
The optically inactive amino acids
A.Lysine
B.Glycine
C.Arginine
D.Alanine
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Amino acids are organic compounds , which combine to form proteins. Amino acids contain amine and carboxyl functional groups along with a side chain ( ${\text{R}}$ group ) which is specific to each amino acid .Most of the amino acids are stereoisomers and are chiral molecules. Stereoisomerism is a type of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula but differ in their spatial arrangement of atoms. Optical isomerism comes under stereoisomerism.
Complete step by step solution:
A general structure of amino acid can written as
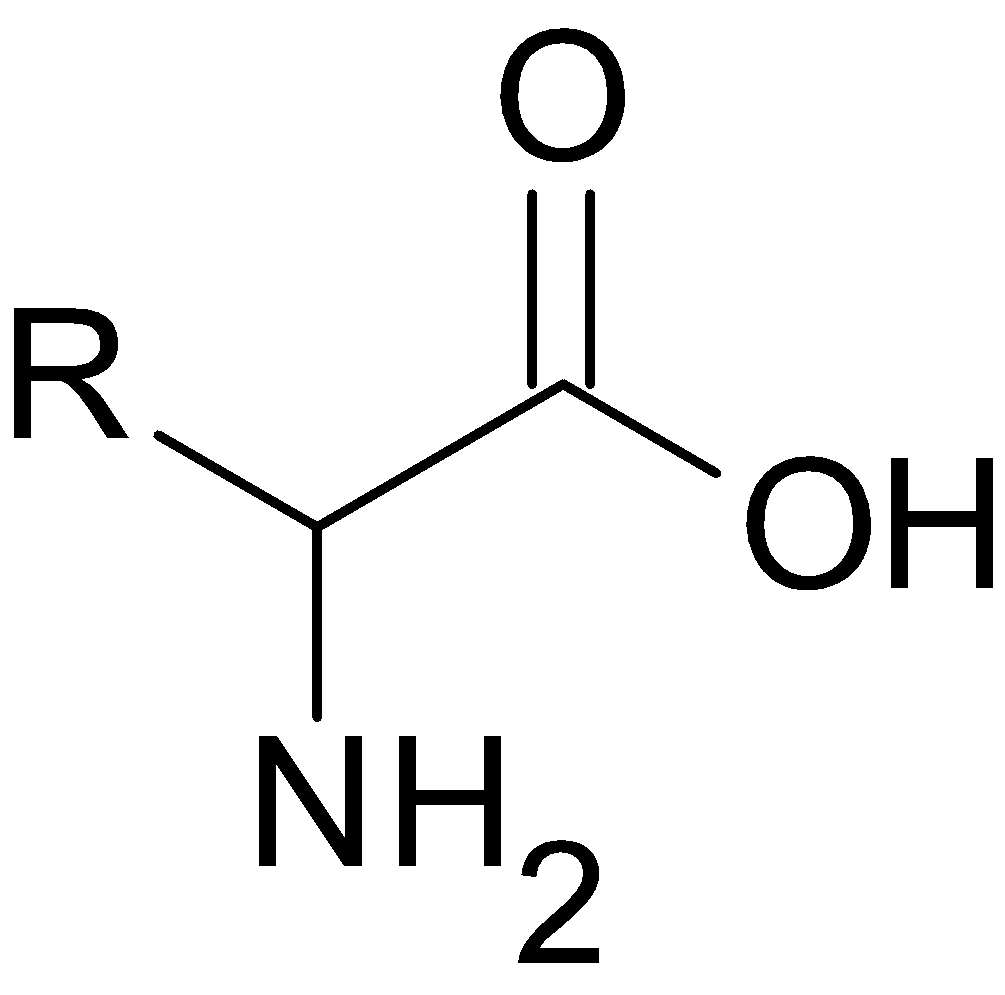
where ${\text{R}}$ is different for different amino acids.
