
The optically inactive compound from the following is:
A. 2-chloropropanal
B. 2-chlorobutane
C. 2-chloro-2-methylbutane
D. 2-chloropentane
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: The answer here is based on the concept of organic chemistry that deals with the topic of the stereochemistry which states that optically inactive compounds are those which cannot rotate the plane polarised light and it is said to be inactive if the compound is symmetrical.
Complete answer:
We have studied the chirality of carbon atoms that is included in the chapter of stereochemistry in the organic chemistry part.
Now, let us see what is the chirality of the compound and how can the compound be said as whether it is optically active or inactive.
- Chirality is defined as if a molecule or ion cannot be superimposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations and translations.
- Optically inactive compounds are those compounds which are incapable of rotating a plane polarized light. To identify which compound is inactive, we must check its symmetry.
Now, in option A. 2-chloropropyl has aldehyde functional group and the structure is,
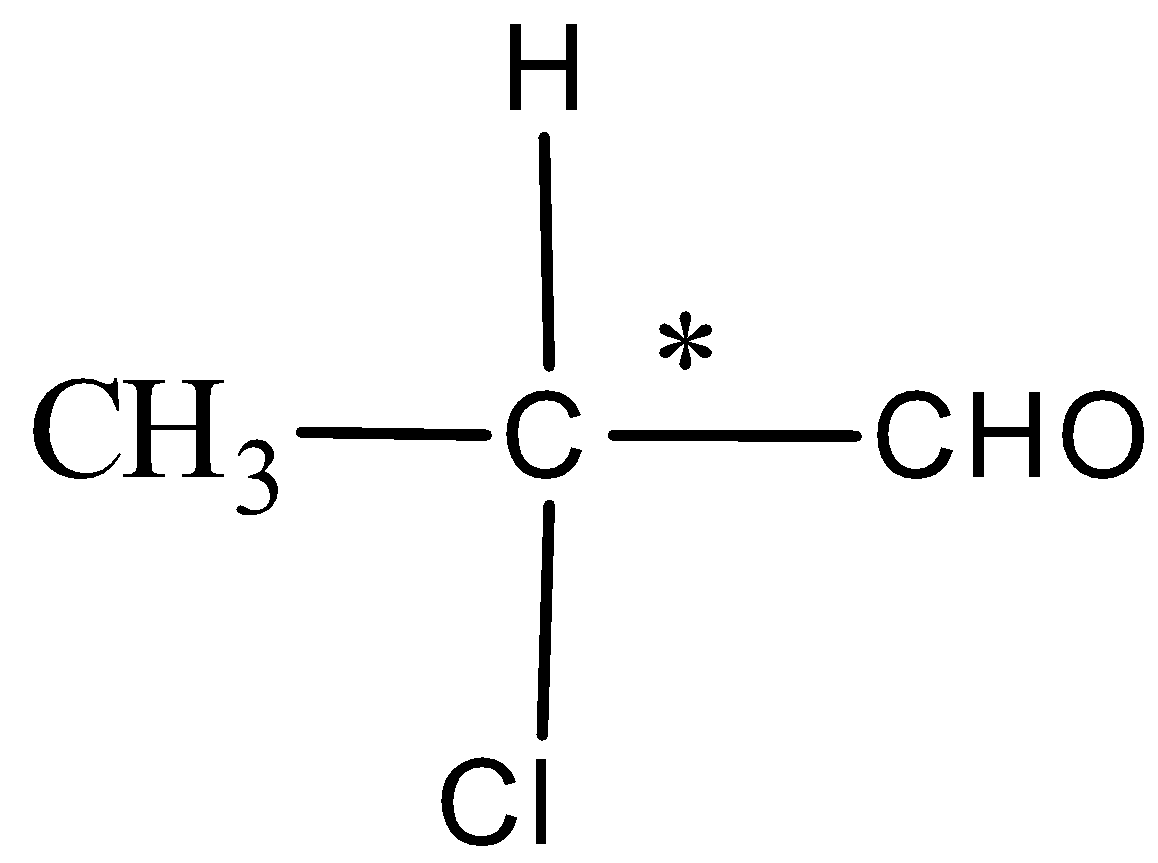
The compound here is having the chiral carbon that is the groups attached to the carbon marked with asterisk are all different and hence this compound is optically active.
