
The oxidation of benzene by \[{V_2}{O_5}\] in the presence of air produces:
A.benzoic acid
B.benzaldehyde
C.benzoic anhydride
D.maleic anhydride
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: The oxidation of benzene by Vanadium pentoxide \[\left( {{V_2}{O_5}} \right)\] in the presence of air is D. A Dowden mechanism. We have to see where the cleavage will take place and what kind of anhydride will be formed.
Complete step by step answer:
When one molecule of benzene reacts with two molecules of vanadium pentoxide and one and a half mole of oxygen, we get one of maleic anhydride, one molecule of glyoxylic or aldehyde acid, two moles of vanadium trioxide and one mole of water. During this process, the cleavage of the benzene ring takes place and form diodic acid and this acid will then undergo dehydration to form an anhydride by the same Vanadium pentoxide \[\left( {{V_2}{O_5}} \right)\] molecules and it will cleave any double bonds that are present in the ring.
The oxidation of benzene by \[{V_2}{O_5}\] in the presence of air produces maleic anhydride. The oxidation is carried out at \[500^\circ C\] .
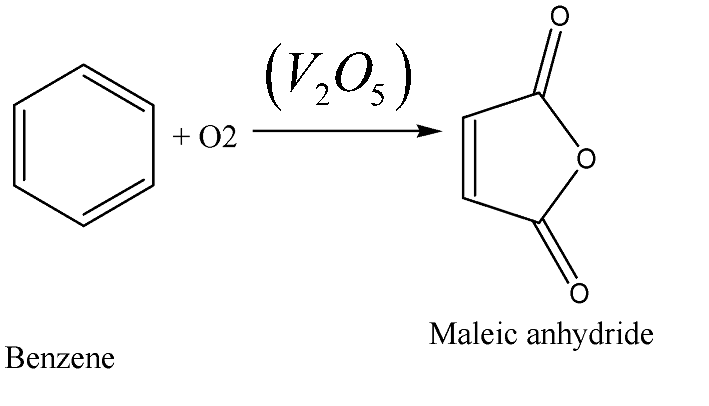
So, the oxidation of benzene by Vanadium pentoxide \[\left( {{V_2}{O_5}} \right)\] in the presence of air produces maleic anhydride.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Vanadium pentoxide \[\left( {{V_2}{O_5}} \right)\] is a yellow to red crystalline powder which is slightly soluble in water and denser than water. Its contact may cause severe irritation to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes and it may be toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Vanadium pentoxide is used in different, industrial processes as catalyst such as in the contact process, it serves for the oxidation of \[S{O_2}\] to \[S{O_3}\] with oxygen at \[440^\circ C\]. Besides it is used in the oxidation of ethanol to ethanal and in the production of phthalic anhydride, polyamide, oxalic acid and further products.
Complete step by step answer:
When one molecule of benzene reacts with two molecules of vanadium pentoxide and one and a half mole of oxygen, we get one of maleic anhydride, one molecule of glyoxylic or aldehyde acid, two moles of vanadium trioxide and one mole of water. During this process, the cleavage of the benzene ring takes place and form diodic acid and this acid will then undergo dehydration to form an anhydride by the same Vanadium pentoxide \[\left( {{V_2}{O_5}} \right)\] molecules and it will cleave any double bonds that are present in the ring.
The oxidation of benzene by \[{V_2}{O_5}\] in the presence of air produces maleic anhydride. The oxidation is carried out at \[500^\circ C\] .

So, the oxidation of benzene by Vanadium pentoxide \[\left( {{V_2}{O_5}} \right)\] in the presence of air produces maleic anhydride.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Vanadium pentoxide \[\left( {{V_2}{O_5}} \right)\] is a yellow to red crystalline powder which is slightly soluble in water and denser than water. Its contact may cause severe irritation to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes and it may be toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Vanadium pentoxide is used in different, industrial processes as catalyst such as in the contact process, it serves for the oxidation of \[S{O_2}\] to \[S{O_3}\] with oxygen at \[440^\circ C\]. Besides it is used in the oxidation of ethanol to ethanal and in the production of phthalic anhydride, polyamide, oxalic acid and further products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