Now we learn about optical isomerism . Simply we can say that optical isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism in which the two isomers of the compound are said to be mirror images of each other that are non superimposable.Let us look at the example of optical isomers amino acid alanine.
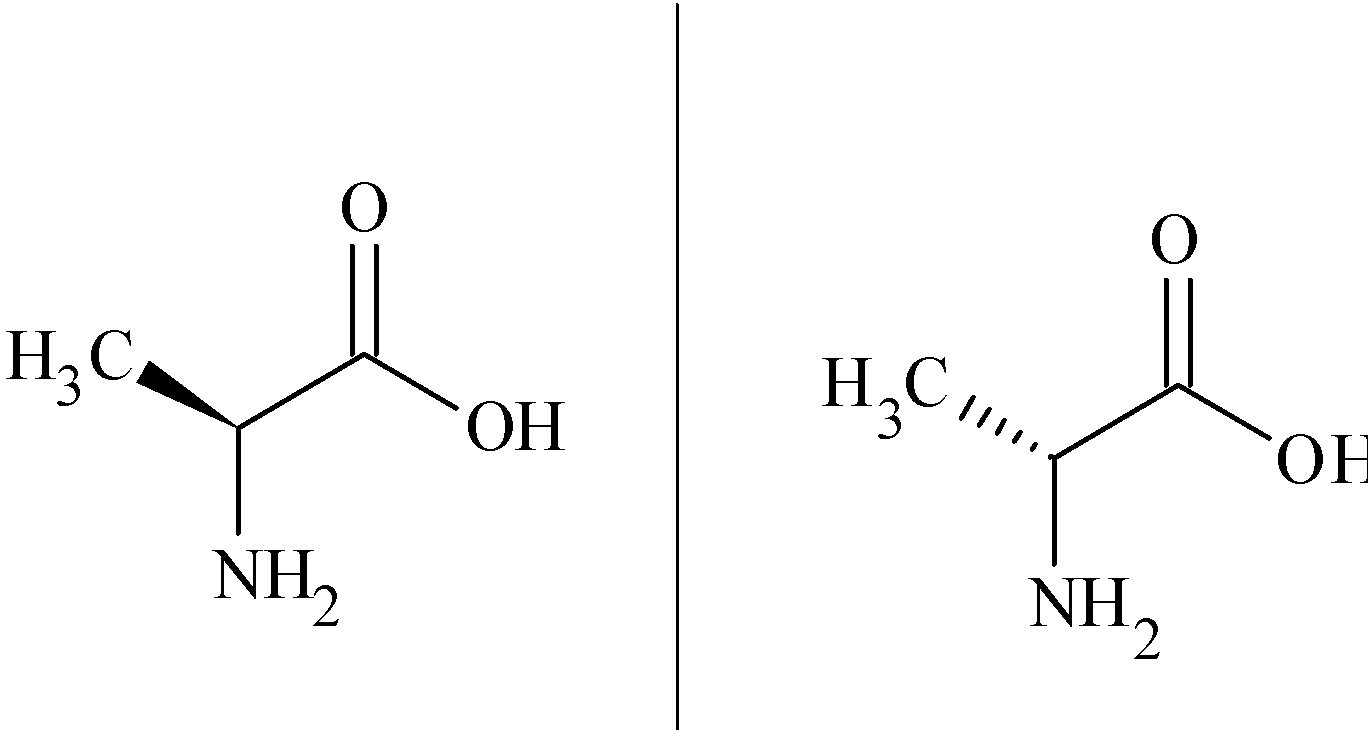
Optical isomers have the same physical properties, but they rotate planes of polarised light in the opposite direction. Most optical isomers are organic compounds , and a chiral centre is necessary for a compound to show optical isomerism, when there are four different groups attached to a carbon atom then it is called chiral carbon. So such compounds which are capable of rotating planes of polarised light are said to be optically active.