In option B. 2-chlorobutane the structure is as shown below,
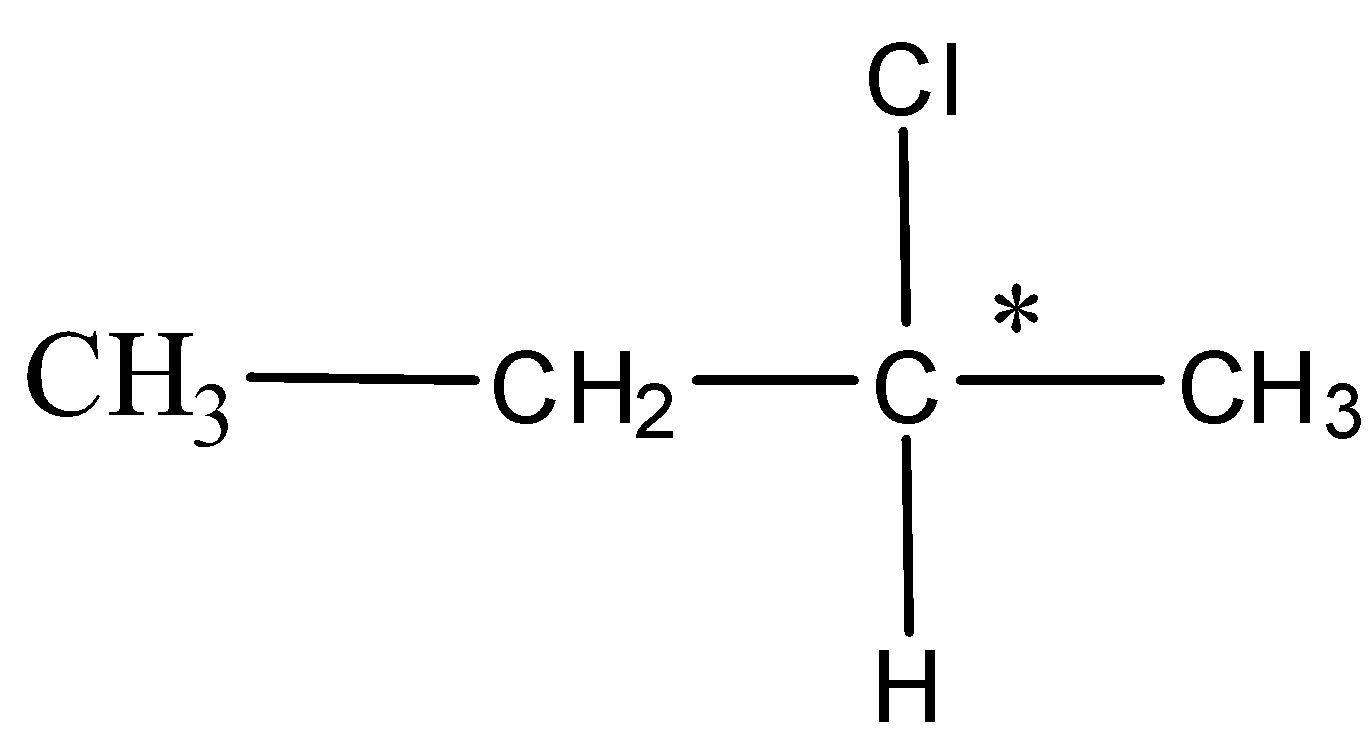
Here, the carbon with the asterisk is a chiral carbon attached to all the different groups and hence it is optically active.
