
The number of stereoisomers of glucose (a six carbon sugar) is:
A. 8
B. 12
C. 16
D. 24
Answer
604.8k+ views
Hint: To find the number of stereoisomers of glucose, we should first draw the structure of it. And in this structure we should find chiral carbons or asymmetric carbon. Asymmetric carbon atom is a carbon atom that is attached to four different types of atoms or groups of atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To solve this question, we should first draw the structure of glucose.
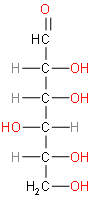
Above represented structure is of glucose. We should know that glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}\]. Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide.
To find the number of stereoisomers of glucose, we should know about Le Bel-van't Hoff rule. It states that the number of stereoisomers of an organic compound is\[{{2}^{n}}\], where n represents the number of asymmetric carbon atoms.
If n is the number of asymmetric carbon atoms then the maximum number of isomers = \[{{2}^{n}}\]
We should know that, each time we add a chiral center to a molecule, we double the possible number of stereoisomers. With 1 chiral center, there are 2 isomers, 2 chiral centers, 4 possible isomers, 3 centers, 8 isomers and 4 centers, 16 possible stereoisomers. For an arbitrary number (n) of chiral centers in a molecule there are as many as 2n possible stereoisomers. Sucrose, with nine chiral carbons, has 29 stereoisomers, or 512. Glucose has four chiral carbons in its aldehyde form, and so there are 24, or 16 possible stereoisomers of this formula.
So, from the discussion above we came to know that our correct answer is 16. There are 16 possible stereoisomers of glucose, making C as the correct option.
Note: We should note that glucose is a type of sugar we get from foods we eat, and our body uses it for energy. As it travels through our bloodstream to our cells, it's called blood glucose or blood sugar. It mainly comes from foods rich in carbohydrates, like bread, potatoes, and fruit. As we eat, food travels down our oesophagus to our stomach. There, acids and enzymes break it down into tiny pieces. During that process, glucose is released. It goes into our intestines where it's absorbed. From there, it passes into your bloodstream. Once in the blood, insulin helps glucose get to our cells.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To solve this question, we should first draw the structure of glucose.

Above represented structure is of glucose. We should know that glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}\]. Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide.
To find the number of stereoisomers of glucose, we should know about Le Bel-van't Hoff rule. It states that the number of stereoisomers of an organic compound is\[{{2}^{n}}\], where n represents the number of asymmetric carbon atoms.
If n is the number of asymmetric carbon atoms then the maximum number of isomers = \[{{2}^{n}}\]
We should know that, each time we add a chiral center to a molecule, we double the possible number of stereoisomers. With 1 chiral center, there are 2 isomers, 2 chiral centers, 4 possible isomers, 3 centers, 8 isomers and 4 centers, 16 possible stereoisomers. For an arbitrary number (n) of chiral centers in a molecule there are as many as 2n possible stereoisomers. Sucrose, with nine chiral carbons, has 29 stereoisomers, or 512. Glucose has four chiral carbons in its aldehyde form, and so there are 24, or 16 possible stereoisomers of this formula.
So, from the discussion above we came to know that our correct answer is 16. There are 16 possible stereoisomers of glucose, making C as the correct option.
Note: We should note that glucose is a type of sugar we get from foods we eat, and our body uses it for energy. As it travels through our bloodstream to our cells, it's called blood glucose or blood sugar. It mainly comes from foods rich in carbohydrates, like bread, potatoes, and fruit. As we eat, food travels down our oesophagus to our stomach. There, acids and enzymes break it down into tiny pieces. During that process, glucose is released. It goes into our intestines where it's absorbed. From there, it passes into your bloodstream. Once in the blood, insulin helps glucose get to our cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