The compounds which don’t have a chiral centre that is incapable of optical rotation is said to be optically inactive. All pure achiral compounds are optically inactive.
Let us consider the general structure of amino acids
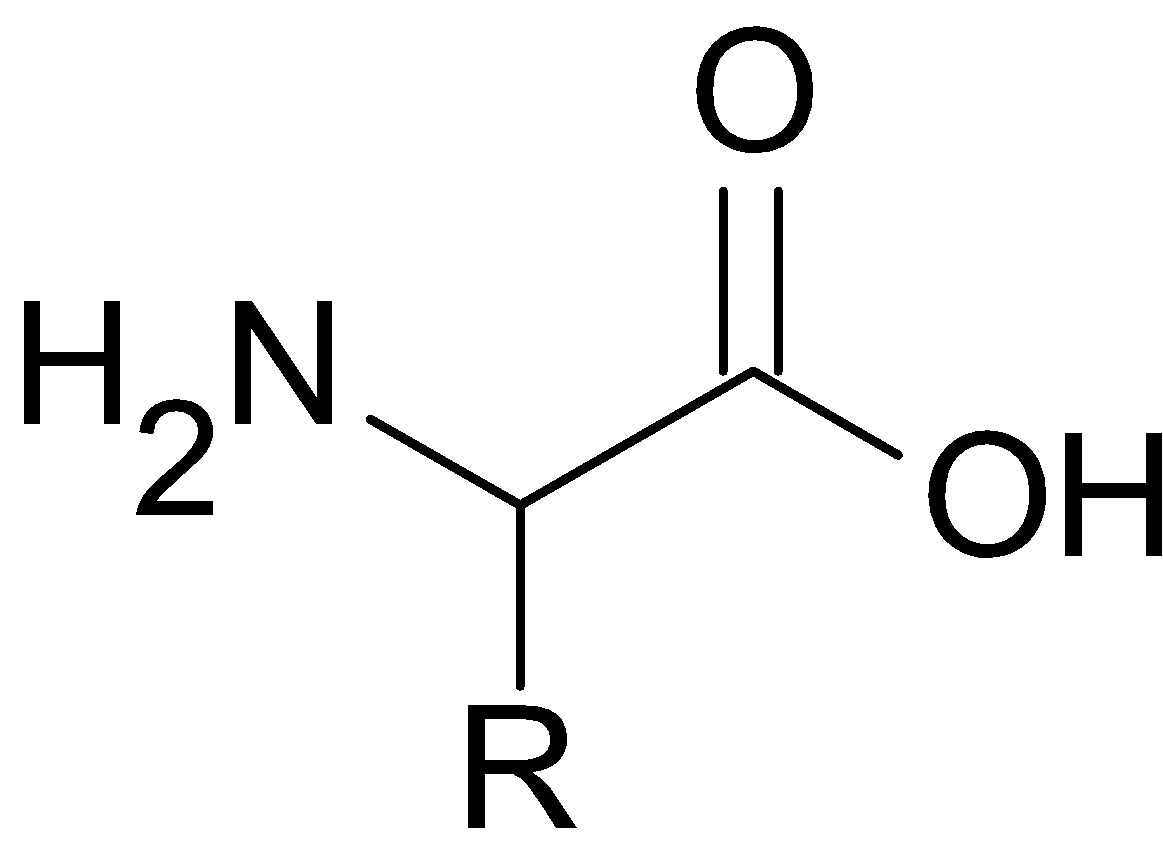
When we look at the structure of amino acid , amino group and that of carboxyl group attached to the $\alpha -$ carbon atom ( carbon atom next to carboxyl group) . The Carbon atom also bonded to the hydrogen atom and ${\text{R}}$ group , hence here the carbon atom is chiral because it is attached to four different groups, making them optically active.
