
The part of the nephron where the action of the ADH hormone takes place is
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 7
E. 8

Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Nephrons are the basic functional units of the kidneys. Each kidney is made up of millions of nephrons, these structures help in filtration of blood to produce urine and also in maintaining osmoregulation.
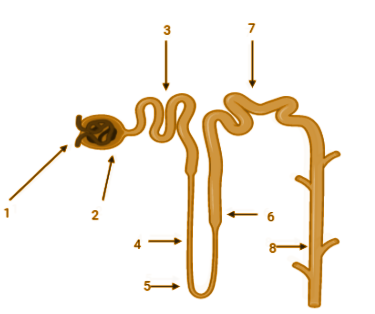
Complete answer: ADH or the Anti-diuretic Hormone helps in the water reabsorption to produce more concentrated urine. A major portion of the water entering the nephron is reabsorbed. The ADH released from the pituitary gland acts on the collecting ducts to facilitate the water reabsorption from the site. Collecting duct corresponds to 8 in the diagram.
Considering the other parts:
-The part corresponding to 1 refers to the glomerulus, which is a structure made of capillaries, which are aggregated in the shape of a ball and the function of this structure is in the filtration of blood and forming urine from it.
-2 refers to Bowman’s capsule which is a cup-like structure surrounding the glomerulus, which also aids in the process of blood filtration.
-3 corresponds to the proximal convoluted tubule or PCT, is the part after and right next to Bowman’s capsule and it extends till the descending loop of Henle. The main function of the part is to maintain the pH of the filtrate.
-4 Is the descending loop of Henle and is freely permeable to water but is impermeable to solutes, therefore easy reabsorption of water takes place here.
-5 Is the loop of Henle, which is the U shaped portion of the tubule, whose function is the recovery of sodium chloride and water from the urine.
-6 Is the ascending loop of Henle passes the filtrate to the next part which is the distal convoluted tubule.
-7 corresponds to the distal convoluted tubule and the major function lies in maintaining the levels of sodium and potassium ions.
Thus, from the options given the part corresponding to the site of action of ADH is the collecting duct, which is the 8th part. Therefore the correct option is E.
Note: The mechanism by which the ADH acts is by stimulation of water reabsorption by aquaporins also known as water channels. It causes a decrease in plasma osmolarity and in turn increases the osmolarity of urine.
Complete answer: ADH or the Anti-diuretic Hormone helps in the water reabsorption to produce more concentrated urine. A major portion of the water entering the nephron is reabsorbed. The ADH released from the pituitary gland acts on the collecting ducts to facilitate the water reabsorption from the site. Collecting duct corresponds to 8 in the diagram.
Considering the other parts:
-The part corresponding to 1 refers to the glomerulus, which is a structure made of capillaries, which are aggregated in the shape of a ball and the function of this structure is in the filtration of blood and forming urine from it.
-2 refers to Bowman’s capsule which is a cup-like structure surrounding the glomerulus, which also aids in the process of blood filtration.
-3 corresponds to the proximal convoluted tubule or PCT, is the part after and right next to Bowman’s capsule and it extends till the descending loop of Henle. The main function of the part is to maintain the pH of the filtrate.
-4 Is the descending loop of Henle and is freely permeable to water but is impermeable to solutes, therefore easy reabsorption of water takes place here.
-5 Is the loop of Henle, which is the U shaped portion of the tubule, whose function is the recovery of sodium chloride and water from the urine.
-6 Is the ascending loop of Henle passes the filtrate to the next part which is the distal convoluted tubule.
-7 corresponds to the distal convoluted tubule and the major function lies in maintaining the levels of sodium and potassium ions.
Thus, from the options given the part corresponding to the site of action of ADH is the collecting duct, which is the 8th part. Therefore the correct option is E.
Note: The mechanism by which the ADH acts is by stimulation of water reabsorption by aquaporins also known as water channels. It causes a decrease in plasma osmolarity and in turn increases the osmolarity of urine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




