
The order of three layers of cells in the retina of the human eye from inside to outside is
(a) Bipolar cells, photoreceptors, ganglion cells
(b) Ganglion cells, rods, cones
(c) Ganglion cells, bipolar cells, photoreceptor cells
(d) Photoreceptor cells, ganglion cells, bipolar cells
(e) Ganglion cells, photoreceptor cells, bipolar cells
Answer
510.9k+ views
Hint: Retina is a layer of nervous tissue that covers the back two-thirds of the inside of the eyeball, in which stimulation by light occurs, initiating the sensation of vision. The retina is an extension of the brain nerve and is connected to the brain by the optic nerve.
Complete Answer:
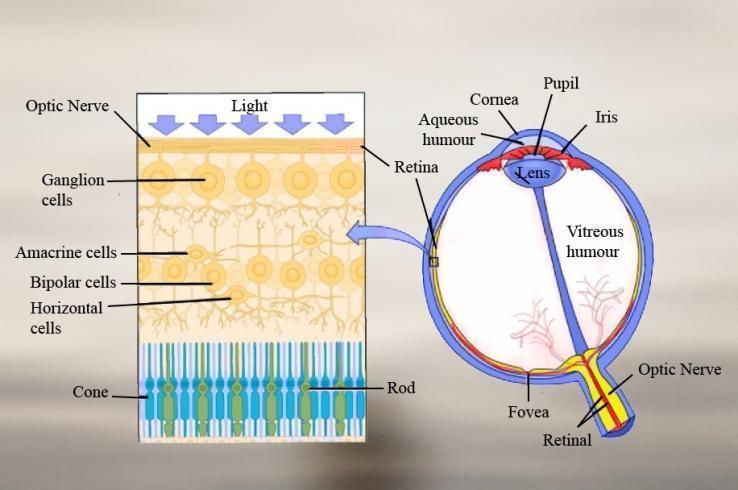
‘Ganglion cells, bipolar cells, photoreceptor cells’ is the correct order of three layers of cells in the retina from inside to outside
The retina has three layers of cell:
Ganglion cells: It is the innermost layer of the retina and carries visual information to the brain. The ganglion cells take information from bipolar cells. It forms the optic nerve.
Bipolar cells: These cells are present next to ganglion cells or the middle layer of the retina. It takes the signal from photoreceptor cells.
Photoreceptor cells: These are the outermost cells of the retina present next to bipolar cells. They detect daylight and low light vision. There are two types of photoreceptor cells in the retina; the cones are responsible for detecting daylight and colored light while the rods detect low light vision.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Ganglion cells, bipolar cells, photoreceptor cells.’
Note:
-The human eye is sensitive to light of wavelength 380-760 nm. It is the wavelength range of the visible spectrum. The human eye is a sense organ that receives visual images, which are then sent to the brain for understanding the view.
-Nearsightedness (can see near but not far objects) and farsightedness (can see far but not near objects) are two very common and very different types of vision defects. Both defects are due to refractive error abnormalities of the eye that affect its ability to focus light on the retina.
Complete Answer:
‘Ganglion cells, bipolar cells, photoreceptor cells’ is the correct order of three layers of cells in the retina from inside to outside
The retina has three layers of cell:
Ganglion cells: It is the innermost layer of the retina and carries visual information to the brain. The ganglion cells take information from bipolar cells. It forms the optic nerve.
Bipolar cells: These cells are present next to ganglion cells or the middle layer of the retina. It takes the signal from photoreceptor cells.
Photoreceptor cells: These are the outermost cells of the retina present next to bipolar cells. They detect daylight and low light vision. There are two types of photoreceptor cells in the retina; the cones are responsible for detecting daylight and colored light while the rods detect low light vision.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Ganglion cells, bipolar cells, photoreceptor cells.’

Note:
-The human eye is sensitive to light of wavelength 380-760 nm. It is the wavelength range of the visible spectrum. The human eye is a sense organ that receives visual images, which are then sent to the brain for understanding the view.
-Nearsightedness (can see near but not far objects) and farsightedness (can see far but not near objects) are two very common and very different types of vision defects. Both defects are due to refractive error abnormalities of the eye that affect its ability to focus light on the retina.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