We can look at the examples of Lysine, Arginine, Alanine
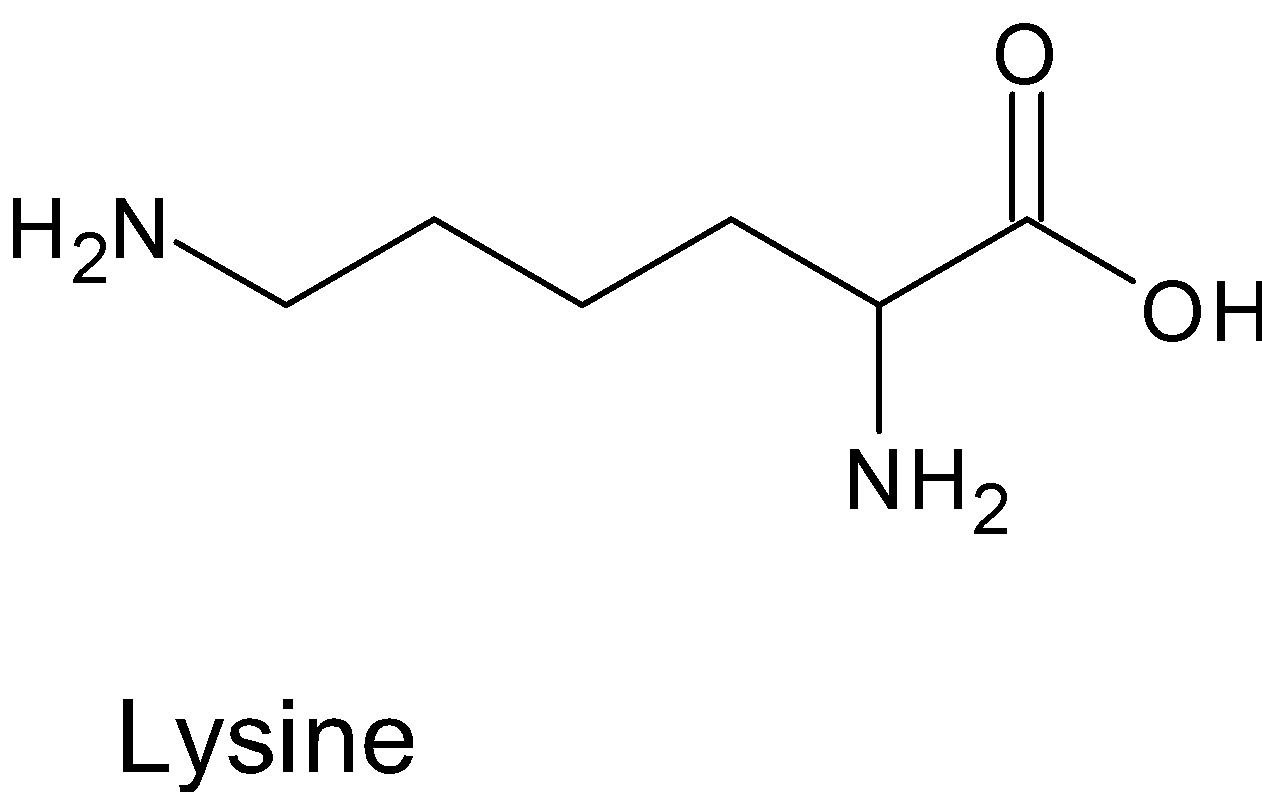
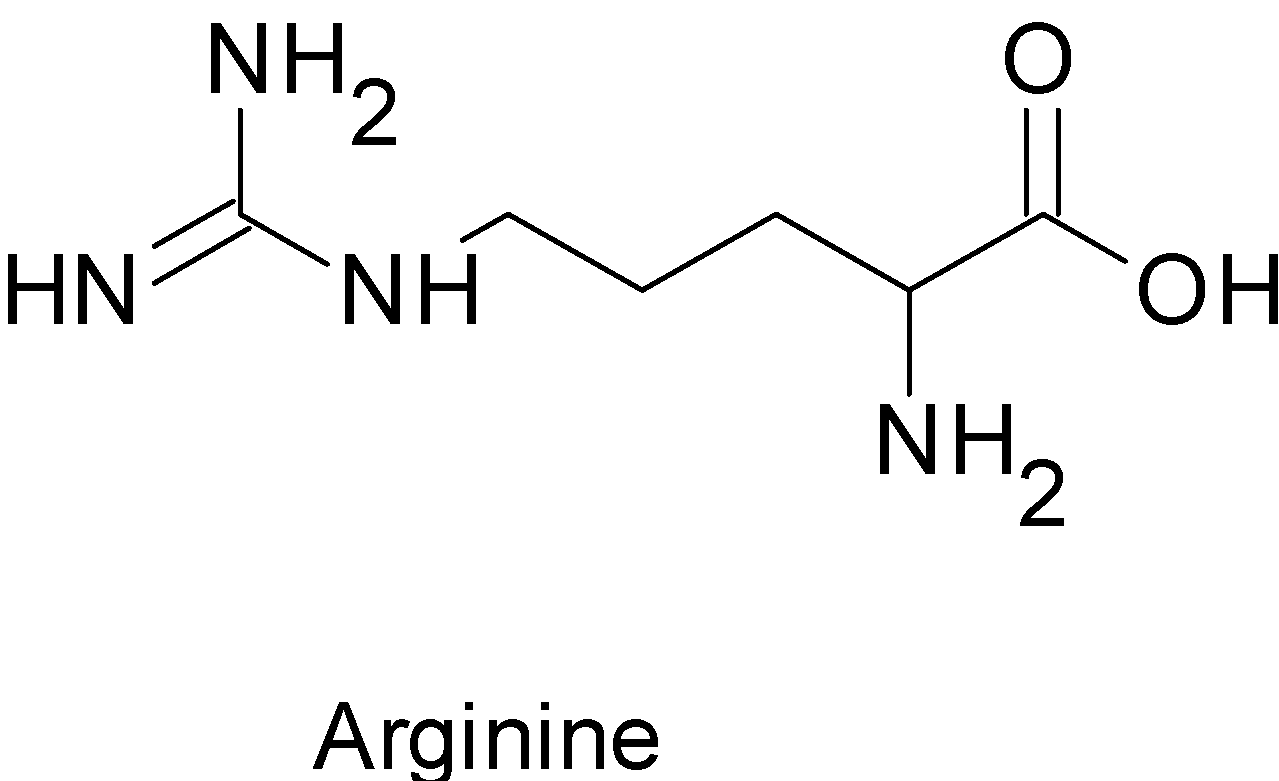
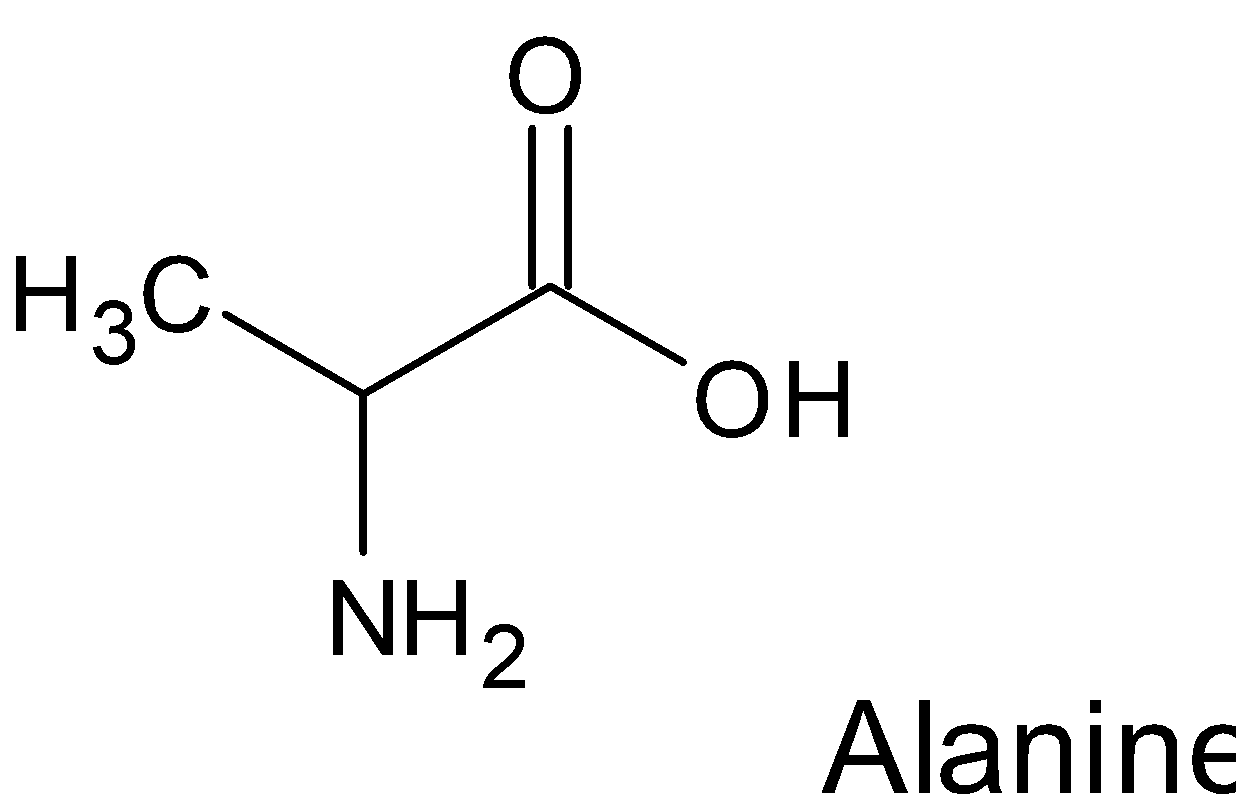
In above given amino acids the $\alpha -$ carbon atom is chiral , hence it all are optically active
Whereas in case of Glycine when we look at the structure
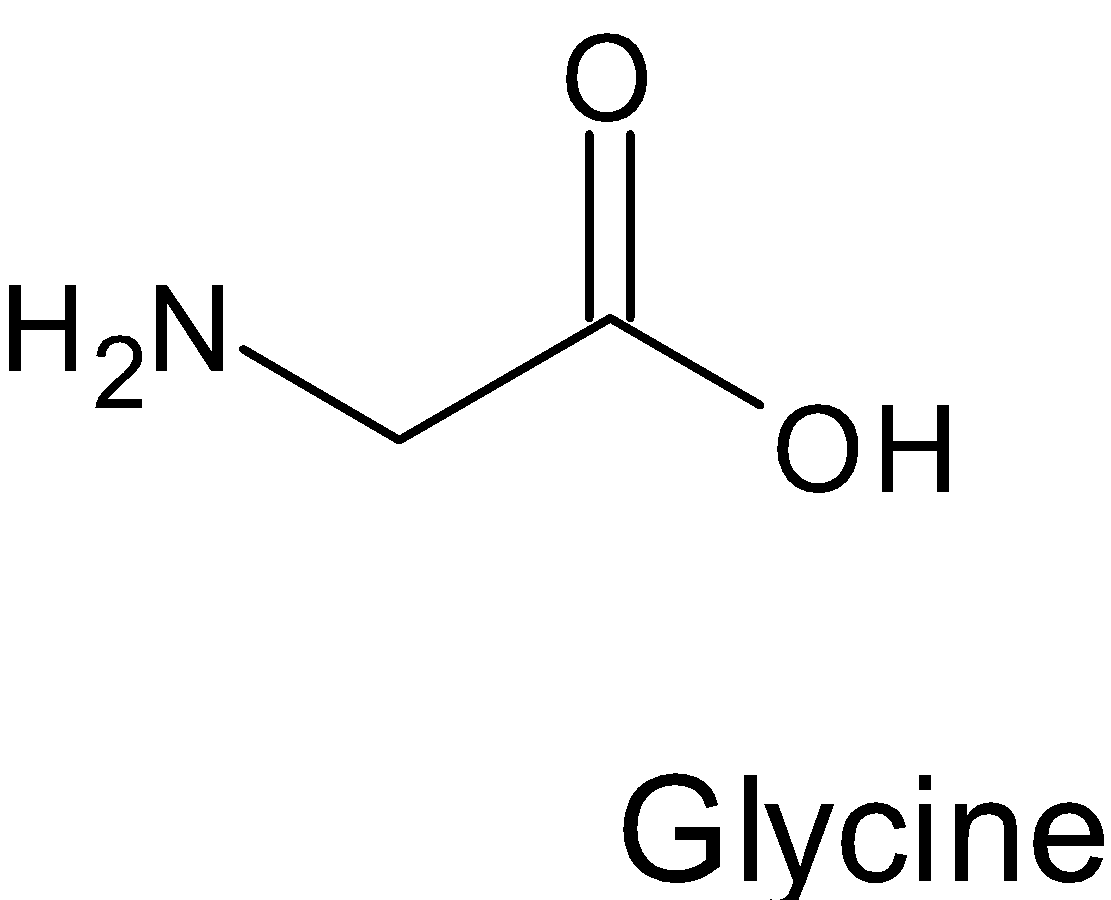
Here the carbon atom is not chiral, because two hydrogen atoms attached to $\alpha -$ carbon make it achiral so glycine is found to be optically inactive.
So here the answer of optically inactive amino acids is glycine.
So, Option B is correct.
Note: A compound is said to have a chiral centre when it has an asymmetric centre , carbon atom bonded to four different groups, and isomers are non superimposable mirror images. Whereas an achiral compound is superimposable on its mirror image.