In option C. 2-chloro-2-methylbutane the structure written is as follows,
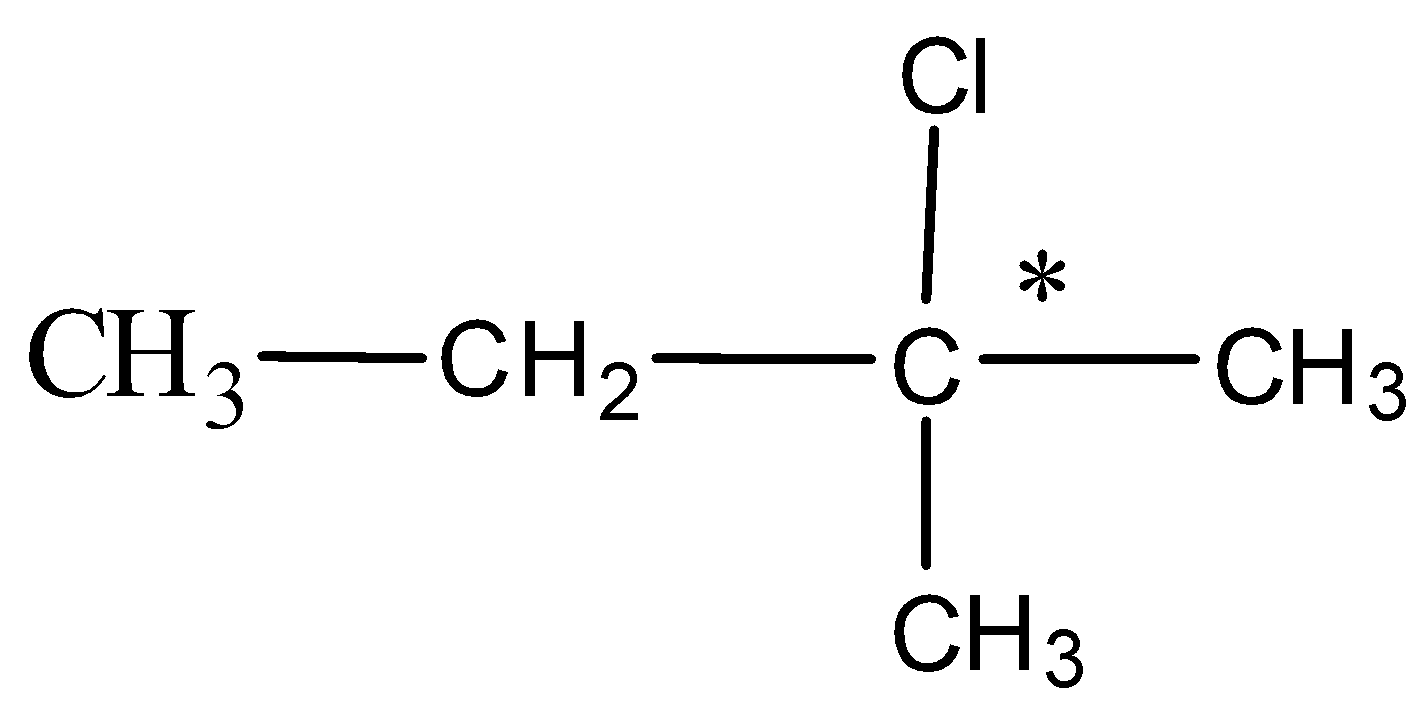
Here, the carbon with an asterisk is attached to two methyl groups which are the same and hence this compound is achiral and is optically inactive.
