
The pentose sugar in DNA and RNA has
A. Open chain structure
B. Pyranose structure
C. Furanose structure
D. All of the above
Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: The genetic material of every organism is DNA or RNA. They are known as nucleic acids. DNA is transcribed into RNA for the synthesis of proteins in advanced or higher species. By the mechanism of reverse transcription, RNA can be translated into DNA. Both are pentose sugars.
Complete answer: Deoxyribose is a pentose sugar that is devoid of oxygen at the 3rd carbon atom. Whereas ribose is a pentose sugar group with hydroxyl (OH) at the 3rd carbon atom.
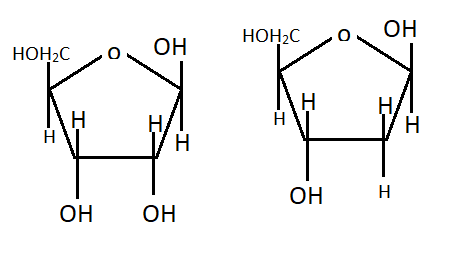
Nucleic acids are a cell's genetic material that consists of repeating units of monomers known as nucleotides. In each nucleotide, there are three main components: pentose sugar with a total of 5 carbons, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
DNA: It is called deoxyribonucleic acid, which is a more stable nucleic acid of the double-stranded type. It stores the cell genetic blueprint. It has a double helix structure. It has antiparallel strands, running in opposite directions. Its base composition is Adenine(A), Guanine(G), Cytosine(C), and Thymine(T).
RNA: It is called ribonucleic acid, a more reactive single-stranded type of nucleic acids. Its base composition is Adenine(A), Guanine(G), Cytosine(C) and Uracil(U). It contains a single strand or helix structure. It does not have a special hydrogen bond, unlike DNA. D-2-deoxyribose and D-ribose are the sugar units in DNA and RNA.
The 5 carbon sugars present in RNA and DNA are ribose and deoxyribose. They have a furanose structure of 4 carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, which is a 5 membered ring system.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note: Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry genetic information in organisms. RNA is the genetic material of viruses, while DNA is present in the nucleus of plants and animals. In eukaryotes, DNA is wrapped around specialized proteins called histones.
Complete answer: Deoxyribose is a pentose sugar that is devoid of oxygen at the 3rd carbon atom. Whereas ribose is a pentose sugar group with hydroxyl (OH) at the 3rd carbon atom.

Nucleic acids are a cell's genetic material that consists of repeating units of monomers known as nucleotides. In each nucleotide, there are three main components: pentose sugar with a total of 5 carbons, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
DNA: It is called deoxyribonucleic acid, which is a more stable nucleic acid of the double-stranded type. It stores the cell genetic blueprint. It has a double helix structure. It has antiparallel strands, running in opposite directions. Its base composition is Adenine(A), Guanine(G), Cytosine(C), and Thymine(T).
RNA: It is called ribonucleic acid, a more reactive single-stranded type of nucleic acids. Its base composition is Adenine(A), Guanine(G), Cytosine(C) and Uracil(U). It contains a single strand or helix structure. It does not have a special hydrogen bond, unlike DNA. D-2-deoxyribose and D-ribose are the sugar units in DNA and RNA.
The 5 carbon sugars present in RNA and DNA are ribose and deoxyribose. They have a furanose structure of 4 carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, which is a 5 membered ring system.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note: Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry genetic information in organisms. RNA is the genetic material of viruses, while DNA is present in the nucleus of plants and animals. In eukaryotes, DNA is wrapped around specialized proteins called histones.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




