
The pea plant with round- shaped seeds with the yellow color seed (RRYY) crossed with another pea plant showing wrinkled shape with green cotyledons (rryy). The results of progeny in the F2 generation are produced in the following number.
(i) Heterozygous for both shape and color of seeds ___ number.
(ii) Dominant for color, but recessive for shape ___ number.
(iii) Homozygous for both shape and color of seeds ___ number.
(iv) Heterozygous for seed shape only ___ number.
(a) i - 2, ii - 4, iii - 3, iv - 8
(b) i - 4, ii - 2, iii - 3, iv - 8
(c) i - 3, ii - 4, iii - 8, iv - 2
(d) i - 4, ii - 3, iii - 2, iv - 8
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: When a cross is carried out between round- shaped yellow color seeds (RRYY) and wrinkled shape green color seeds (rryy) it is a dihybrid cross as two characters are taken at a single time in a single cross. According to Mendel's law of independent assortment, when two characters are observed in a single cross both the characters separate independently from one another.
Complete step by step answer:
When Mendel crossed yellow colored round shape seeds (RRYY) with green colored wrinkled shape seeds (rryy) he observed a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 (i.e., 9 round yellow seeds, 3 round green seeds, 3 yellow wrinkled seeds, and 1 green wrinkled seeds). In the F2 generation,
(i) heterozygous for both shape and color of seeds (RrYy) is 4 numbers.
(ii) dominant for color, but recessive for shape (rrYY/rrYy) is 3 numbers.
(iii) homozygous for both the shape and color of seeds (RRYY/rryy) is 2 numbers.
(iv) heterozygous for seed shape only (Rryy/RrYY) is 8 numbers
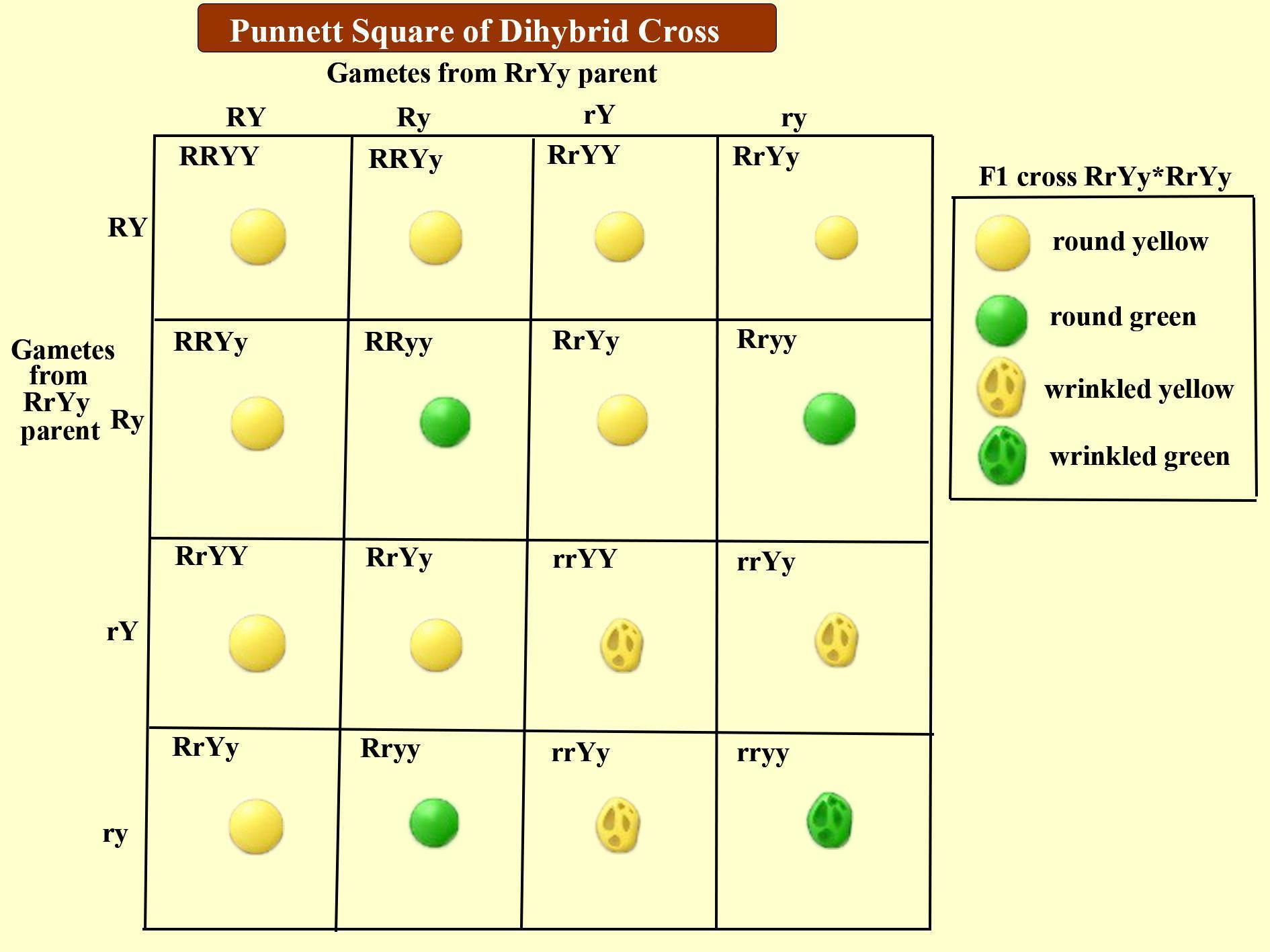
So, the correct answer is `i - 4, ii - 2, iii - 3, and iv - 8`.
Additional information:
- When round yellow seeds (RRYY) are crossed with wrinkled green seeds (rryy) in filial 1 generation we obtain a progeny of RrYy i.e., round yellow seeds. When F1 progeny undergoes self cross, in F2 generation we obtain a progeny in the ratio of 9 (round, yellow seeds) : 3 (yellow, wrinkled) : 3 (green, round) : 1 (green, wrinkled).
- Characters separate independently of one another, and thus shape and color of seeds characters separate independently.