In option D. 2-chloropentane, the structure is,
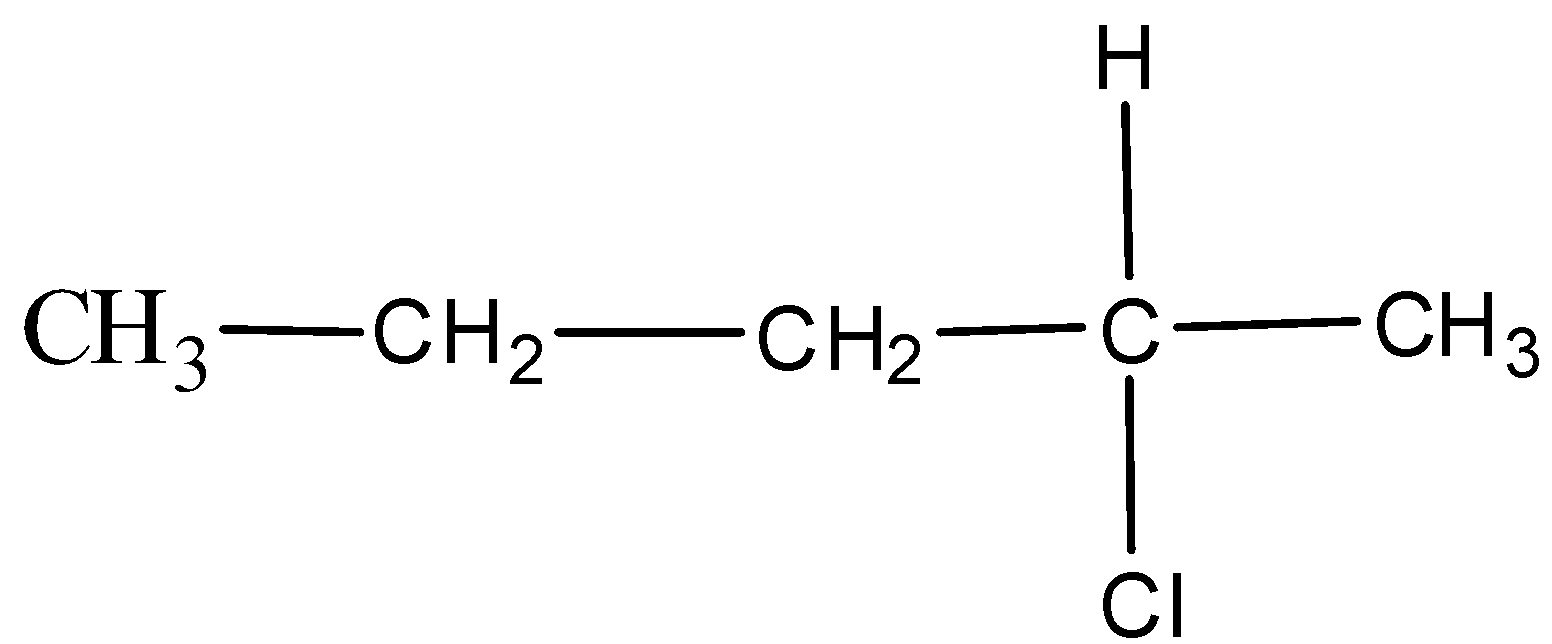
Here, the carbon with an asterisk is attached to the different groups which mean that it is a chiral compound that is optically active.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
Note that the optical rotation is also called by name polarization rotation or circular birefringence and is nothing but the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarisation about the optical axis of the linearly polarized light when it travels through certain materials.
Complete answer:
We have studied the chirality of carbon atoms that is included in the chapter of stereochemistry in the organic chemistry part.
Now, let us see what is the chirality of the compound and how can the compound be said as whether it is optically active or inactive.
- Chirality is defined as if a molecule or ion cannot be superimposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations and translations.
- Optically inactive compounds are those compounds which are incapable of rotating a plane polarized light. To identify which compound is inactive, we must check its symmetry.
Now, in option A. 2-chloropropyl has aldehyde functional group and the structure is,

The compound here is having the chiral carbon that is the groups attached to the carbon marked with asterisk are all different and hence this compound is optically active.
In option B. 2-chlorobutane the structure is as shown below,

Here, the carbon with the asterisk is a chiral carbon attached to all the different groups and hence it is optically active.
In option C. 2-chloro-2-methylbutane the structure written is as follows,

Here, the carbon with an asterisk is attached to two methyl groups which are the same and hence this compound is achiral and is optically inactive.
In option D. 2-chloropentane, the structure is,

Here, the carbon with an asterisk is attached to the different groups which mean that it is a chiral compound that is optically active.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
Note that the optical rotation is also called by name polarization rotation or circular birefringence and is nothing but the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarisation about the optical axis of the linearly polarized light when it travels through certain materials.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




