
The number of moles of acetic anhydride $\left( {A{c_2}O} \right)$ needed to react completely with sucrose is:
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: In this problem firstly, we will put light on a very basic yet very important topic of chemistry. In this question we will learn about Biomolecules and Disaccharides and we will be learning all the related information on them which will help us in approaching our answer. Below here these concepts are explained properly.
Complete answer:
Biomolecule: Biomolecules are chemical compounds built by living organisms, which include chemicals that are composed of mainly carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus. Biomolecules are the building blocks of life which perform important functions in living organisms.
Disaccharides: Disaccharides are sugar molecules that form when two simple sugars.
$i.e$ monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are those carbohydrates that on hydrolysis with acids or enzymes give two molecules of monosaccharides which can either be the same or different. Monosaccharide units are joined together via a linkage called glycosidic linkage.
It has been observed that the structure of Sucrose, it can be seen that it has .$8 - OH$ groups and each $ - OH$ reacts with the acetic anhydride. So, $8\,moles$ of acetic anhydride are required from one mole of sucrose
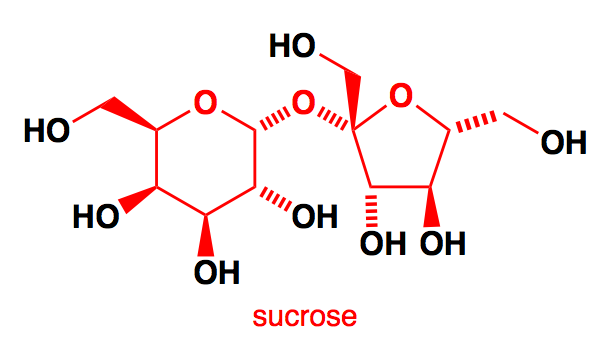
Note: Sucrose is found in all photosynthetic plants. It is commonly obtained from sugarcane and sugar beets via an industrial process. The molecular formula of sucrose is ${C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}$ . If sucrose goes through acid catalyzed hydrolysis it produces one mole of D – Glucose and one mole of D- Fructose. Sucrose is a non- reducing sugar. Sucrose structure is combined at the hemiacetal oxygen and does not have a free hemiacetal hydroxide.
Complete answer:
Biomolecule: Biomolecules are chemical compounds built by living organisms, which include chemicals that are composed of mainly carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus. Biomolecules are the building blocks of life which perform important functions in living organisms.
Disaccharides: Disaccharides are sugar molecules that form when two simple sugars.
$i.e$ monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are those carbohydrates that on hydrolysis with acids or enzymes give two molecules of monosaccharides which can either be the same or different. Monosaccharide units are joined together via a linkage called glycosidic linkage.
It has been observed that the structure of Sucrose, it can be seen that it has .$8 - OH$ groups and each $ - OH$ reacts with the acetic anhydride. So, $8\,moles$ of acetic anhydride are required from one mole of sucrose

Note: Sucrose is found in all photosynthetic plants. It is commonly obtained from sugarcane and sugar beets via an industrial process. The molecular formula of sucrose is ${C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}$ . If sucrose goes through acid catalyzed hydrolysis it produces one mole of D – Glucose and one mole of D- Fructose. Sucrose is a non- reducing sugar. Sucrose structure is combined at the hemiacetal oxygen and does not have a free hemiacetal hydroxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




