name “kingdom “. The kingdom is the highest taxa in classification. There were various classifications proposed, they were: two kingdoms (Aristotle), three kingdoms (Carl Linnaeus), four kingdoms (Herbert. F. Copeland), and five-kingdom classification (R. H Whittaker).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




