
The path length of one oscillation of a simple pendulum of length of $ 1 $ meter is $ 16cm $ . Its maximum velocity is ( $ g = {\pi ^2}m{s^{ - 2}} $ )
$ \left( A \right)2\pi m{s^{ - 1}} \\
\left( B \right)4\pi m{s^{ - 1}} \\
\left( C \right)8\pi m{s^{ - 1}} \\
\left( D \right)16\pi m{s^{ - 1}} \\ $
Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to draw a schematic diagram of the pendulum and then calculate the height $ h $ of the pendulum bob from the length $ AOB $ and then, by equating the potential and the kinetic energies of the pendulum bob, the maximum velocity is calculated.
The formula used in this question is
The angle $ \theta = \dfrac{{arc}}{{radius}} $
All of the potential energy at $ A $ is converted to the kinetic energy at $ O $
$ P.E. = K.E. \\
mg\Delta x = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} \\ $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us first draw the figure for the given arrangement
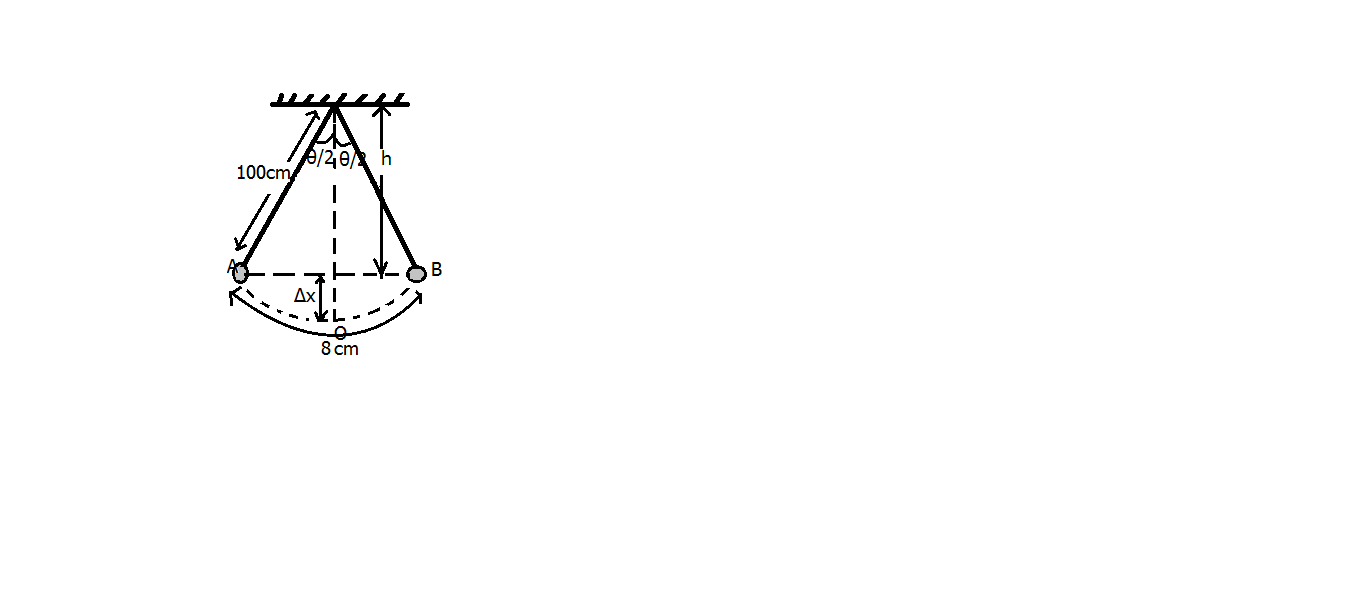
As it is given that the length of the complete oscillation is $ 16cm $ so, the length of $ AOB $ will be $ 8cm $ , Now the angle $ \theta = \dfrac{{arc}}{{radius}} $
Putting the values of the arc and the radius
$ \theta = \dfrac{{8cm}}{{100cm}} = 0.08 $
So, the angles $ \dfrac{\theta }{2} $ equals $ 0.04 $ radians
So, the height, $ h $ is calculated as
$ h = 100cm \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = 100cm \times \cos \left( {0.04} \right) \\
\Rightarrow h = 100cm \times 0.9992 = 99.92cm \\ $
Therefore, $ \Delta x = 100cm - h = 100 - 99.92 = 0.08cm $
Now, all of the potential energy at $ A $ is converted to the kinetic energy at $ O $
$ P.E. = K.E. $
So,
$ mg\Delta x = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} $
Now, as it is given that, $ g = {x^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} = 100{\pi ^2}cm{s^{ - 2}} $
Since, $ 1m = 100cm $
Therefore,
$ g\Delta x = \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} \\
{v^2} = 2g\Delta x \\
{v^2} = 2 \times 100{\pi ^2}cm{s^{ - 2}} \times 0.08cm \\
{v^2} = 16{\pi ^2}c{m^2}{s^{ - 2}} \\
v = 4\pi cm{s^{ - 1}} \\ $
Note :
The angle $ \theta $ is divided equally by the perpendicular bisector to the line segment. As the pendulum bob moves from a certain height to the reference level, all of its potential energy due to a particular height gets converted to the kinetic energy and when the bob goes from the reference level to the extreme point, the kinetic energy gets converted to the potential energy , this gives an energy equivalence.
The formula used in this question is
The angle $ \theta = \dfrac{{arc}}{{radius}} $
All of the potential energy at $ A $ is converted to the kinetic energy at $ O $
$ P.E. = K.E. \\
mg\Delta x = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} \\ $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us first draw the figure for the given arrangement

As it is given that the length of the complete oscillation is $ 16cm $ so, the length of $ AOB $ will be $ 8cm $ , Now the angle $ \theta = \dfrac{{arc}}{{radius}} $
Putting the values of the arc and the radius
$ \theta = \dfrac{{8cm}}{{100cm}} = 0.08 $
So, the angles $ \dfrac{\theta }{2} $ equals $ 0.04 $ radians
So, the height, $ h $ is calculated as
$ h = 100cm \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = 100cm \times \cos \left( {0.04} \right) \\
\Rightarrow h = 100cm \times 0.9992 = 99.92cm \\ $
Therefore, $ \Delta x = 100cm - h = 100 - 99.92 = 0.08cm $
Now, all of the potential energy at $ A $ is converted to the kinetic energy at $ O $
$ P.E. = K.E. $
So,
$ mg\Delta x = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} $
Now, as it is given that, $ g = {x^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} = 100{\pi ^2}cm{s^{ - 2}} $
Since, $ 1m = 100cm $
Therefore,
$ g\Delta x = \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} \\
{v^2} = 2g\Delta x \\
{v^2} = 2 \times 100{\pi ^2}cm{s^{ - 2}} \times 0.08cm \\
{v^2} = 16{\pi ^2}c{m^2}{s^{ - 2}} \\
v = 4\pi cm{s^{ - 1}} \\ $
Note :
The angle $ \theta $ is divided equally by the perpendicular bisector to the line segment. As the pendulum bob moves from a certain height to the reference level, all of its potential energy due to a particular height gets converted to the kinetic energy and when the bob goes from the reference level to the extreme point, the kinetic energy gets converted to the potential energy , this gives an energy equivalence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