- Exception to the law of independent assortment is found incomplete dominance (when the dominant gene does not completely mask the effect of the recessive gene and thus the phenotypic appearance shows a blending of both) and codominance (when both the alleles express themselves equally).
Note: Mendel gave his first two laws- the law of dominance and law of segregation with respect to monohybrid cross and the third law- the law of independent assortment with respect to dihybrid cross. This law was given by Mendel in 1865. The genotypic ratio shown by this cross is 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1.
Complete step by step answer:
When Mendel crossed yellow colored round shape seeds (RRYY) with green colored wrinkled shape seeds (rryy) he observed a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 (i.e., 9 round yellow seeds, 3 round green seeds, 3 yellow wrinkled seeds, and 1 green wrinkled seeds). In the F2 generation,
(i) heterozygous for both shape and color of seeds (RrYy) is 4 numbers.
(ii) dominant for color, but recessive for shape (rrYY/rrYy) is 3 numbers.
(iii) homozygous for both the shape and color of seeds (RRYY/rryy) is 2 numbers.
(iv) heterozygous for seed shape only (Rryy/RrYY) is 8 numbers

So, the correct answer is `i - 4, ii - 2, iii - 3, and iv - 8`.
Additional information:
- When round yellow seeds (RRYY) are crossed with wrinkled green seeds (rryy) in filial 1 generation we obtain a progeny of RrYy i.e., round yellow seeds. When F1 progeny undergoes self cross, in F2 generation we obtain a progeny in the ratio of 9 (round, yellow seeds) : 3 (yellow, wrinkled) : 3 (green, round) : 1 (green, wrinkled).
- Characters separate independently of one another, and thus shape and color of seeds characters separate independently.
- Exception to the law of independent assortment is found incomplete dominance (when the dominant gene does not completely mask the effect of the recessive gene and thus the phenotypic appearance shows a blending of both) and codominance (when both the alleles express themselves equally).
Note: Mendel gave his first two laws- the law of dominance and law of segregation with respect to monohybrid cross and the third law- the law of independent assortment with respect to dihybrid cross. This law was given by Mendel in 1865. The genotypic ratio shown by this cross is 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