All amino acids except Glycine have a chiral centre , making them optical active.
Complete step by step solution:
A general structure of amino acid can written as

where ${\text{R}}$ is different for different amino acids.
Now we learn about optical isomerism . Simply we can say that optical isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism in which the two isomers of the compound are said to be mirror images of each other that are non superimposable.Let us look at the example of optical isomers amino acid alanine.

Optical isomers have the same physical properties, but they rotate planes of polarised light in the opposite direction. Most optical isomers are organic compounds , and a chiral centre is necessary for a compound to show optical isomerism, when there are four different groups attached to a carbon atom then it is called chiral carbon. So such compounds which are capable of rotating planes of polarised light are said to be optically active.
The compounds which don’t have a chiral centre that is incapable of optical rotation is said to be optically inactive. All pure achiral compounds are optically inactive.
Let us consider the general structure of amino acids

When we look at the structure of amino acid , amino group and that of carboxyl group attached to the $\alpha -$ carbon atom ( carbon atom next to carboxyl group) . The Carbon atom also bonded to the hydrogen atom and ${\text{R}}$ group , hence here the carbon atom is chiral because it is attached to four different groups, making them optically active.
We can look at the examples of Lysine, Arginine, Alanine



In above given amino acids the $\alpha -$ carbon atom is chiral , hence it all are optically active
Whereas in case of Glycine when we look at the structure

Here the carbon atom is not chiral, because two hydrogen atoms attached to $\alpha -$ carbon make it achiral so glycine is found to be optically inactive.
So here the answer of optically inactive amino acids is glycine.
So, Option B is correct.
Note: A compound is said to have a chiral centre when it has an asymmetric centre , carbon atom bonded to four different groups, and isomers are non superimposable mirror images. Whereas an achiral compound is superimposable on its mirror image.
All amino acids except Glycine have a chiral centre , making them optical active.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




